Choosing the right online advertising platform in digital marketing can greatly impact your success in reaching potential customers. In this guide, we explore the key differences between Google Ads and Facebook Ads, two of the most powerful tools to help you find and engage your target audience across search engines and social media platforms.”
Facebook and Google are two giants in the digital advertising landscape, each offering unique strengths and targeting options. Let’s explore the key differences between these two advertising platforms.

Ready to optimize your digital advertising strategy?
Google Ads:
- Intent-Based Advertising: Intent-Based Advertising: Google Ads’ advantage lies in user intent targeting within its Search Network. When users search for specific products or services, text-based ads and Shopping Ads appear alongside search results, connecting businesses with active users ready to make a purchase.
- Keyword Targeting: Google Ads relies heavily on keywords. Advertisers bid on relevant keywords, and their ads appear when users search for those terms. This makes it a powerful platform for businesses aiming to target specific search queries.
- Search Network vs. Display Network: Google Ads offers a dual network approach. The Search Network displays text-based ads on the search engine results pages, while the Display Network showcases visual ads on websites within the network. This versatility caters to different advertising goals.
- Shopping Ads: Google is renowned for its Shopping Ads, which are ideal for e-commerce businesses. These ads directly showcase product images, prices, and details in the search results, capturing active users in the purchase decision phase.
Facebook Ads:
- Audience-Centric Advertising: With Facebook Ads, you can create ads tailored for advanced audience targeting based on demographics and Audience Network behaviors. Its social media platform design supports engaging image ads and video ads, letting advertisers connect visually with a wider audience. Advertisers can define their audience precisely, reaching users who actively search for their type of product or service.
- Visual Content: Facebook is a visual-centric platform ideal for advertisers leveraging images and videos. Ad creatives play a significant role in capturing users’ attention as they scroll through their newsfeeds.
