When you type a search query into Google, you typically get millions of results; most likely, though, you never even navigate to the second page (neither do 91.5% of other users), making that sweet, sweet “first page of Google” prime digital real estate.
But how do you end up in one of these top spots? The answer is search engine positioning.
If you’re an SEO, you might be reading this and thinking: how is this different from regular SEO? While SEO overall focuses on site-wide health and long-term authority, search engine positioning is a granular subpractice: It’s the process of taking a page on your site (or set of pages) and micro-optimizing them to increase their position on the search engine results page (SERP).
Traditionally, this meant optimizing pages to try to earn Position 1 on the SERP (the most highly ranked organic result on Google), or a Featured Snippet. Now, though, AI Overviews are top of mind, as over 50% of Google queries trigger an AI Overview.
Staying on top of this practice is salient with Google’s constant evolution. Recently, for example, Google retired num=100, which is the ability to view 100 results per page. This change has changed how rank-tracking tools work, resulting in a perceived drop in impressions while making it even more important to rank on the first page since anything beyond that won’t be counted accurately.
What this should tell you is that nothing is set in stone with search; it’s constantly evolving, and you should be, too.
On the bright side, we’re here to help. In this article, we’ll break down search engine positioning for you and provide some actionable strategies for you to do it so that you’re ahead of the game, not falling behind.
What’s the Difference Between Search Engine Positioning & SEO?
Okay, we know we just went over it, but let’s address the elephant in the room: just how different is search engine positioning from regular SEO?
We’ll say it again: SEO is the process of optimizing your entire website for search engines. Search engine positioning gets more granular as the process of optimizing specific pages on your website for search engines.
But let’s break it down even further. Think of it this way:
Your SEO strategy might include writing blog posts in your niche, performing keyword research, and doing topic clustering. For search engine positioning, you would instead target specific pages that you would like to rank higher, and optimize their content.
SEO is a comprehensive process that requires ongoing effort to update and improve all aspects of a website. It can take months or years to see results from your SEO efforts; it’s not one-and-done, and it’s definitely not something that gives you overnight results.
Search engine positioning, however, has the potential to produce faster results because you’re working with a few specific pages at a time. It doesn’t, however, mean that you should be neglecting your general SEO efforts. Search engine positioning only works if you have a solid SEO foundation.
Why Search Engine Positioning Is Important
It doesn’t matter how good your content is; If people can’t find it in the SERP, they won’t be reading it.
A case study by Backlinko found that the top result on Google is 10x more likely to receive a click than the 10th position, with the first result receiving an average click-through-rate (CTR) of 27.6%. The data shows a pattern: the lower you rank, the lower your CTR is.
However, Semrush found that keywords that triggered an AI Overview had higher zero-click behavior. This means that if you’re not populating as a source in AI Overviews for your target keywords, you’re already behind.
The Takeaway: With clicks going down as a whole, it’s more important than ever to make sure you’re visible in the right places, as long-term brand visibility is the new play.
How SEO & Search Engine Positioning Impact AEO
We know we’ve been raving on about AI Overviews, but the good news is that if your SEO and search engine positioning efforts are up to modern day standards, they play a role in helping you get that sweet, sweet AI Overview placement.
Strong SEO and effective search engine positioning are part of the foundation of Answer Engine Optimization (AEO), the practice of optimizing your content to be cited and mentioned in AI Overviews and LLMs.
