The rise of generative AI isn’t just another passing wave, it’s a change in the current that’s redefining both how consumers discover and digest information and how businesses connect with audiences. LLMs are rapidly becoming the gate keepers of information on the web with ChatGPT rapidly becoming one of the most popular sites on the web.
In traditional organic search and SEO, most strategies revolve around climbing rankings on search engine results pages (SERPs). But with Generative Engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini are driving more and more search behavior, users are asking questions in a conversational way and receiving synthesized, context-rich answers that often eliminate the need to click on external links.
The concept of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) emerges as the strategic framework to ensure your brand is both discoverable and cited by these new highly intelligent engines. This is an area that we have research and written about extensively. To succeed in this new landscape, brands need a playbook that weaves together the sustainable SEO fundamentals as well as AI Search insights.
This guide will walk you through why GEO matters, how it differs from standard SEO, what ranking factors drive AI-based visibility, and how to implement effective GEO strategies and measure impact.
Why GEO Matters More Than Ever
Generative AI has turned the concept of “search” on its head. Users no longer need to browse through lists of blue links; advanced LLMs can synthesize meaningful answers in real time, often without sending the user to an additional website. This answers-first paradigm carries big implications for brands and marketers:
- Visibility is more elusive: Simply ranking #1 on Google doesn’t guarantee you’ll be featured in an AI-generated response.
- Users expect concise, context-rich replies: They might never see your well-optimized landing page if the AI chat interface provides everything they need.
- Multi-turn conversations: Users can refine queries on the fly and ask follow-up questions, shifting from “What are the best running shoes?” to “Which brand is eco-friendly?” and “Where can I buy them locally right now?”—all in a single session.
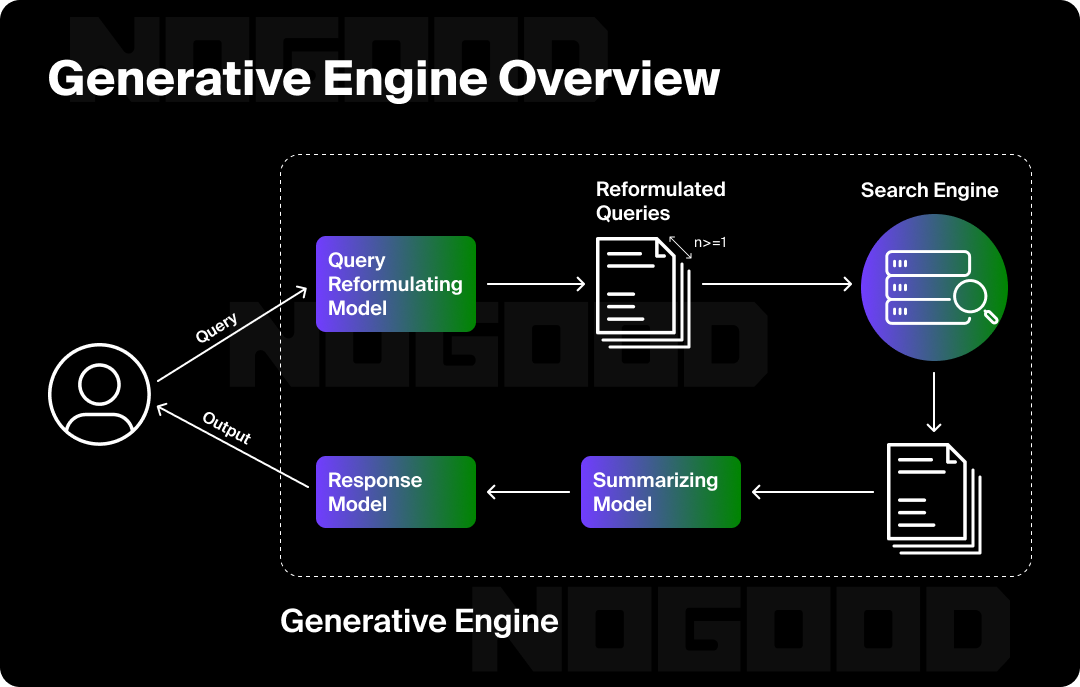
In this environment, your brand must be recognized by AI engines as authoritative, trustworthy, and contextually relevant. Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) ensures that you not only exist in a search index, but also become a central piece of the conversation—that is, the conversation between the user and the AI model.
