As brands struggle to make sense of where to allocate their marketing dollars, Media mix modeling (MMM), often also known as marketing mix modeling, stands as a pivotal tool to help arrive at an answer statistically. In this guide, we’re cutting through the complexity to bring you a straightforward, comprehensive look at how MMM works, why it’s crucial for your marketing strategy, and how to implement it effectively.
Whether you’re looking to fine-tune your ad spend, understand your ROI across various channels, or simply make more data-driven decisions, this guide is your starting point. Let’s dive into the world of MMM and unlock the secrets to optimizing your marketing efforts in today’s complex and dynamic media landscape.
What is Media Mix Modeling (MMM)?
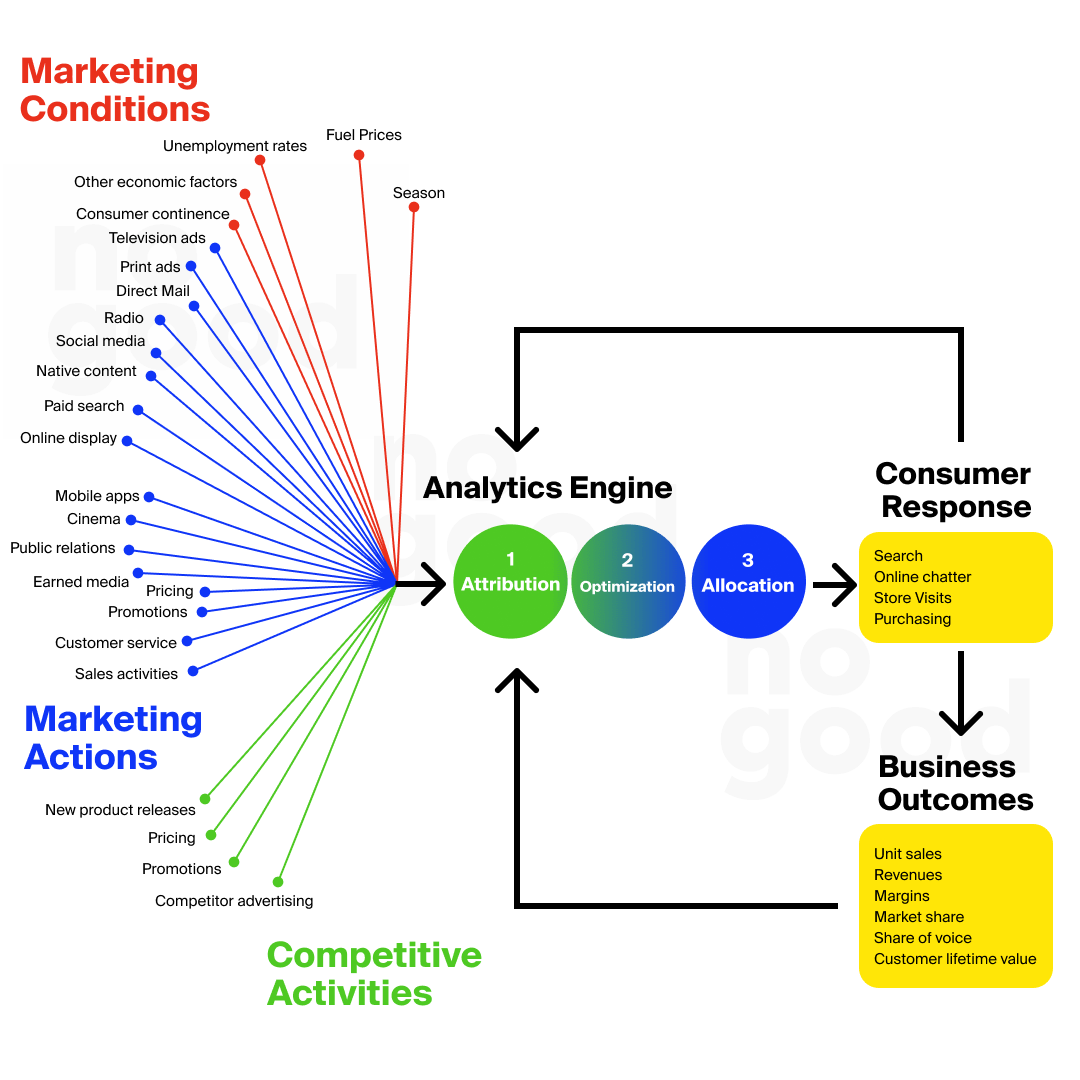
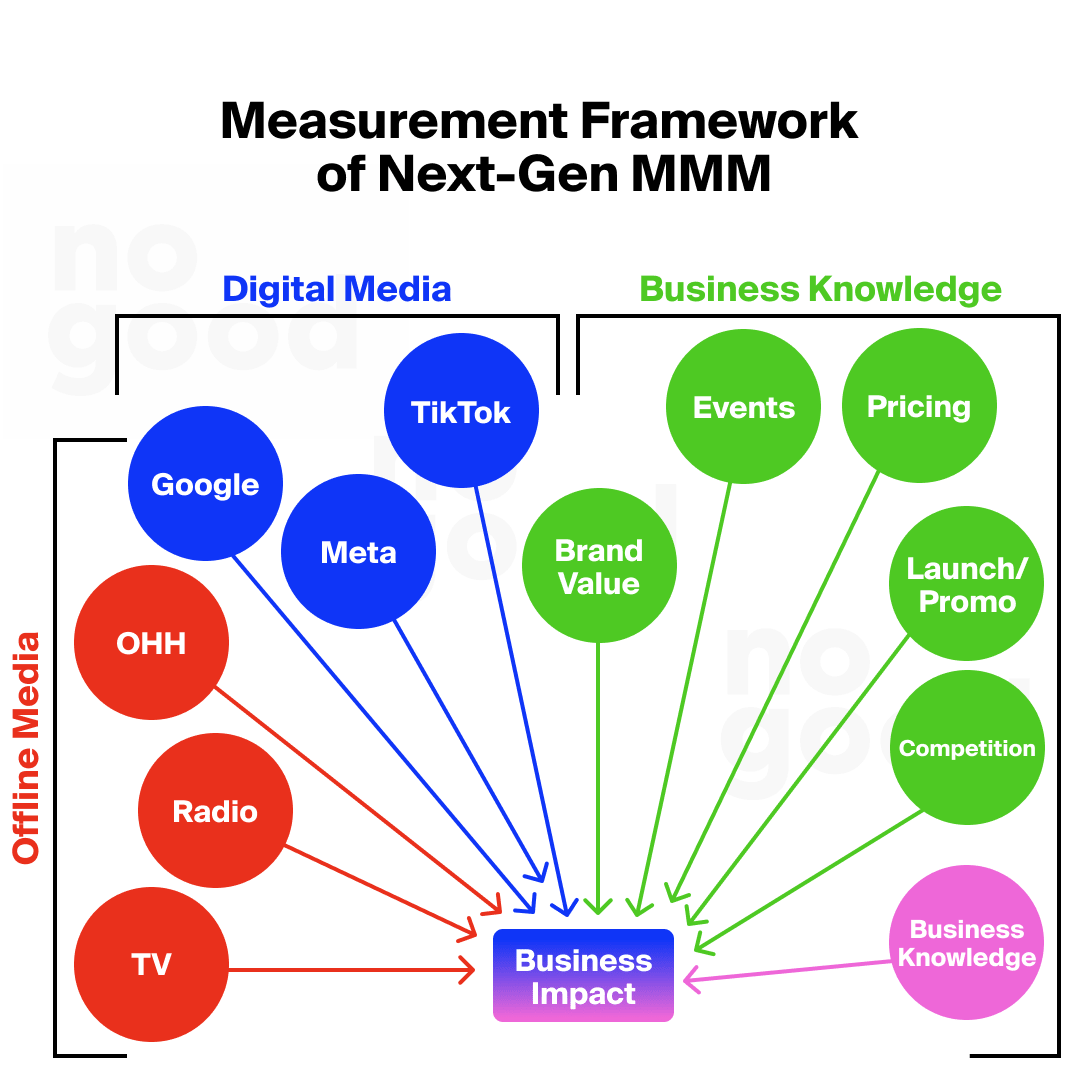
Media mix modeling (MMM) is a quantitative analysis technique used to assess the impact of different marketing efforts on sales and other key performance indicators (KPIs). This method leverages historical data to determine the effectiveness of each marketing channel, including digital, traditional, and emerging media, by isolating and measuring their individual contributions to overall marketing success.
