Here is the best way to explain attribution:
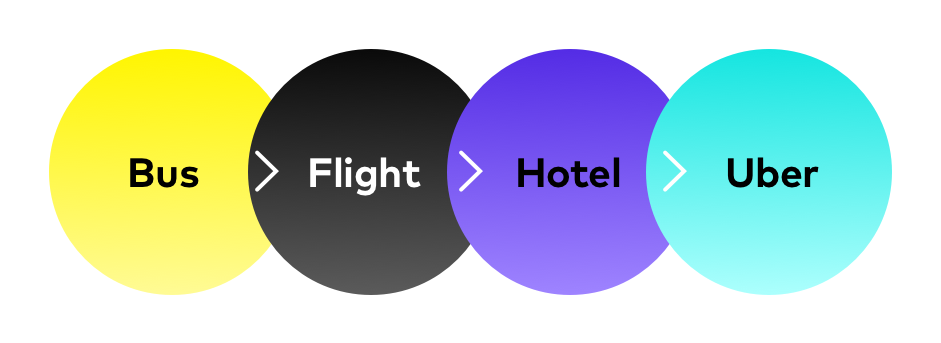
Let’s say I have an important meeting in New York City. To get there from where I live in California, I need to take the bus from my home to the airport, then a flight to New York, spend a day at a hotel then grab an Uber in the morning to the meeting location.
When people at the meeting ask, how did you get here? I say that I took an “Uber,” but that is an incomplete answer. The right answer would be the following: Bus>>Flight>> Hotel>>Uber.
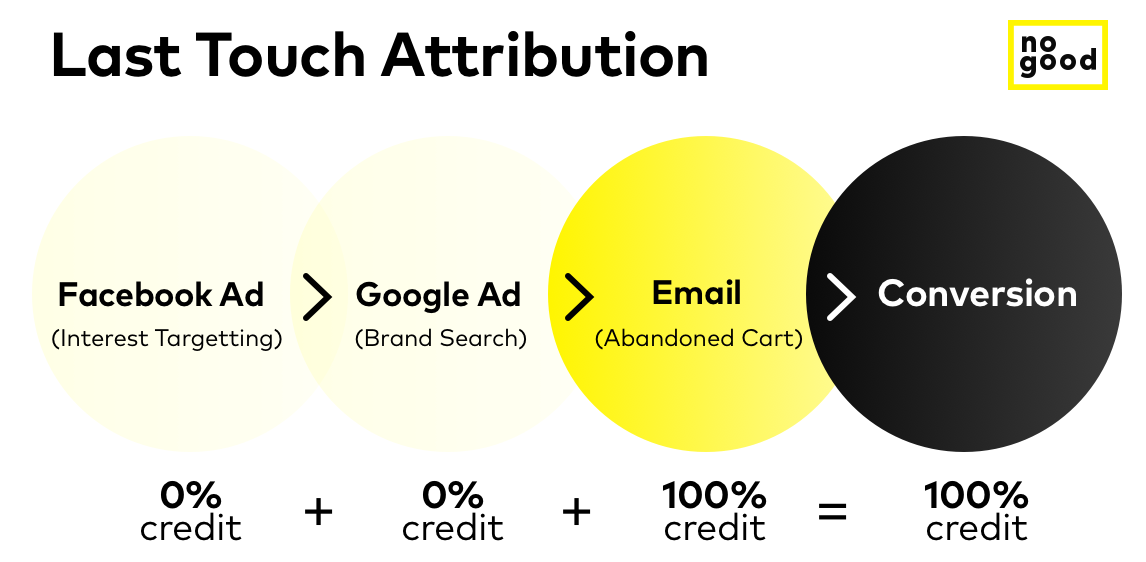
This is exactly how marketing attribution works. Most tools give us the incomplete answer of the last touch before conversion. It credits their last step to conversion (the Uber) rather than acknowledging all the things that came before. The last touch is the default attribution model of mainstream analytics tools like Google Analytics and Facebook’s Analytics.