SEO: The Foundation of AEO
Your general SEO strategy is the baseline of trust and authority AI needs to even consider your site to be cited in its responses. AI is trained to prioritize reliable sources, meaning that general SEO best practices are a prerequisite for AEO success:
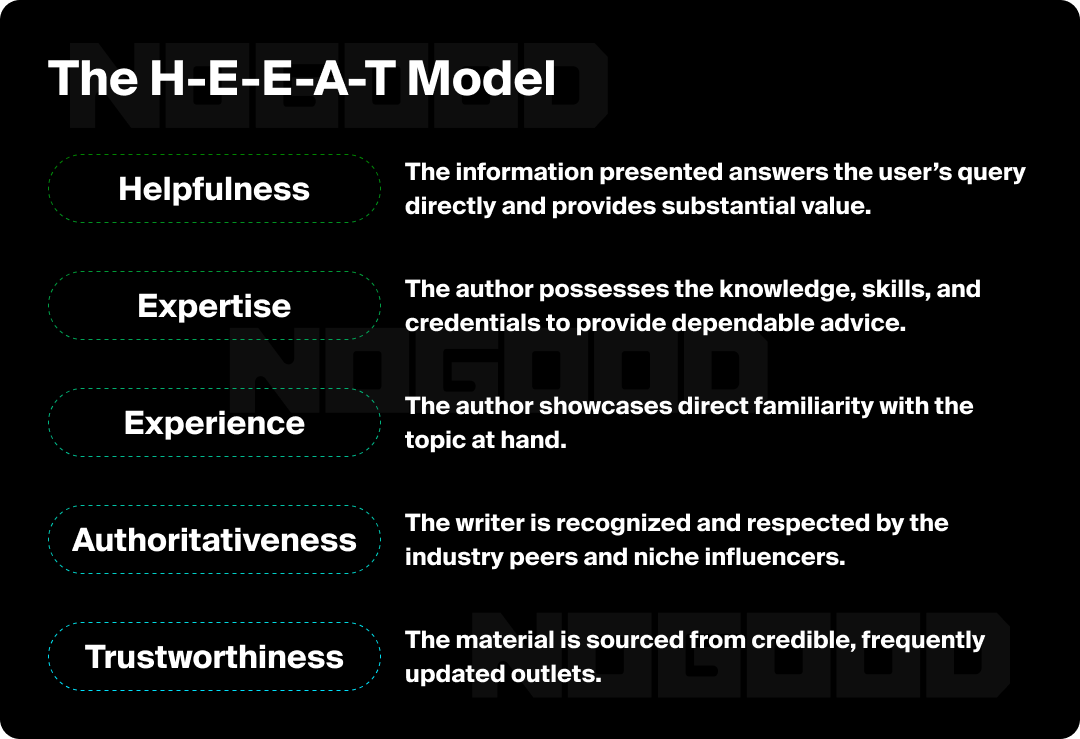
- Trust & H-E-E-A-T: A strong, site-wide SEO foundation built on high H-E-E-A-T (Helpfulness, Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) is essential. Without proven credibility, AI will default to more established domains, regardless of how perfect your content or formatting is.
- Crawlability & Indexing: If your technical SEO is flawed due to slow page speed, broken structure, or mobile issues, AI may struggle to access and parse your content efficiently, effectively blocking it from being cited in the first place.
Search Engine Positioning for AEO
Search engine positioning takes an already well-vetted page and micro-optimizes it to be the best possible answer for the AI model to select. When you’re doing this, here are some practices to keep in mind if you want your content to populate in an AI Overview:
- Direct, Concise Answers: AI aims to answer questions immediately, because that’s what people have come to expect. Your page should open with a single, concise, and accurate answer to the target query, ideally kept within 40-60 words.
- Structured Formatting: Use semantic HTML and clear formatting (like bulleted or numbered lists for procedural content) to provide clarity.
- Schema Markup: Implement relevant schema (like FAQPage or HowTo) to explicitly tell the search engine and AI the context and purpose of your content, boosting the likelihood of it being selected for a generative answer in the SERP.
6 Search Engine Positioning Strategies to Drive Organic Traffic
Now that you know all about search positioning, we’re gonna give you some strategies to help you start.
1. Descriptive Meta Description & Title Tag
The meta description is the description under the link on the SERP that users see before they click on your website. The title tag is the name of the page that the user sees on the SERP. Both are critical and can determine whether the user clicks on your website or your competitor’s.