The Consequences of Not Adapting
Brands that ignore GEO risk fading out of AI-driven ecosystems, losing mindshare and, ultimately, conversions. Traditional SEO alone is no longer sufficient; even if your page ranks well on Google, AI results may overshadow standard SERPs or reduce click-through rates. Thus, investing in GEO now is an investment in future-proofing your brand’s discoverability.
What Is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the practice of influencing and optimizing how AI-driven search systems—especially those powered by LLMs—access, interpret, and include your content in their automatically generated answers.
While SEO focuses on ranking in traditional SERPs, GEO goes a step further. With GEO, your objective is to:
- Embed your brand, data, and expertise into the knowledge base and training sets of AI models.
- Align your content structure and signals so that real-time AI search engines (e.g., Perplexity, Bing Chat, ChatGPT Search) see you as a relevant, high-authority source.
- Encourage AI to cite or reference your brand and offerings in the final, synthesized response it delivers to the user.
It’s a holistic approach that blends technical SEO with content quality, brand authority, and community engagement, all under the lens of how advanced AI systems process and produce information.
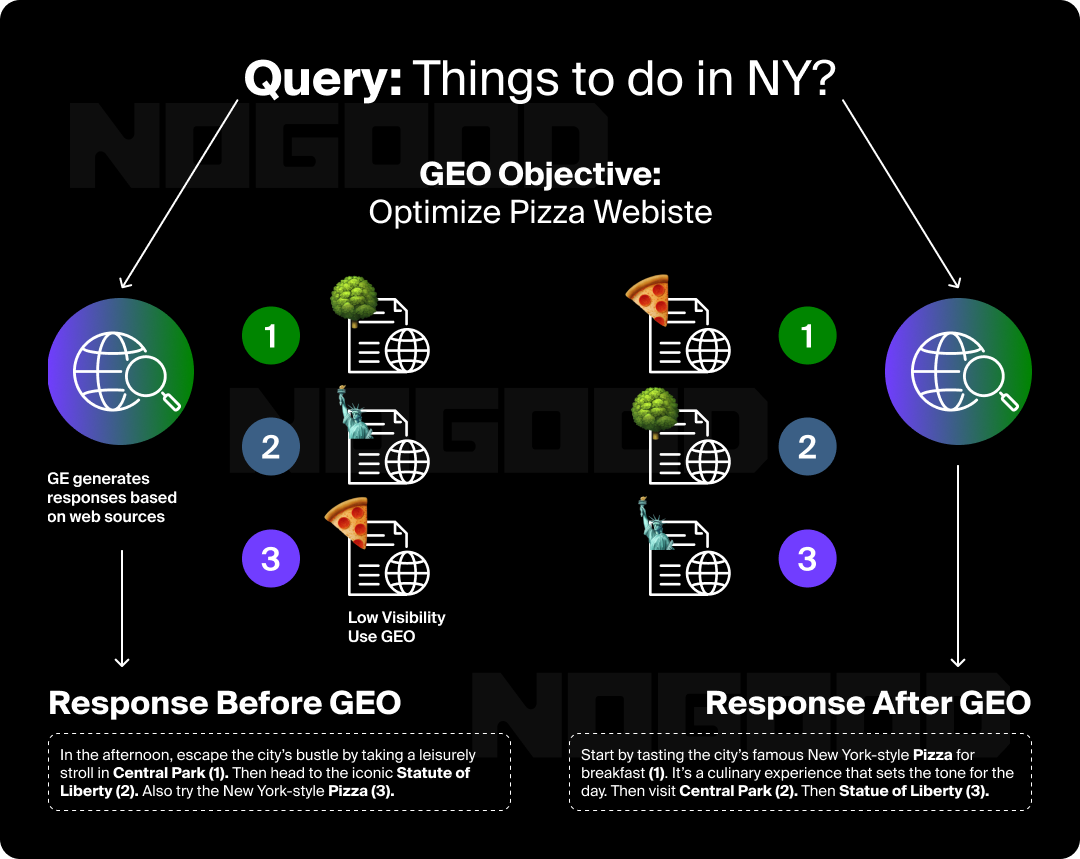
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) vs. Answer Engine Optimization (AEO): What’s the Difference?