MMM accounts for external factors like economic conditions, seasonality, and competitive actions, enabling marketers to optimize their media spend for maximum return on investment. In the age of performance marketing, where media, creator, and influencer impact is significant yet often nebulous, MMM provides clarity and actionable data.
MMM encompasses several elements:
- Media Spend Across Channels: This includes traditional channels like TV, radio, print, and digital platforms, along with creator and influencer marketing spends.
- Sales Data and KPIs: Historical sales data is correlated with marketing efforts to identify patterns.
- External Factors: Elements like economic indicators, seasonality, and market trends are considered.
- Brand Factors: These include product launches, price changes, and brand equity.
Steps to Implementing Media Mix Modeling
Implementing MMM is a multi-step process that requires meticulous planning and execution.
1. Define Objectives and KPIs
- Objective Setting: Clearly define what the brand aims to achieve with MMM. This could be understanding the ROI of marketing channels, optimizing the marketing mix, or forecasting sales.
- KPI Identification: Determine the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be used to measure success. Common KPIs include sales, market share, website traffic, and conversion rates.
2. Data Collection
- Marketing Spend Data: Collect data on marketing spend across all channels, including digital (social media ads, search engines, email, etc.), traditional (TV, radio, print advertising), and other channels (events, sponsorships).
- Sales Data: Gather historical sales data corresponding to the same period as the marketing data.
- External Data: Collect data on external factors that could influence sales but are outside the marketing efforts, like economic trends, seasonality, and competitive actions.
- Granularity of Data: Ensure the data is as granular as possible (e.g., weekly level or monthly data, region-specific data).
3. Data Preparation and Cleaning
- Data Aggregation: Aggregate data from various sources into a consistent format.
- Cleaning and Normalization: Clean the data for inconsistencies or missing values and normalize it to ensure comparability across different data types and sources.
- Data Segmentation: Segment data if necessary (e.g., by product lines, regions, customer segments).
4. Model Selection
- Choosing the Model Type: Decide on the type of statistical model to use. Regression models are common, but more complex approaches like Bayesian models or machine learning algorithms can also be used.
- Customization: Customize the model to fit the brand’s specific needs and market dynamics.
5. Variable Selection and Model Building
- Identifying Variables: Identify independent variables (marketing spends, external factors) and dependent variables (sales, other KPIs).
- Model Construction: Build the model using statistical software, incorporating the identified variables.
- Incorporating Lag Effects: Account for the lag effect, which is the delay between marketing exposure and consumer response.
6. Model Calibration and Validation
- Calibration: Adjust the model to align with known data points and historical-, or long-term trends.
- Validation: Validate the model using a subset of data or historical data to ensure its accuracy in predicting business outcomes.
7. Analysis and Insight Generation
- Running the Model: Run the model with the full data set.
- Interpreting Results: Analyze the output to understand the direct impact of different marketing channels on sales and other KPIs.
- Insight Generation: Generate actionable insights, such as which traditional or digital channels have the highest ROI or how different channels interact with each other.
8. Strategy Development and Implementation
- Strategy Formulation: Based on the insights, formulate a marketing strategy that optimizes the marketing mix.