- Social Engagement: Facebook Ads capitalize on the social aspect, encouraging interaction and engagement. Users can like, share, and comment on ads, fostering a sense of community around the brand.
- Advanced Targeting Options: Facebook offers advanced targeting options such as lookalike audiences, allowing advertisers to target users like their existing customer base. This is particularly effective for expanding reach to potential customers.
- Facebook Messenger Ads: Businesses can use Facebook Messenger for direct communication with prospective customers. Messenger Ads facilitate real-time engagement and personalized interactions.
While Google Ads is laser-focused on capturing users actively searching for information, products, or services, Facebook Ads excel in reaching a broader audience based on their interests and behaviors. The choice between Facebook Ads and Google Ads depends on business objectives. For prospective customers looking to engage, Facebook offers social network strengths, while Google ensures qualified traffic through search queries. Together, these digital advertising channels can maximize ROI.
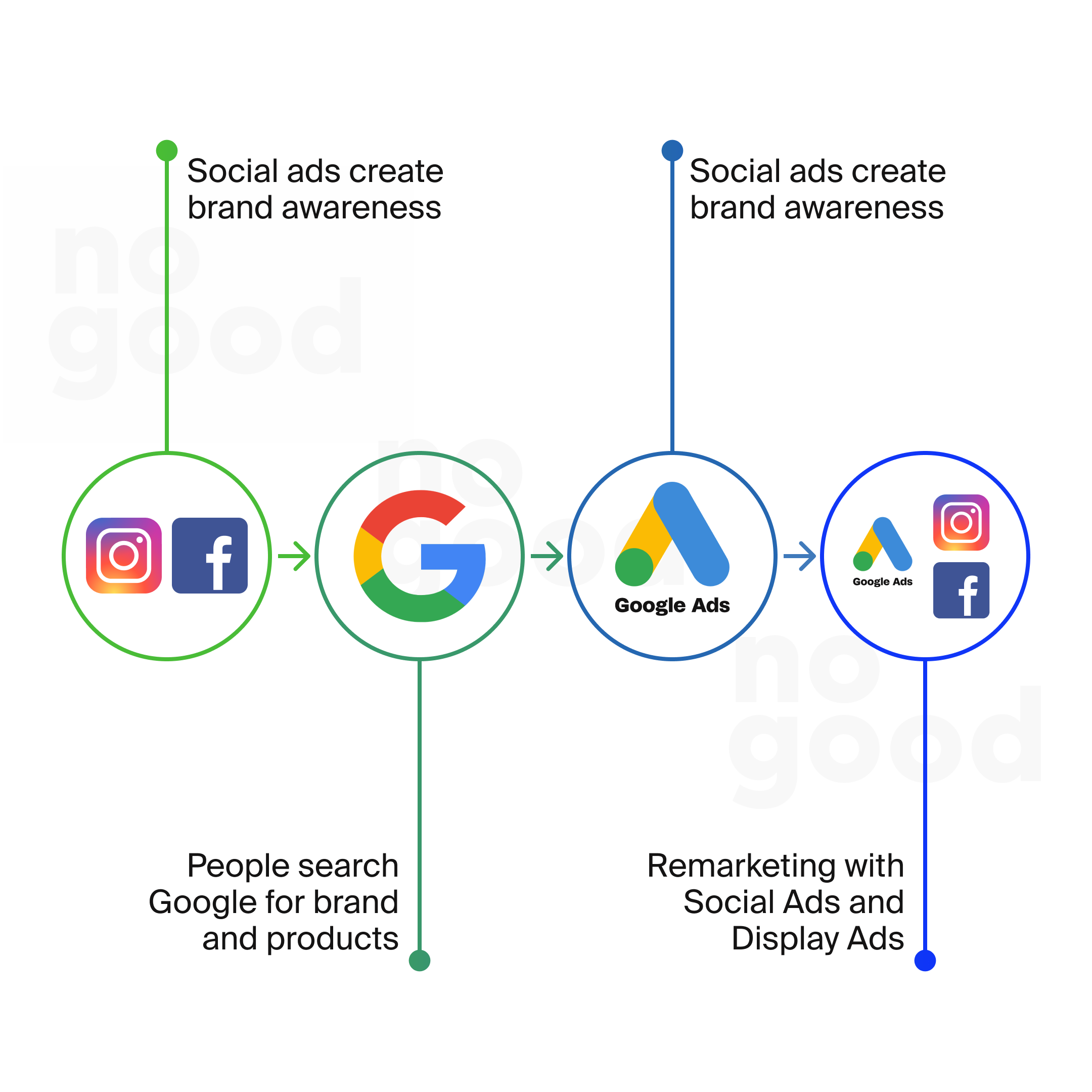
Targeting Audience
Google Ads focuses on user intent through keyword targeting, allowing brands to appear in search results based on what users are actively seeking. Conversely, Facebook Ads excel at interest-based audience targeting, leveraging data from user profiles on its social media platform. With advanced audience segmentation, Facebook enables highly specific targeting across its social network and Audience Network.
Ad Formats
In Google Ads, text-based formats are the standard, especially in the Search Network, while image and Shopping Ads offer visual ad alternatives in the Display Network. On the other hand, Facebook Ads provide a dynamic range of visual content options like image ads, video ads, and carousel ads, each designed to maximize social media engagement and connect with a target audience through compelling visual storytelling.
Cost Structure & ROI
When assessing return on investment (ROI), consider how Google Ads typically focuses on pay-per-click (PPC), where advertisers pay based on clicks. This makes it suitable for qualified leads who are ready to engage. Facebook Ads often focus on impressions and social engagement metrics, allowing for cost-effective brand awareness strategies. Each platform’s cost structure can be optimized based on specific budget constraints and campaign objectives.