Attribution modeling is one of the most critical methods of understanding your customers’ conversion funnel. This process is signaled by a series of touchpoints that your audience engages with before converting from potential into paying customers.
Attribution modeling acknowledges the interactions your customer has with your company and when they convert. Modeling allows you to credit which channels and campaigns have been effective and, ultimately, where to spend your budget. The goal of these models is to have clarity on how customers interact with all the various touchpoints on their path to conversion.
This guide will break down why you NEED to be using attribution models and how to use them.
Why Marketing Attribution Matters?
An attribution is an essential tool for connecting products to consumers. It allows you as the company to understand what makes you attractive to customers, how efficient your processes and channels are, and identifying your highest ROI and where you should be spending your budget. According to a HubSpot report, 52% of marketers are using attribution reporting in 2020. This makes it an essential tool to optimize and gauge the effectiveness of your strategy.
The Top Five Benefits of Attribution Modeling:
Improve your ROI-conversions are directly related to your ROI! Understanding why your customer converts are the first step.
Optimize your Strategy– Which platforms are attracting people to your site? What ad copy is working? These are all facets that come from your attribution data. Where are your customers clicking and WHY?
Measure Customers Lifetime Value (LTV)– LTV is the potential revenue a customer can generate. So, customers are your value. Why do they make their decisions? How do they make their decision? These are the answers that ultimately drive your customer experience and how they continue to engage with your company.
Improve Customer Experience– Do your customers hate pop-ups? Do they understand your product after clicking on a landing page? Is it a straightforward path? These all affect your customer experience and what draws customers to not only purchase from your company but then tell others about it. Knowing how much time is spent and where your customers are getting held up can make their experience more enjoyable.
Effective Customer Communication– companies communicate with customers in various ways- not only through text and clicks but also through videos and visuals. By using attribution models to evaluate your marketing’s creative elements, you can tailor your messaging to be clear, concise, and convert.
What is Multi-touch Attribution?
Marketers, on average, use 13 different types of touchpoints. This includes different social media platforms as well as multiple paid advertising channels. On average, it takes about eight touchpoints to get a customer to convert. Multi-touch attribution refers to the use of various types of touchpoints and measuring each of these points’ effectiveness. By determining each of these points’ value, marketers can understand which touchpoints lead to more conversions and ultimately allocate their budget accordingly.

Using multi-touch attribution creates a more detailed picture of how and where credit should be given across channels and budgetary spending. The data becomes more granular and shows a more in-depth breakdown showing which platforms drive traffic and which aren’t. Marketers can use this information to evaluate how they spend their budget and which touchpoints are causing attraction to the funnel and going through funnel conversions.
Types of Attribution Models and When to Use Them
Last touch: Using this mode, credit is given to the final touchpoint in the buying experience. This may be a paid search or an abandoned cart email effort, the last step that leads to the customer’s conversion. This model does not credit the various upper funnel touchpoints that generated the initial interest. It does not always accurately depict how effective your marketing spend is and which exact marketing effort has resulted in your conversion. It is a useful model to remind the audience to come back and is typically used in conjunction with other attribution models.
The last touch attribution model’s key benefit is that it is the simplest model for attribution systems to measure. By measuring and crediting the entire conversion on the final touch, this model gives the smallest time window for the analytics technology to result in a data error. Many tracking cookies have a 30 to 90 day expiry period, and due to this, if the conversion doesn’t happen during that time window, the marketing channel data will be lost. This expiration window becomes unnecessary through the last touch attribution since no time elapses between the last touch and the conversion’s final goal. Channel-specific attribution models come with their own attribution model (e.g., Google Ads uses the Last Interaction model). These models are highly biased towards their own channel and overestimate the effectiveness. If you were to aggregate all of these attribution models together, you would probably end up overcounting the conversions.