- Budget Allocation: Adjust the marketing budget allocation across channels to maximize ROI.
- Tactical Adjustments: Make tactical adjustments, like changing the creative approach or targeting strategy in specific channels.
9. Continuous Monitoring and Model Updating
- Ongoing Monitoring: Continuously monitor the performance of the marketing efforts against the model’s predictions.
- Model Updating: Regularly update the model with new data and adjust for any market dynamics or consumer behavior changes.
10. Reporting and Communication
- Stakeholder Reporting: Create reports for stakeholders summarizing the findings, insights, and recommended actions.
- Cross-Departmental Collaboration: Ensure that insights are shared across departments (marketing, sales, finance) for integrated decision-making.
Advanced Considerations in MMM
The implementation of MMM involves intricate details and considerations.
Model Sophistication
- Time-Series Analysis: Some models incorporate time-series analysis to account for lag effects in marketing impact.
- Non-linear Modeling: To capture the complex nature of market response, advanced models may employ non-linear approaches.
Data Granularity
- Micro-Level Data: Leveraging granular data, such as geographical sales data or product-level sales, can enhance model accuracy.
- Cross-Channel Synergies: Recognize and account for the interplay between different marketing channels.
Challenges in Media Mix Modeling
While MMM is powerful, it comes with its own set of challenges.
- Data Quality and Availability: The accuracy of MMM is heavily reliant on the quality and granularity of available data.
- Attribution Complexity: Disentangling the specific impact of overlapping marketing channels, especially in digital domains, is challenging.
- Evolving Digital Landscape: The digital marketing world is dynamic, requiring continuous model updates and adjustments.
Case Studies and Examples
To illustrate MMM’s efficacy, consider hypothetical case studies:
- Brand A: After implementing MMM, Brand A identified that their influencer marketing campaigns were significantly driving online sales, leading to an increased budget allocation towards influencer collaborations.
- Brand B: Brand B realized through MMM that their social media campaigns were not effectively translating to sales, prompting a strategic shift towards more ROI-effective channels.
When does it make sense to use media mix modeling?
Ideal Scenarios for Using MMM
- Mature Markets with Ample Historical Data:
- Brands in established markets with years of sales and marketing data can leverage MMM effectively. The richness of historical data allows for more accurate modeling and analysis.
- Complex Marketing Mix:
- Brands utilizing a diverse range of marketing channels (digital, traditional, influencer, etc.) benefit from MMM. It’s adept at dissecting the impact of each channel in a multi-channel strategy.
- High Marketing Spend:
- For brands with huge marketing budgets, MMM helps allocate resources more efficiently, ensuring better marketing ROI and reducing wasteful spending.
- Market Share Growth or Retention Goals:
- Brands aiming to expand or defend their market share can use MMM to understand which channels most effectively drive these goals.
Solving Specific Marketing Problems
- Optimizing ROI Across Channels:
- Problem: A brand is unsure which marketing channels yield the best return on investment.
- MMM Solution: By quantifying the impact on sales each channel has, MMM provides clarity on where to allocate budget for maximum effectiveness.
- Understanding the Impact of External Factors:
- Problem: Sales are affected by external factors (e.g., economic changes, competitor actions) that the brand struggles to quantify.
- MMM Solution: MMM can isolate the impact of these external factors, allowing brands to adjust strategies accordingly.
- Attribution in Multi-Channel Marketing:
- Problem: Brands face difficulty in attributing sales to specific marketing efforts, particularly in a multi-channel context.
- MMM Solution: MMM provides a more holistic view of how various channels contribute to sales, overcoming the limitations of last-click attribution models.
- Forecasting Sales and Market Trends:
- Problem: Brands need to forecast future sales and market trends to plan effectively.
- MMM Solution: With predictive capabilities, MMM helps forecast sales based on different marketing scenarios.