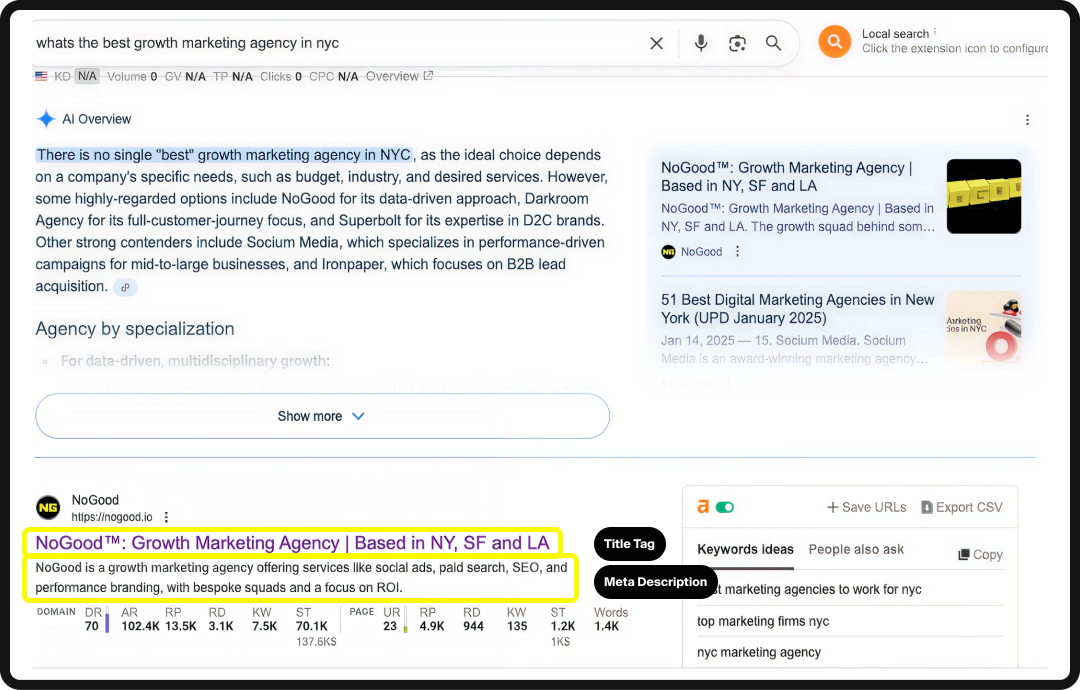
Basic SEO tactics tell you to do this:
Make sure the text is concise, aligns with the user intent, and accurately describes what your page is about. Ideally, it should also contain the primary keyword for that page.
It also tells you that your title tag should be between 50 and 60 characters, and your meta description should be no more than 160 characters to prevent the search engine from truncating it. Here’s an (ironic) example:
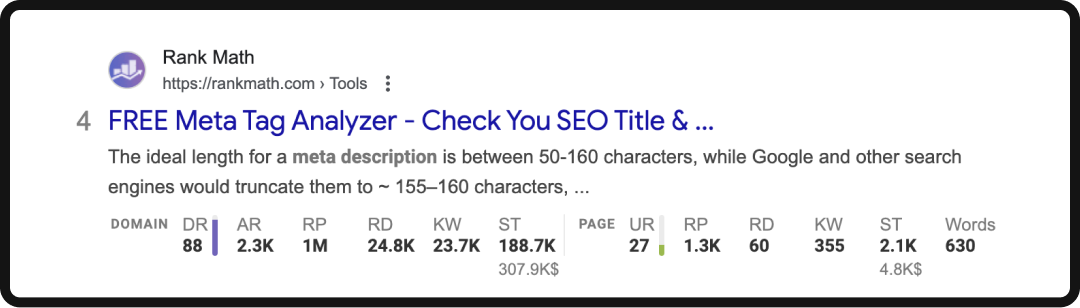
But to really practice search engine positioning, you should be elevating your basic SEO practices. This means stating the content of the page clearly and concisely, even including the keyword in its entirety closer to the front of the page title and within the meta description.