Conversion Tracking and Reporting
Google Ads offers detailed conversion tracking tools, enabling brands to assess click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates (CVR), and ROI for each campaign objective. Facebook Ads provides robust analytics through its Facebook Pixel and Custom Audiences tools, helping brands understand social engagement metrics, website actions, and ad performance across the social network.”
| Feature | Google Ads | Facebook Ads |
| Targeting | Intent-based through keywords and search queries | Audience-based, using demographics and interests |
| Ad Formats | Text-based ads, Shopping Ads, visual ads via Display Network | Visual-centric with image, video, and carousel ads |
| Conversion Tracking | Detailed CTR, CVR, ROI data | Social engagement metrics and Pixel tracking |
| Cost Structure | PPC model, often higher conversion rates | CPM, cost-effective for brand awareness and impressions |
| Audience Reach | Active users with high intent | Broad audience based on interest and behavioral data |
Which is better, FB ads or Google Ads?
The choice between Facebook Ads and Google Ads is not a matter of superiority but a strategic decision based on campaign objectives and audience targeting. Both platforms play distinct roles in the marketing funnel, addressing different stages of customer engagement.
Facebook Ads:
Top-of-Funnel Engagement: Facebook Ads create brand awareness and engagement at the top of the marketing funnel. The platform’s advanced targeting options, including lookalike audiences and interests, enable businesses to reach a vast and diverse audience.
Visual Storytelling: Leveraging the visual-centric nature of Facebook, advertisers can craft compelling narratives through images and videos. This fosters an emotional connection with users, driving brand affinity.
Social Interaction: The interactive and social nature of Facebook Ads encourages users to engage with content, share, and participate in discussions. This builds a community around the brand, fostering a sense of belonging.
Google Ads:
Bottom-of-Funnel Precision: Google Ads, on the other hand, excels in precision targeting at the bottom of the marketing funnel, capturing users actively searching for specific products or information. This results in high-quality leads and conversions.
Search Intent Optimization: Google Ads is synonymous with capturing user intent through search queries. Advertisers bid on keywords relevant to their offerings, ensuring their ads are displayed when users seek information.
Evolved Targeting Features: Google has expanded its targeting capabilities, incorporating features akin to Facebook Ads. This includes audience-specific targeting based on affinity segments, topics of interest, and detailed audience demographics, providing advertisers with a comprehensive toolkit.
Creativity in Display Campaigns: Google’s Display Network allows for creative and visually appealing ad formats, bringing a level of artistic expression to advertising. This is particularly advantageous for businesses seeking to convey a brand message through visually engaging content.
Integration of Features: Google Ads has evolved to incorporate many features traditionally associated with Facebook Ads. The platform’s audience targeting options have become more refined, allowing advertisers to leverage user interests, behaviors, and demographics, similar to Facebook’s approach.
Pricing and Conversion Rates: The pricing dynamics on both platforms can vary. While Facebook Ads may offer cost advantages in reach and impressions, Google Ads can yield higher conversion rates and a more direct return on investment due to its focus on capturing high-intent search traffic.
Ultimately, the choice between Facebook Ads and Google Ads hinges on the specific goals of a marketing campaign. For holistic marketing strategies, leveraging the strengths of both platforms may be the most effective approach.
The evolving features of Google Ads and its precision in capturing audience intent and creative potential in display campaigns position it as a formidable force in the digital advertising landscape. Strategic marketers often find success by integrating both platforms into their advertising campaigns, tailoring their approach to the unique strengths of each to achieve a well-rounded and effective marketing strategy.