- Long-Term Strategic Planning:
- Problem: Brands looking for long-term strategic planning need insights beyond short-term performance metrics.
- MMM Solution: MMM offers a long-term view of marketing effectiveness, aiding in strategic decision-making.
- Adapting to Market Changes:
- Problem: A brand needs to understand how to adjust its marketing in response to market shifts or new competitor strategies.
- MMM Solution: By incorporating external market factors, MMM allows brands to adapt their marketing strategies to dynamic market conditions.
- Evaluating Offline Marketing Impact:
- Problem: Measuring the impact of offline marketing channels is challenging.
- MMM Solution: MMM is particularly useful for quantifying the impact of traditional marketing channels like TV, radio, and print.
Tools you will need to implement MMM
Data Collection and Management
- Google Analytics: For digital data collection, particularly website traffic, user behavior, and conversion tracking.
- CRM Systems (like Salesforce or HubSpot): Useful for managing and integrating customer data, including purchase history and interactions across different marketing channels.
- Social Media Analytics Tools (like Sprout Social or Hootsuite): For collecting data on social media engagement and ad performance.
Statistical Analysis and Modeling Software
- R or Python: Both are powerful programming languages for statistical analysis and modeling. They offer extensive libraries and packages specifically designed for data analysis (e.g., pandas, numpy, scipy in Python; ggplot2, dplyr in R).
- SAS: A comprehensive analytics suite many large organizations use for advanced data analysis, including media mix modeling.
- SPSS (IBM): Known for its user-friendly interface, SPSS is suitable for complex statistical data analysis.
Visualization and Reporting Tools
- Tableau: Highly effective for creating interactive and shareable dashboards that visualize the results of the MMM.
- Microsoft Power BI: Offers robust data visualization capabilities, integrating data from various sources for comprehensive reporting.
- Google Data Studio: A free tool that integrates well with other Google services for creating reports and dashboards.
Integrated Marketing Analytics Platforms
- Nielsen Marketing Mix Modeling: Provides custom MMM solutions, widely respected for their data quality and comprehensive analysis.
- Kantar Millward Brown: Offers detailed MMM services, combining market research data with advanced analytics.
- MarketShare (by Neustar): A marketing analytics platform that provides MMM solutions, often used for strategic planning and budget allocation.
Cloud Computing Platforms
- AWS (Amazon Web Services): Useful for storing and processing large data sets, with services like Amazon S3 for storage and AWS Lambda for data processing.
- Google Cloud Platform: Offers wide-ranging data analytics and machine learning services that can be leveraged for MMM.
Specialized MMM Software
- Adverity: A marketing data integration tool that can help in aggregating data from multiple sources, which is crucial for MMM.
- Allocadia: Focuses on marketing performance management, offering tools for budgeting and planning that can complement MMM efforts.
Conclusion
In an era where creator and influencer marketing is becoming increasingly dominant, marketing mix models emerge as an indispensable compass for brands grappling with the intricacies of creator and influencer-dominated strategies. This comprehensive guide sheds light on the pivotal role of MMM in unraveling the nuanced impact of various marketing channels on essential KPIs. In today’s era of data-driven decision-making, MMM offers a systematic and adaptive approach, enabling brands to quantify the impact of their marketing mix and optimize it for heightened ROI.
As brands navigate the digital and offline channels, MMM becomes a strategic ally, providing valuable insights into marketing activities and tactics. By embracing MMM, marketing teams can better understand channel performance and refine marketing plans for future campaigns. This quantitative analysis technique considers historical performance, acknowledging the impact of advertising on base sales and broader business performance.
It allows brands to identify marketing drivers and assess the positive impact of advertising campaigns. Through this lens, MMM facilitates a data-driven approach to marketing, offering a granular examination of marketing inputs on sales and KPIs. In this period of time, where the customer journey is multifaceted, MMM stands as a beacon, guiding brands toward optimized marketing strategies tailored to target audiences and ensuring the continued success of their marketing endeavors.