2. Prioritize the User Experience
Google’s algorithm prioritizes content that is tailored to the user’s experience. This is a developing discipline of SEO called Search Experience Optimization (SXO), which blends SEO with user experience (UX). Here are some ways to put it into practice:
- Directly answer the user’s question in the first 100 words, then elaborate using examples, images, and infographics.
- Format your content with H2s and H3s so that it’s logical and easy to follow.
- Add anchor links or a table of contents (like the one in the left sidebar of this article) to help users easily navigate through your page.
Prioritizing UX allows users to get more value from your website, leading to higher engagement, increased CTRs, and more engaged sessions. When you create content that puts the user first, you give Google a reason to serve that content to those searching for it.
3. Create User & Keyword-Optimized Content
Semantically related keywords help Google show users the most relevant content for their query. To make sure your pages are showing up for the right queries, perform keyword research to target terms with high monthly search volume and low keyword difficulty. Striking this balance can be difficult, but if you use a keyword matrix, it’ll set you on the right track.
After you’ve chosen your primary keyword, avoid keyword stuffing (throwing the keyword into content as much as possible) and adding unnecessary secondary keywords to achieve a higher keyword ranking. Adding too many keywords will likely confuse the user and the search engine, and could even hurt your ranking potential.
To make sure users are getting value from your content and not just search engines, you should be doing tactics like conducting a SERP analysis to ensure you’ve answered all questions related to the topic at hand. The SERP can tell you a lot: It can tell you what kind of content is ranking highly, the follow-up questions people tend to have, what types of content formats people are consuming for that keyword, and more.
The SERP is essentially the blueprint for your content, so make sure you’re tapping it for all its value and keep the user at top-of-mind, especially as Google values high H-E-E-A-T content.
4. Use Internal Linking
Internal links help Google understand how different pages of your website relate to each other. This means that if you’re writing content related to topics you have already written about, include text with embedded hyperlinks to those pages. This helps avoid content cannibalization, which is when two or more webpages compete for the same keyword due to their similarity, effectively hurting both their chances of ranking.
Using Links to Funnel Authority to a Target Page
To practice effective search engine positioning, your internal links should be used to clearly designate a pillar page for a specific core keyword.
Let’s use the example of a consumer brand that sells yoga clothes. The brand has two pieces of content it wants to rank:
- A high-converting product page for “Performance Yoga Pants.”
- A supporting blog post about “The Best Pants for Every Type of Workout.”
Your goal is to ensure the product page ranks for transactional keywords like “buy yoga pants,” and the blog post should rank for informational keywords like “best pants for workout.”
Throughout the blog post, they include links to the Product Page. By using clear anchor text like “shop our Performance Yoga Pants,” the brand achieves two things essential to search engine positioning:
- Avoids Cannibalization: The internal link clearly signals to Google that the product page is the final authority for the transactional query, preventing the blog post from accidentally competing for the wrong spot.
- Improves User Experience (UX): If a reader is interested in one of the pants, they can click the link and convert without having to leave the article and search again. This facilitates an engaged session, sending positive signals to search engines about the page’s quality.
By linking with intention, you funnel authority and relevance to the specific page you want to rank for a specific keyword, refining your search engine positioning strategy.
Here are some best practices for internal linking:
- Don’t Include Too Many Links: A good rule of thumb is 3-4 internal links for every 300-500 words. Be sure links are relevant to the topic and genuinely helpful for the user; don’t just throw links in there for the sake of it.
- Test All of Your Links: After you add links to the page, click on them to make sure they take the user to the correct page.
- Make Your Anchor Text Brief: The highlighted text should be a key phrase of about 3-5 words that explains the topic and tells the user what to expect if they click the link.
5. Reduce Page Load Time
Okay, so search engine positioning and your overarching SEO strategy are going to converge with this one. Page load speed is important from two standpoints: Google prioritizes pages that load fast, but also, pages that take too long to load decrease engaged sessions.
The thing is, with proper technical optimization, all of your pages should be technically sound, not just some of them. A few bad apples hurts your site as a whole, and as a result, your ranking potential on an individual level.