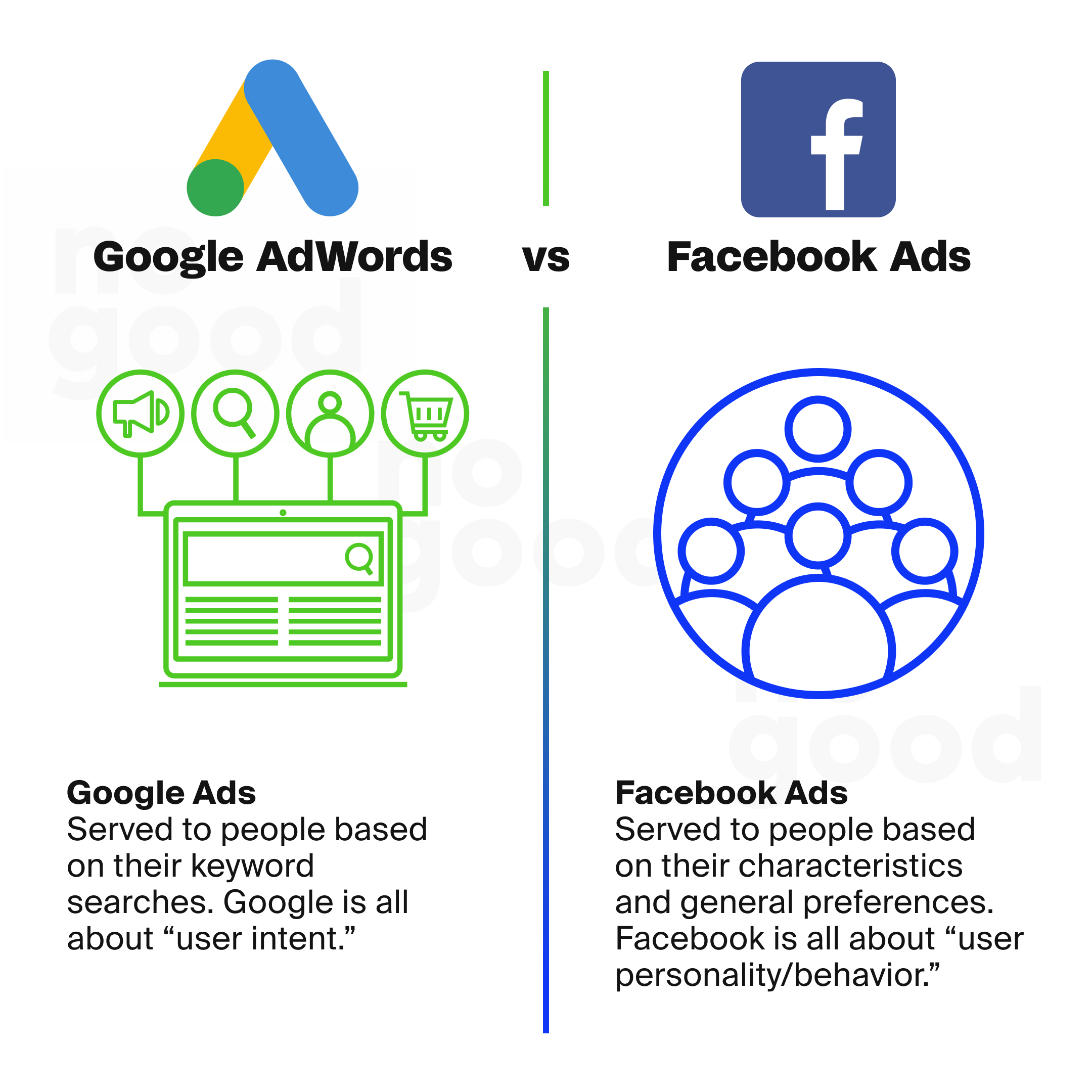
Are Google Ads harder than Facebook ads?
Google Ads presents distinct challenges that stem from its emphasis on search intent and keyword-centric approach. Here’s a detailed breakdown of why Google Ads can be considered more challenging:
Keyword Complexity: Success in Google Ads hinges on effective keyword management. Identifying and bidding on relevant keywords demands meticulous research and ongoing refinement. Finding the right keywords that strike a balance between specificity and search volume can be challenging for niche products or services.
Example: A boutique software solution might struggle to identify highly targeted keywords compared to broader software categories.
Search Intent Alignment: Google Ads requires advertisers to align their ad copy precisely with diverse search intents. Crafting compelling ad copy that resonates across a spectrum of user queries necessitates a deep understanding of the target audience and their varied search behaviors. Google provides the ability to test custom audiences using first-party data and measuring your audience size immediately, which can help you understand the reach possibilities very quickly in the process.
Example: Advertisers in competitive markets may find it challenging to create ad copy that stands out while maintaining relevance to different search queries.