GEO and AEO are both strategies aimed at boosting the visibility of your content online in AI-driven search functions, but AEO encompasses additional platforms beyond those targeted by GEO practices, and GEO is geared toward ensuring your content is one of many sources used in the synthesis process that enables AI platforms to provide succinct and summarized answers.
Both AEO and GEO methodologies strive to provide concise, direct answers to user queries to increase the chance of appearing in AI-generated results. With GEO, as we’ve discussed, this refers to AI-driven search systems, and particularly LLMs. With AEO, this can also mean AI Overviews or other AI-powered aspects that are beginning to populate more traditional search engines.
At the foundation of both AEO and GEO is understanding user intent, incorporating relevant keywords, structuring content effectively to align with algorithms and AI crawlers, and using clear language throughout your content. The same techniques are used for both AEO and GEO since all generative engines are a type of answer engine.
Market Growth and User Adoption of Generative Search and LLMs
To understand the urgency behind GEO, consider the rapid adoption of LLMs and AI-based search technologies:
- ChatGPT reached 100 million monthly users within two months of launch, making it one of the fastest-growing consumer applications in history. In November of 2024, it had 3.8 billion visits, showing that initial hype is transitioning into mainstream usage.
- According to a recent survey from investment banking firm Evercore, 8% of Americans use ChatGPT as their go-to search engine.
- A McKinsey survey in mid-2024 found that 65% of organizations now regularly use generative AI, up from just 33% the previous year. This aligns with the broad enterprise pivot toward AI-driven insights.
- Gartner projects that by 2026, 25% of all queries could shift from traditional search engines to AI-driven interfaces, reducing organic search traffic for many companies by up to 50%.