You can test your page load speed using free tools Page Speed Insights, or by running a comprehensive technical SEO audit on your website.
Page Speed Insights will tell you what can be improved on your site, but you should be focusing on making sure your Core Web Vitals are up to par. If you don’t know how to address this, don’t worry: Page Speed Insights gives you some recommendations to help you improve these scores. Here’s a snapshot of recommendations for Nike; the dropdown gives more details on specific areas to target for fixes:
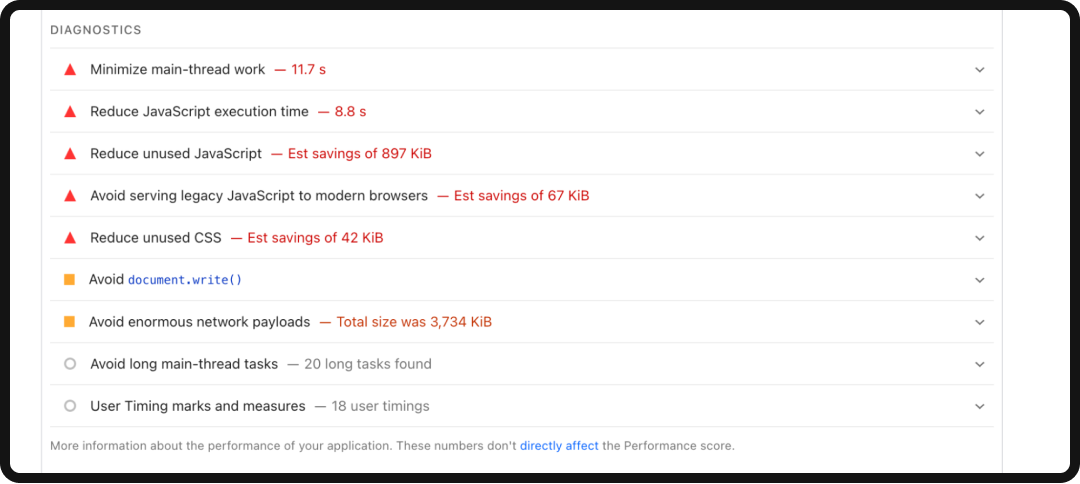
6. Optimize to Rank for Specific SERP Features
Search engine positioning is the practice of micro-optimizing to win the top spots, and today, that means aiming beyond the traditional SERP or even AI Overviews. We’re gonna break down some specific SERP features you can try to rank for anywhere on the SERP.
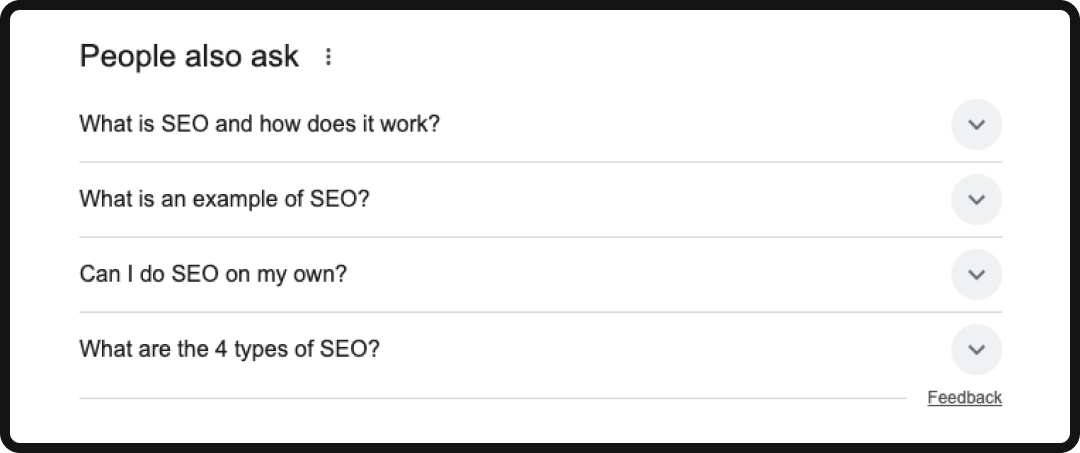
People Also Ask Boxes
People also ask boxes to appear as expandable questions that address related user intent.