First touch: This model, similar to the last touch, attributes the conversion after a user’s first interaction through a paid ad or organic search. However, just like the last touch, this model will not account for the other steps your customer traverses throughout the conversion funnel. First touch attribution gives 100% of the credit to the marketing efforts that first drove a visitor to your website. The top-of-the-funnel marketing channels driving awareness are emphasized by this first interaction. Ηowever, this model type is more susceptible to errors due to technical limitations than other single-touch attribution models. For example, if you were using conversion tracking for a B2B business, the time between the first and last interaction that would lead to conversion could be longer than the cookies’ expiration. Consequently, this model gives credit to the first touch within that expiration window, not in the actual first touchpoint.
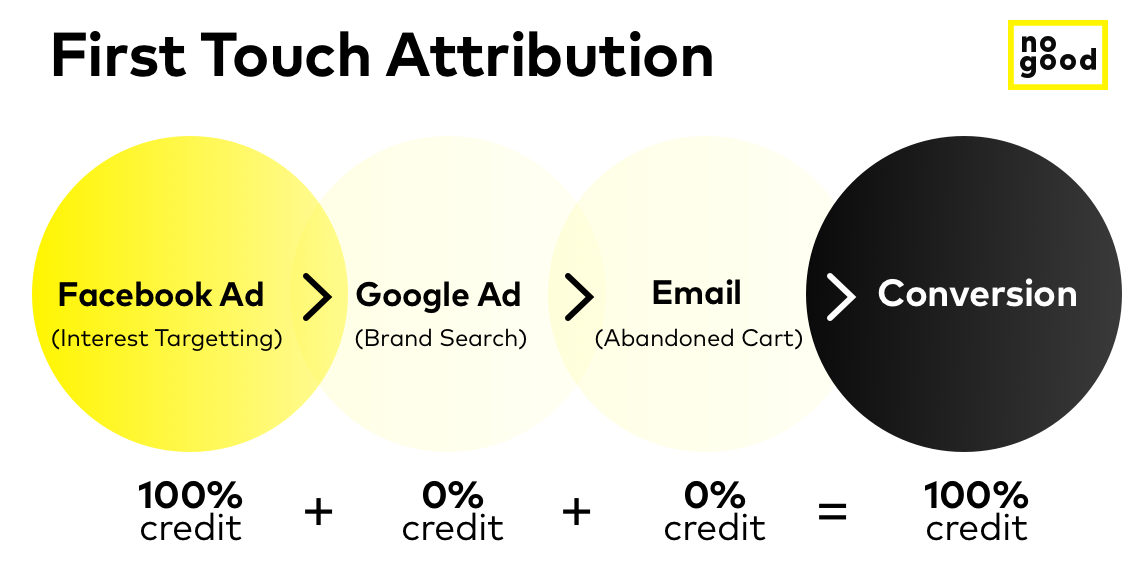
Linear: Linear attribution is a simple model that distributes credit by applying it equally to every single touch throughout the customer’s journey. This model’s advantage is that it is multi-touch, applying credit throughout the multiple stages of the conversion funnel. However, the negative of using a linear attribution model is that the potential of other marketing efforts leading to that conversion is not taken into consideration. For example, if a prospective customer has visited your website three times through a paid ad but then converts while entering your website through organic search, your paid efforts will receive 25% of the credit, while all the organic searches receives 75% of the credit.