Intense Competition and Bidding Dynamics: In competitive industries, bidding wars are commonplace, impacting ad visibility and costs. Striking the right balance between bid prices and profitability requires strategic management and constant adjustment, especially during peak seasons.
Example: E-commerce businesses may face challenges maintaining cost-effective bidding strategies while vying for top positions during high-demand periods.
Transition to Visual Creativity: While the search network primarily relies on text-based ads, the display network opens avenues for visual creativity. This shift demands a diversified skill set, and advertisers must adapt to crafting visually engaging content that complements their brand message.
Example: A service-oriented business may find it challenging to translate intangible offerings into visually compelling display ads compared to businesses with tangible and visually appealing products.
Continuous Optimization Demands: Google Ads necessitates ongoing optimization efforts, including bid adjustments, ad copy refinement, and format testing. Staying abreast of changes in the competitive landscape and promptly adapting strategies is essential for sustained success.
Example: Advertisers in rapidly evolving industries, such as technology, may find it hard to keep up with the constant need for optimization and adjustments to stay ahead of the competition.
In essence, the challenges in Google Ads are intricately tied to the platform’s precision-driven nature, where success hinges on effective keyword management, ad alignment with diverse search intents, adept bidding strategies, visual creativity in specific contexts, and a continuous commitment to optimization in a dynamic landscape.
Both Google Ads and Facebook Ads come with their complexities, but the perceived difficulty depends on the expertise of the advertiser, the nature of the campaign, and the target audience. Successful marketers often integrate both platforms into their strategies, leveraging the strengths of each to create a well-rounded and effective digital advertising approach.
Are Google Ads cheaper than Facebook ads?
Google Ads:
Bidding Model: Google Ads operates on a pay-per-click (PPC) model, where advertisers bid on keywords. The cost per click (CPC) is influenced by factors such as keyword competitiveness, industry demand, and ad position.
Example: In competitive industries like finance or legal services, the CPC for particular keywords can be higher compared to less competitive sectors.
Looking for a paid search agency?
Search Intent: Google Ads captures users actively searching for products or information, representing a high-intent audience. While this can lead to higher conversion rates, it may also result in a more competitive and potentially expensive bidding landscape.
Example: E-commerce businesses targeting users searching for specific products may find that the cost per conversion is worth the investment due to the high purchase intent.
Ad Positioning: Advertisers can influence their ad positions by adjusting bids. Higher ad positions typically result in increased visibility but may also require higher bids, impacting overall campaign costs.
Example: Businesses aiming for top ad positions on competitive keywords may face higher costs but could benefit from increased click-through rates.
Facebook Ads:
Auction-Based System: Facebook Ads also operates on an auction-based model, where advertisers bid for ad placements based on their target audience criteria. The cost is influenced by audience targeting, ad relevance, and competition.
Example: Advertisers targeting a broad audience may encounter lower competition and, consequently, lower costs than highly specific targeting.
Audience Targeting: Facebook Ads excels in precise ideal audience targeting based on demographics, interests, household income, and behaviors. While this granularity can improve ad relevance, it may also impact costs, especially if targeting a niche audience.
Example: A luxury fashion brand targeting a specific income bracket and interests may find that reaching this highly targeted audience comes at a higher cost.
Ad Format: The choice of ad format, such as image or video ads, can impact costs. Video ads, for instance, may command higher costs but can also offer higher engagement.
Example: An advertiser using video ads to tell a brand story may find that the higher costs are justified by increased brand awareness and engagement.
Overall
Campaign Goals: The cost-effectiveness of each platform depends on campaign goals. Google Ads may be more cost-effective for immediate conversions, while Facebook Ads may excel in building brand awareness and engagement.
Industry Dynamics: The competitiveness of the industry plays a significant role. Highly competitive industries may lead to higher costs on both platforms.
Ad Quality: Both platforms reward high-quality ads with lower costs. Ad relevance, engagement rates, and overall ad quality can impact costs positively or negatively.