- The Tactic: Use subheadings (H3 or H4) that are phrased as common questions related to your main topic (e.g., “What are the benefits of X?”) based on keyword research. Immediately follow each question with a direct, single-paragraph answer that’s concise.
- The Benefit: You answer multiple related queries on a single page, potentially capturing multiple People Also Ask slots and demonstrating topical breadth to the search engine.
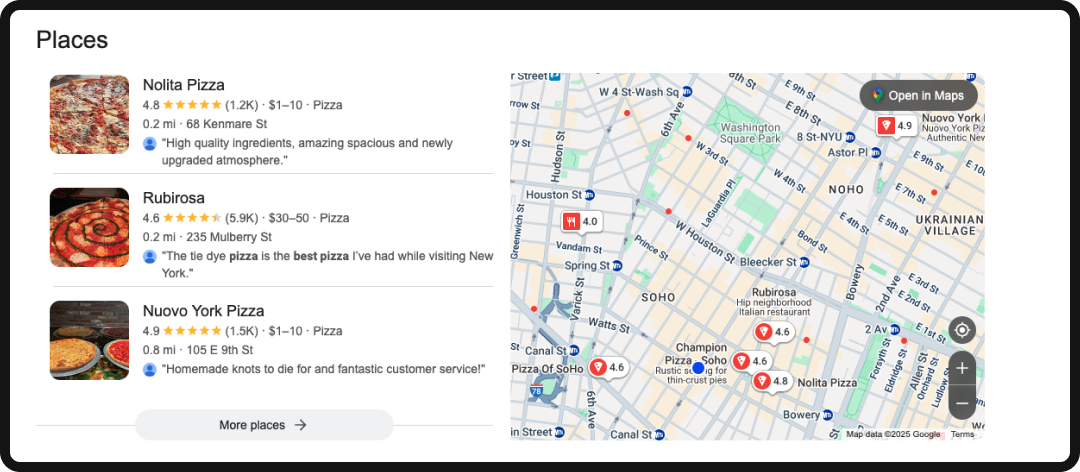
Local Pack
The Local Pack is the boxed result that shows a map and three local businesses, usually triggered by queries with local intent (e.g., “best pizza near me”).
- The Tactic: While dependent on Google Business Profile optimization, the search engine positioning angle is to create content that supports your local intent. This includes having pages with geographically specific keywords in the titles (e.g., “SEO Agency in Brooklyn”) and embedding a map widget with your correct location.
- The Benefit: Ranking in the Local Pack offers unparalleled visibility for local queries, driving high-intent phone calls and store visits, two critical conversion goals.