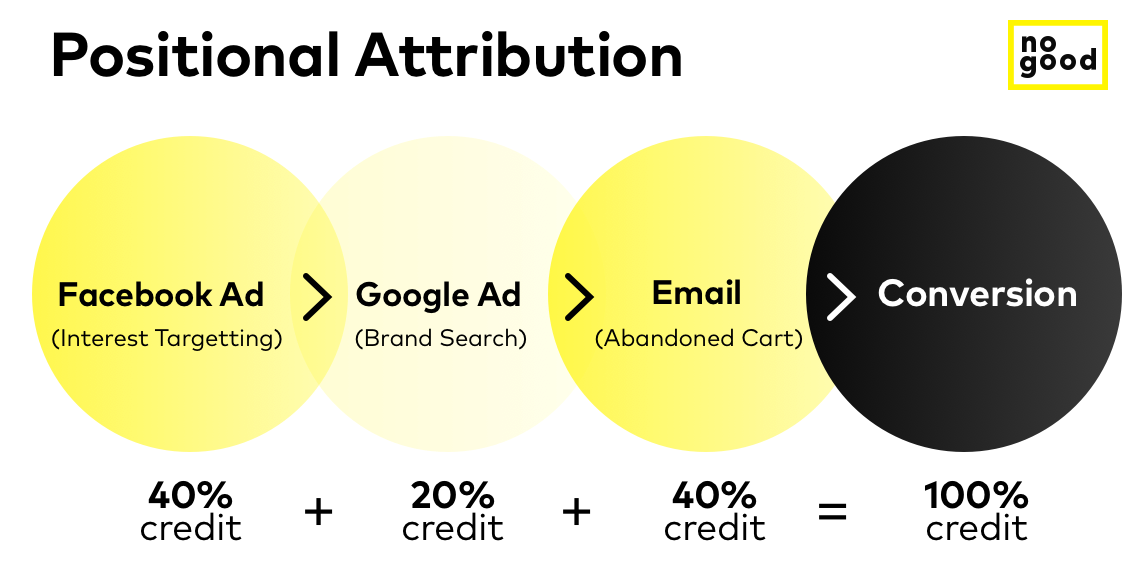
Positional: For marketing teams concentrating on lead generation, positional attribution monitors every single touchpoint but emphasizes the value of two main touchpoints rather than giving equal credit to all of them as the linear attribution model does. Also known as the U-shaped model, it gives extra credit to the first interaction of the visitor and the last interaction that leads to conversion. These two touchpoints earn 40% of the attribution, while the rest of the touchpoints are each rewarded for only 20%. The disadvantage of this attribution model is that beyond lead conversion, it doesn’t consider any of the marketing efforts that have led to it. As a result, this type of attribution model is excellent for companies that do not advertise beyond the lead generation stage.
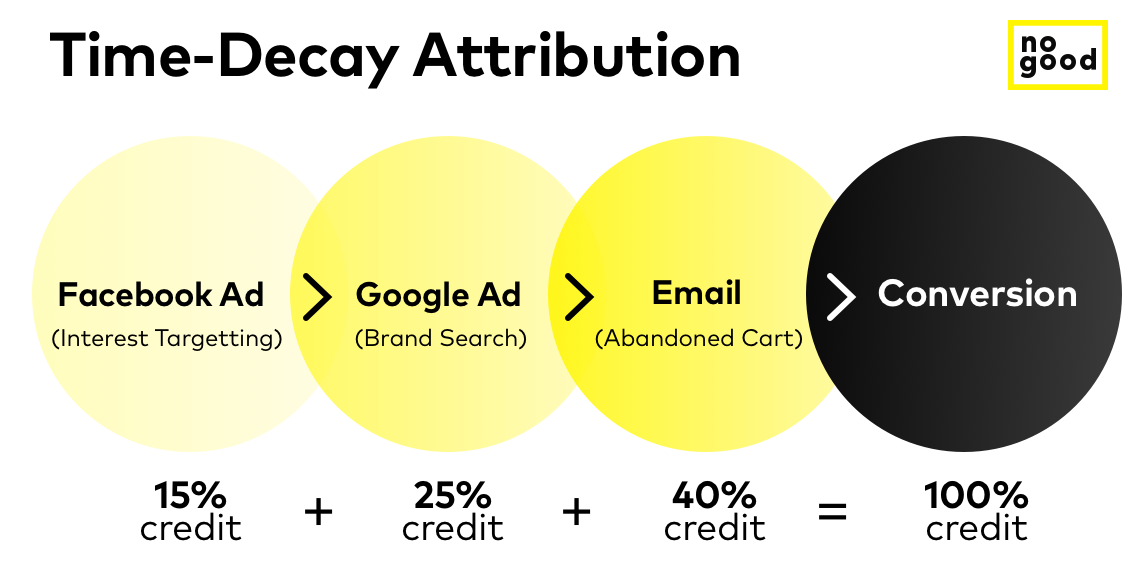
Time-decay: In the time-decay attribution model, the touchpoints closest to conversion get most of the credit as it attributes the highest credit to the step closest to conversion, and hence, it is the most preferred model by most marketers. The issue with this approach is that it will never offer top-of-the-funnel marketing activities a reasonable amount of credit since the touchpoints closest to conversion are what matter most. In other words, an ad interaction earns half as much credit eight days before conversion as an ad interaction one day before a conversion.