In conclusion, determining whether Google Ads or Facebook Ads is cheaper requires a detailed assessment of specific campaign objectives, target audience, and industry dynamics. While Google Ads may be perceived as more immediate in driving conversions, Facebook Ads can offer cost-effective options for building brand presence and engaging a broader audience. The key lies in aligning the advertising strategy with overall business goals and choosing the platform that best complements the desired outcomes.
Why is Google Ads better?
Google Ads is a superior advertising platform due to its continuous innovation, advanced capabilities, and commitment to leveraging cutting-edge technologies. Here’s a detailed exploration of why Google Ads is considered a leader in the digital advertising landscape:
Data-Driven Advertising Strategies: Machine Learning and Algorithmic Optimization: Google Ads integrates machine learning and sophisticated algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data, enabling advertisers to make data-driven decisions. The platform’s algorithms continuously learn and adapt, ensuring campaigns are optimized for maximum efficiency and performance.
Advanced A/B Testing: Google Ads facilitates A/B testing on a granular level, allowing advertisers to experiment with different ad elements, audiences, and strategies. The platform’s robust analytics provide insights into what works best, empowering advertisers to refine their approach based on real-time data.
AI-Powered Campaigns: Intelligent Campaigns: Google Ads introduces AI-powered campaigns, like Performance Max and Demand Gen, designed to simplify the advertising process for small businesses. These campaigns leverage machine learning to automate ad creation, targeting, and optimization, making it easier for advertisers to reach their goals without extensive manual intervention.
Performance Max (pMax): Performance Max is an AI-powered campaign type that enables advertisers to extend their reach across multiple ad spaces, including Search, Display, YouTube, and more. This campaign type leverages Google’s machine learning algorithms to allocate advertising budgets across channels dynamically, maximizing performance based on campaign goals.
Lookalike Audiences and Demand Generation Campaigns:
Lookalike Audiences: Google Ads now offers lookalike audience capabilities, particularly within Demand Generation campaigns. This feature allows advertisers to expand their reach by targeting users with characteristics and behaviors similar to their existing customer base. It’s a powerful tool for finding new, high-potential, and high-quality, ideal customers.
Demand Generation Campaigns: These campaigns generate interest and demand for products or services. By leveraging machine learning and algorithmic optimizations, advertisers can automate the targeting and delivery of ads to users most likely to engage and convert. This approach ensures efficient use of ad spend and maximizes the impact of demand generation efforts.
Scalability and Bottom-Line Impact:
Scale Sales: Google Ads, with its advanced features and data-driven approach, provides advertisers with the tools to scale sales effectively. By reaching the right audience at the right time and continuously optimizing campaigns based on performance metrics, businesses can grow their customer base and revenue.
Data-Driven Decision Support: Google Ads doesn’t just provide data; it empowers advertisers with actionable insights. The platform’s analytics and reporting tools enable advertisers to understand customer behavior, measure the impact of their campaigns, and make informed decisions to drive bottom-line results.
In essence, Google Ads’ commitment to staying ahead of the curve with innovations in machine learning, AI-powered campaigns, and advanced targeting capabilities makes it a go-to choice for advertisers seeking reach, efficiency, and effectiveness in their digital marketing efforts. The platform’s data-driven approach and continuous evolution enable advertisers to navigate the complexities of the digital landscape, making informed decisions that lead to scalable and impactful results.
Final Thoughts
In summary, Google Ads stands out as a powerhouse in digital advertising, fueled by its continuous innovation and integration of advanced technologies. The platform’s embrace of machine learning and AI exemplified through Smart Campaigns and Performance Max, not only simplifies the advertising process but elevates precision and efficiency in reaching target audiences.
Adding lookalike audiences within Demand Generation campaigns showcases Google’s commitment to providing advertisers with powerful tools for expanding reach and driving meaningful engagement. As a strategic ally, Google Ads empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions, automate complex processes, and optimize campaigns with algorithmic finesse, making it an indispensable asset for scaling sales and achieving impactful bottom-line results in the dynamic landscape of online marketing.