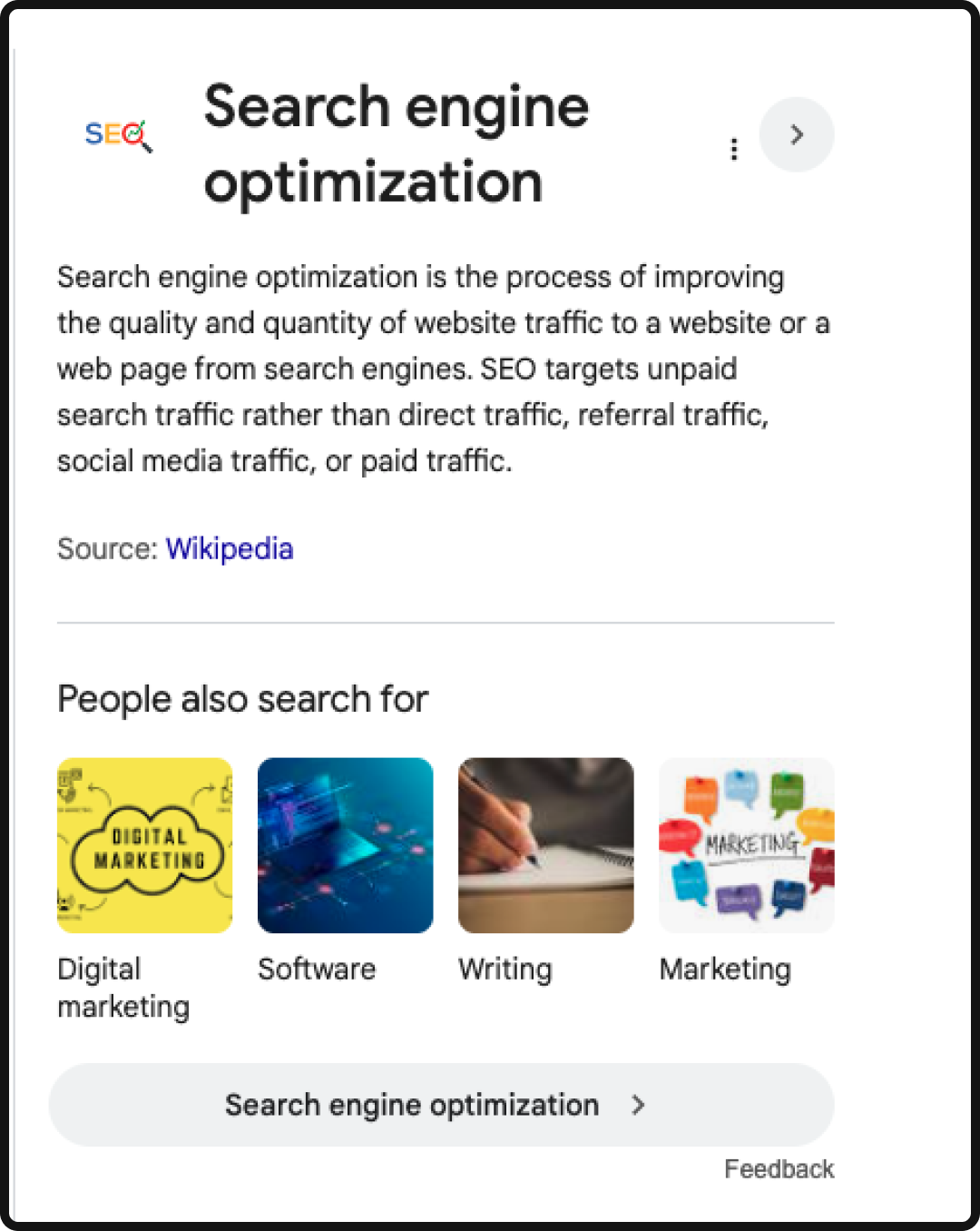
Knowledge Graph
The Knowledge Graph is a large information box that typically appears at the right-hand side of the SERP, offering broken down information about a person, place, or thing.
- The Tactic: While Google often pulls data from its own sources (like Wikipedia or official entity sites), you can influence it by ensuring your target page features authoritative, factual content that is structured like a profile or summary. Use a definitive, dedicated section for key facts, dates, and official names. The most effective method is to implement schema on your target page to explicitly tell the search engine: “This is the official information for this entity.”
- The Benefit: Securing the Knowledge Graph panel establishes your brand as the single source of truth for your own entity. This feature builds trust and authority, and it positions your brand in a unique position on the SERP, maximizing your search real estate and reinforcing your credibility as a potential source for the AI Overview.