Which Attribution Model is Best for Measuring ROI?
There is no correct answer. While all of these attribution models allow you to understand various touchpoints that make a difference in the customer journey, they also come with pros and cons. Leveraging these touchpoints is specific to your data and your customer base. Using and understanding your data allows you to optimize where you are successful or falling short. This can shift where and when to spend your budget and lead to a more significant ROI.
LTV and Assisted Conversions
Data is the driving force behind your conversions and, ultimately, your LTV. So how do you use your data effectively and know how to support your customer’s conversion path? This is ideally done through assisted conversions. These are the additional points, such as social media posts, sales/deals, and even reviews. They are the channels your consumers may visit but don’t directly drive conversions. Most of your consumers (up to 98%) will not purchase on their first visit or first click, but by giving them additional points of engagement, they develop trust and help guide their decision to spend on your product.
Google Analytics can help breakdown various features and conversion paths your customers are following. The “Conversions” and “Attribution” tabs allow you to get a holistic view of where your conversions are taking place.
The Conversion reports from Google Analytics include metrics to measure your online business value, whether that is sales or other important events, such as signups, purchases, leads, etc. You can drill down through the conversion funnel with the preset tracking options or customize your own.
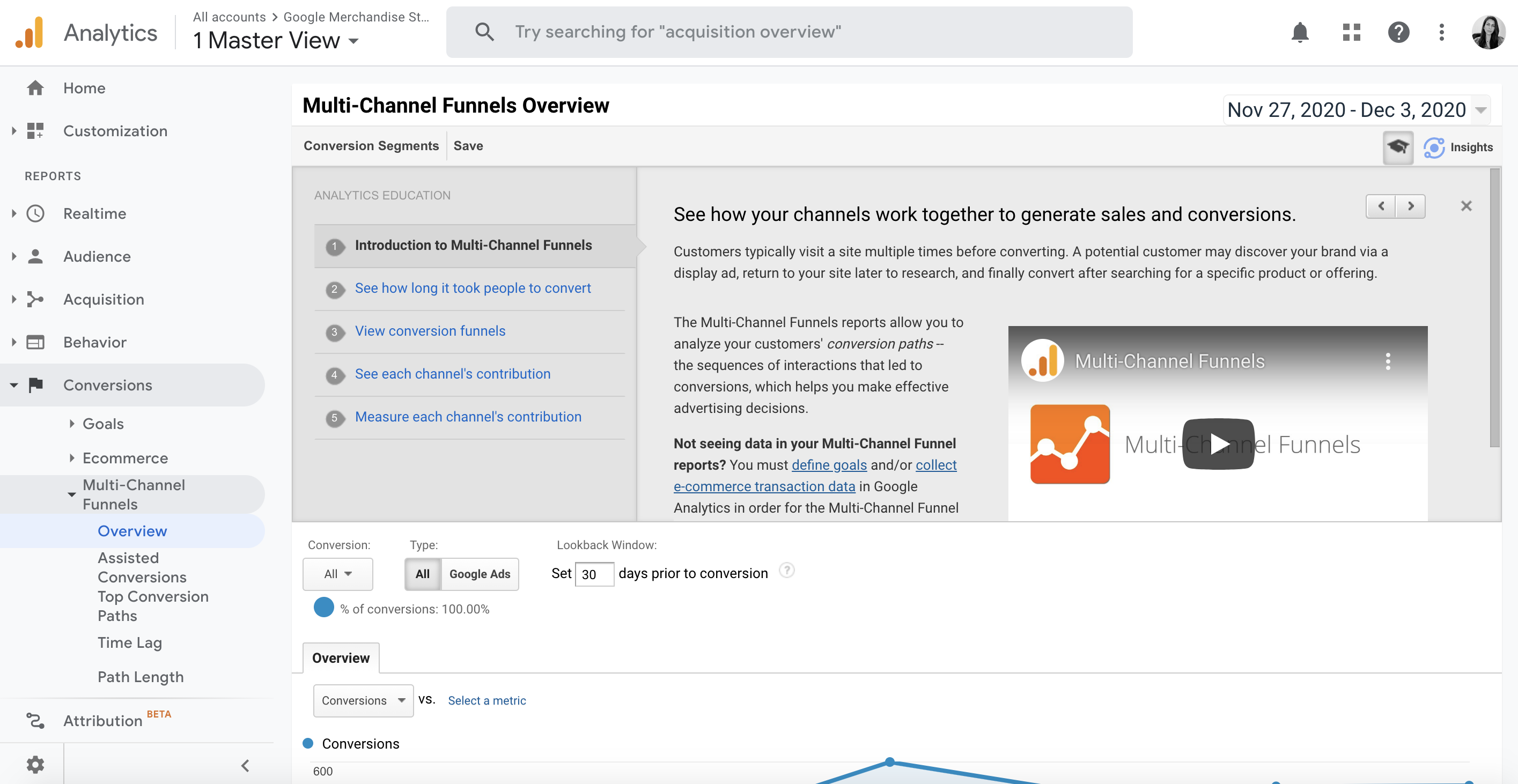
On the other hand, the “Attribution” in Google Analytics, brings free, cross-channel data-driven attribution to all customers. By using this Google Analytics feature, allows you to accurately report conversion totals across digital channels, see a unified view of all digital performance, and create knowledge of your business’s customer journey.
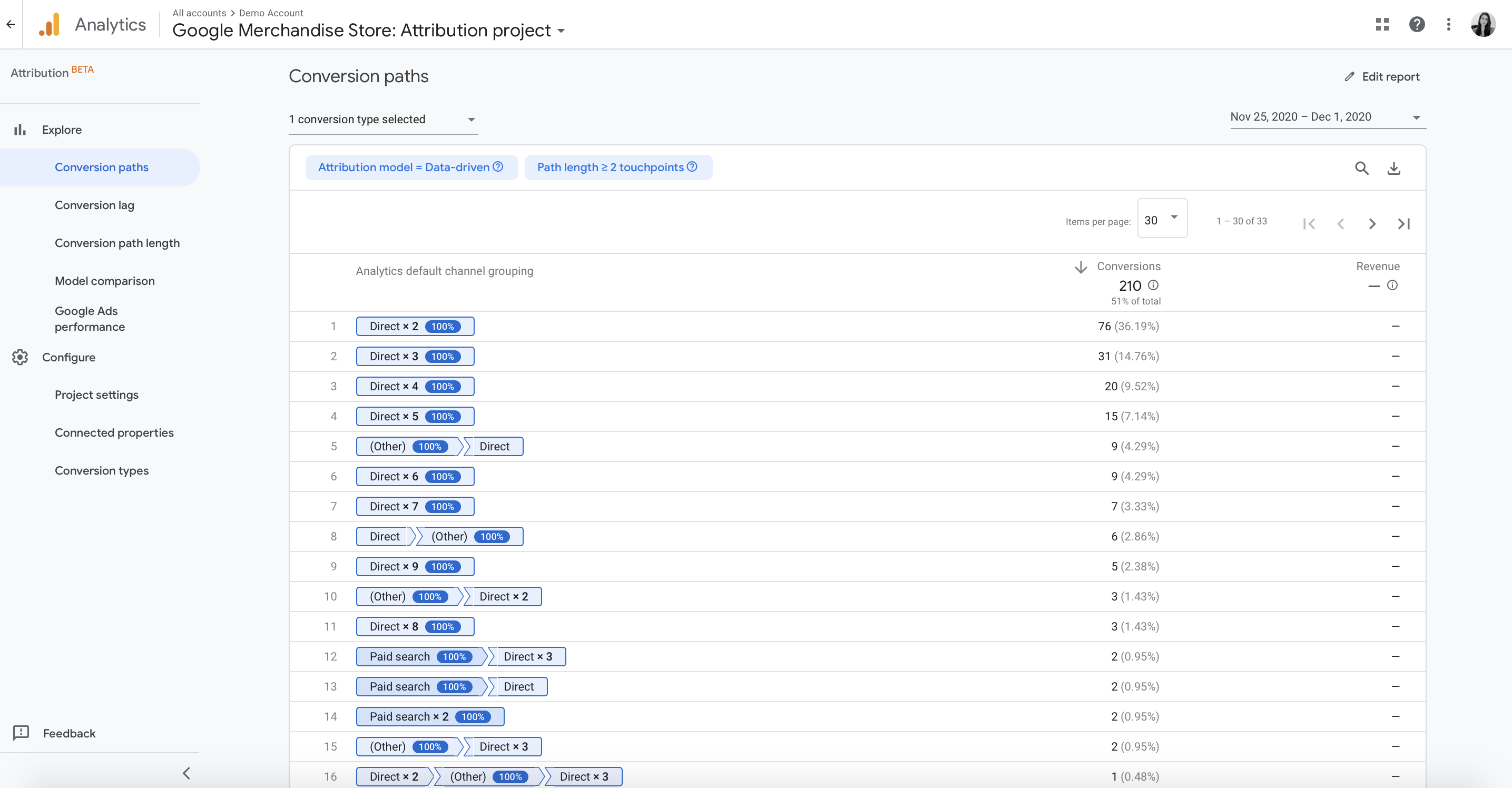
How does this data support assist conversions? Google Analytics can help you measure how effective your various marketing efforts are. By tracing your Path Length and Assisted Conversions, you can view what happens after one, two, or more touchpoints as well as the average amount of touchpoints needed for conversions.
Paving the Way to Successful Marketing Attribution
Ultimately, marketing attribution models give us a better understanding of how our customer maneuvers their journey. However, we will never know exactly how each step in that journey affected them. We can only ensure that our mechanisms and tactics are accurate and efficient. You can ensure that your conversion tracking is accurate and correct if there is consistency in your UTM and data collection, and continue to evaluate and adapt all types of attribution models to support your goals and decisions.
Importance of UTM (Urchin Tracking Module) and How Does it Work?
Ever look at a URL and see all the labels and symbols that come after a “?”. These are used by digital marketers to cleanly and efficiently track where their traffic is coming from. There are two parts to your UTM: the parameters and the variables. The parameters all begin with “utm_” and five potential parameters: utm_source, utm_campaign, utm_content, utm_term, and help your analytics accurately track your traffic. The variables allow for more specific tracking elements such as the source or details that define a campaign.
Keeping accurate and precise records of your UTM taggings and parameters ultimately allows you to identify and analyze which sources are performing well at a detailed level. Make sure the steps you are taking for your UTM’s are clear, organized, tested, and recorded to ensure your analytics team can understand exactly where and how your traffic is being sourced.