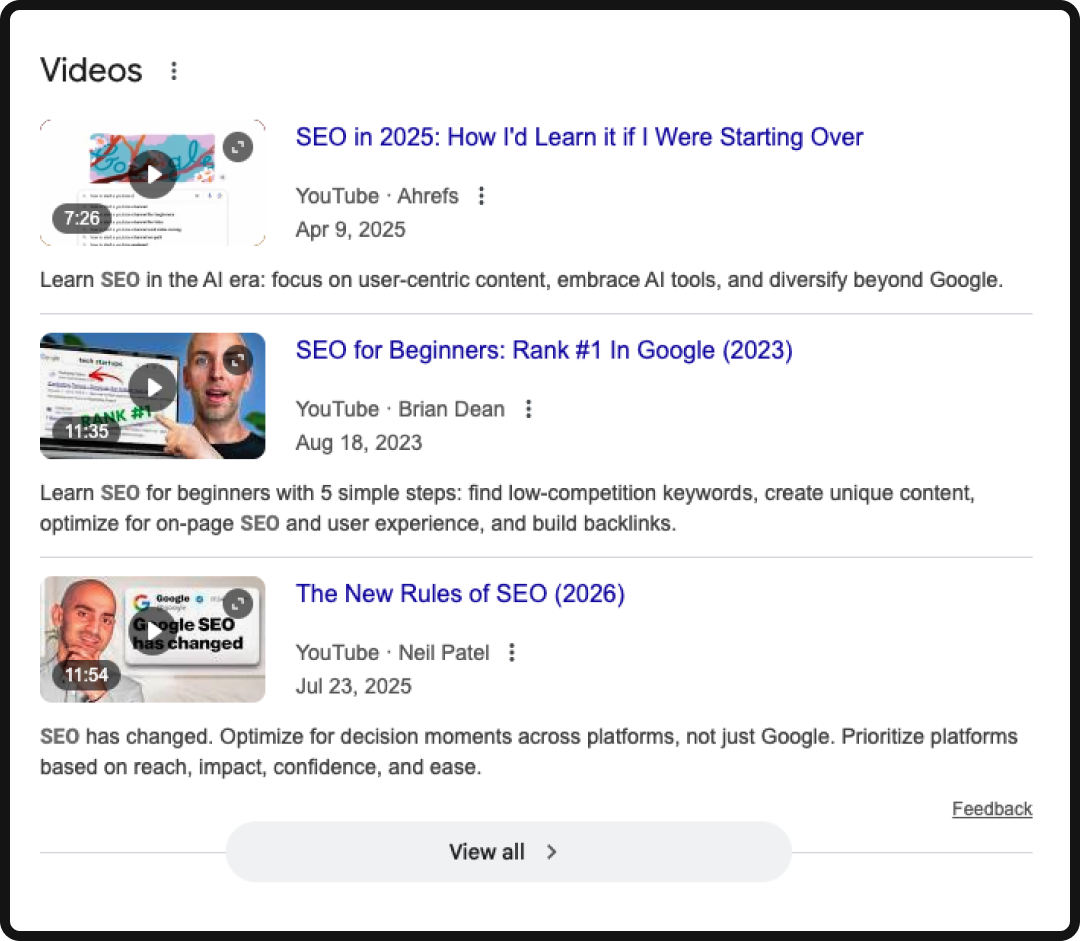
Visual Content (Image & Video Thumbnails)
Visual results often appear in dedicated carousels throughout the SERP for some keywords, which can include images, videos, or short-form content.
- The Tactic: Ensure all images and videos have descriptive file names and alt text that contain relevant keywords. For videos, embed them on their own page with a clear title and description, and utilize schema to ensure they are easily discoverable. For YouTube specifically, we have a guide that you can follow to make sure your videos are visible.
- The Benefit: Visuals break up the monotony of the SERP, drawing the user’s eye and increasing your chances of a click, even if your accompanying written content isn’t at the top of the SERP.
Securing Your Digital Real Estate
As we’ve established, search engine positioning isn’t a replacement for SEO; it’s an effective microstrategy. And with Google and its algorithms constantly changing, you have to stay on top of it so that you’re not falling behind on the SERP.
By doing search engine positioning consistently, you’re not ensuring that you’re visible; You’re ensuring you’re the definitive choice for users, the traditional SERP, and AI, maximizing your search real estate.
Ready to start? Reach out to our team for comprehensive SEO and AEO services and to assist in your search engine positioning endeavor.