As we have talked about, your customers often do not see an Instagram ad and convert. More times than not, they re-visit and explore your site through various channels, searches, and even devices. Using a CRM and Google Analytics allows you to group these visitations into one cohesive pathway your customer takes. This is primarily done by creating non-personal identifiable IDs that can integrate data across these platforms under one user ID.
By creating these user IDs, you can see these journeys come to life and their processes more explicitly than individualized visits. These links and touchpoints are crucial to understanding how to credit your channels and how to model your attribution. This also gives clarity into how your customers are engaging and which platforms they may return to.
Recommended Attribution Tools for eCommerce Brands:
Wicked Report – A smart attribution platform that detects revenue-based conversions that are scalable. The tool provides expertise in marketing attribution, customer and subscription LTV, spending optimization, and easily accessible conversion data.
Funnel.io – A cloud-based deployment system that provides conversion tracking, cross channel attribution, and multi-touch attribution. The funnel allows you to seamlessly aggregate your data and use it with ease.
SegMetrics – A reporting tool designed to track and analyze your customer journey from start to finish. SegMetrics provides a holistic view of how your customer is converting using ad analytics, LTV, lead attribution, lead tracking, and cohesive account management.
Kochava – A mobile app and analytic attribution software created for scalable solutions. This system integrates omnichannel data, gives real-time app analytics, and cross-device identification, and audience segmentation.
LeadsRX Attribution Software – A B2B and B2C marketing attribution platform designed to help marketers see how their customers are engaging with advertising channels and converting. This tool provides attribution modeling, conversion tracking, cross channel attribution, customer journey mapping, and multi-touch attribution.
Dreamdata.io – A B2B revenue attribution platform that allows marketers to accurately assess and budget their money based on what drives their revenue. The system includes attribution modeling, conversion tracking, cross channel attribution, customer journey mapping, and multi-touch attribution.
Rule-Based Attribution vs Machine-Learning Attribution:
Attribution Models have both their benefits and limitations depending on how you use your data. Traditional models, such as last touch or first touch, linear, positional, and time decay, are simplistic and assign values based on basic understandings of touchpoints and their importance in regards to conversions. However, as these systems become more complex, they also need to learn and adapt as new information and data become available.
Rules-Based attribution models use predetermined rules based on your market data to credit each step in the conversion process. It does not take into account any historical or personalized data. It simply follows the pe-created formula of your input. For example, first-touch or last-touch attribution models are Rules-Based. They assign credit based on the first touch or the last-touch without considering other pathways or touchpoints that drive conversion. This makes rules-based models more simplistic and easier to implement.
Machine Learning or Data-Driven attributions use integrated data and algorithms to predict and credit each touchpoint along the conversion pathway accurately. This is done by gathering data and implementing the model with machine learning so that it adapts as more data is collected. Machine Learning and Data-Driven models allow for forecasting and raise potential scenarios to optimize and strategize. The more information and analytics given to the model allows the process to get more efficient and accurate.
When comparing Rules-Based vs. Machine Learning models, the most significant benefit comes from machine learning being able to detect, report, and improve in real-time. The model is never perfected but gradually adjusts and becomes more accurate over time. Rules-based models are much simpler and provide snapshots and data after the fact and must be manually improved. Rules-based models are much more straightforward and inexpensive to implement, while machine learning may be harder to build and then take results and insights and operationalize them for future models.
Overall, Machine Learning Attribution models have the potential to be long-term and integrated solutions to measure all aspects of engagement from your consumer at a higher cost. In comparison, Rules-Based models are simplistic but give you less detail when it comes to the process.
In conclusion, getting your customer to convert is what drives and moves your business forward. Understanding how and where they convert is a valuable tool that allows you and your customer to convert efficiently and effectively. Marketing attribution models are the key to driving that success and giving you insight into how, why, and what to spend your budget. These models can be simplistic or data-driven but ultimately give you the clarity you need to make strategic decisions and how your customer can convert more efficiently. We hope this guide enlightened you on the merits of marketing attribution but if you’re looking to take your marketing to a new level we’d love to talk!