These trends highlight the explosive growth of AI search channels. If your brand is absent from these channels—or if your mentions are inaccurate—you could be missing out on millions of high-intent users.
What’s the Difference Between GEO and SEO?
At a glance, GEO seems like a natural extension of SEO. Both revolve around making content visible and authoritative, but the mechanics of each differ significantly.
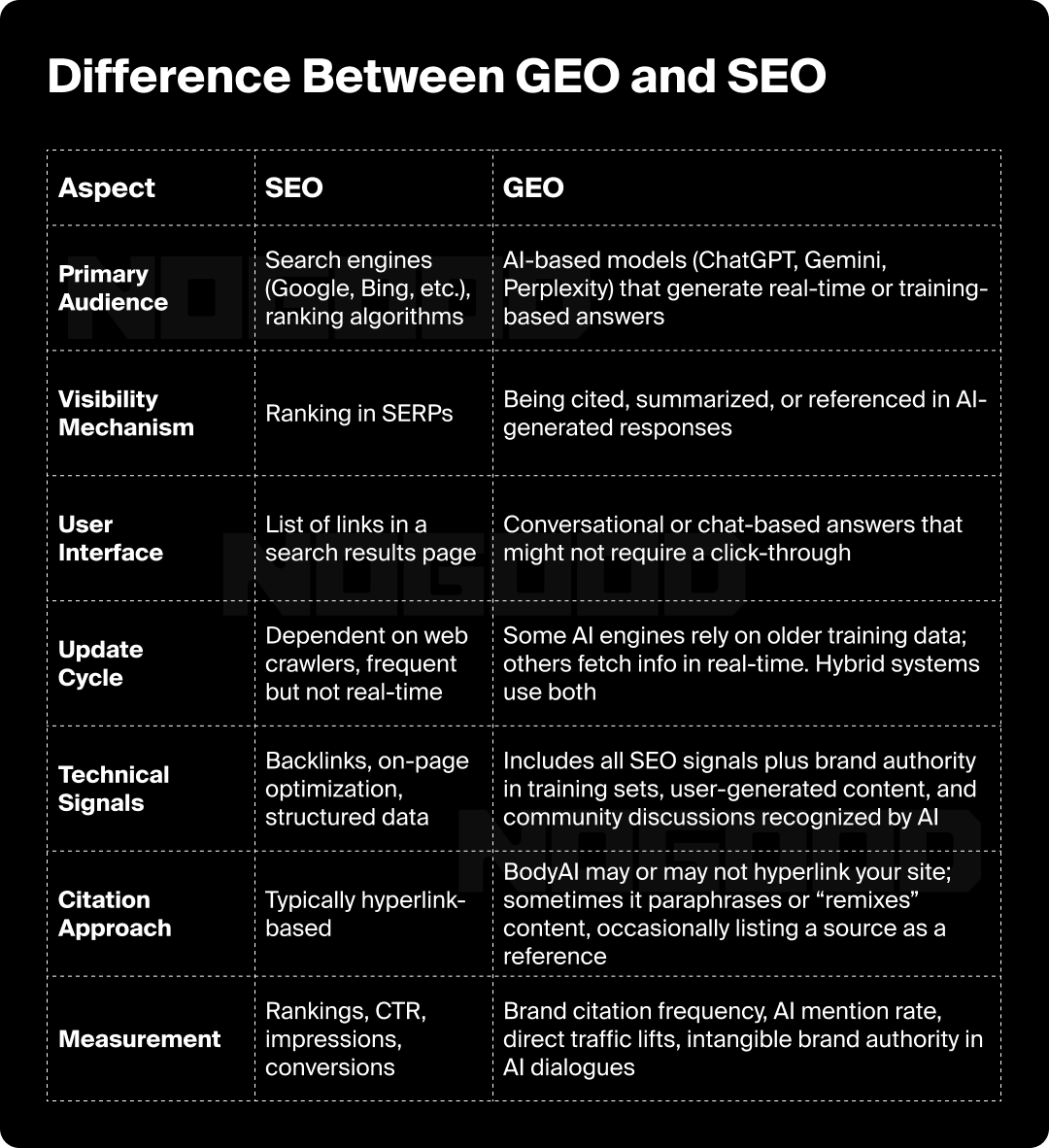
One of the biggest contrasts is that SEO is built around competition for finite SERP positions (rank #1, #2, #3, etc.), whereas GEO is more about influencing what an AI engine “thinks” and “says” when it fields questions.
Because AI’s answers are generated dynamically—and often vary from user to user—traditional ranking trackers don’t apply. Instead, you might look at brand presence across AI responses, the quality of mentions, and how these mentions convert into brand searches or direct visits later.
GEO Optimization and Ranking Factors
AI systems weigh a combination of technical, content, brand, and engagement signals when generating answers. While each generative model has its own training and referencing logic, several overarching factors frequently determine whether (and how) your brand appears.
Content Quality & Context
Generative models thrive on detailed, high-quality content. If your pages offer superficial or repetitive information, an LLM may ignore them. Focus on:
- Topical Depth: Provide unique data, expert opinions, or original research.
- Contextual Relevance: Align content around real user questions and pain points, anticipating the queries people pose to AI.
- Readability & Structure: Format text with headings, bullet points, and concise paragraphs to make it easy for AI to parse.
Technical Accessibility & Structured Data
As with SEO, you must ensure your site is crawlable and indexed. You should:
- Include Schema Markup (JSON-LD): e.g., FAQ, Article, Product, and Author schema help AI understand your site.
- Ensure Open Access: Allow GPTBot and other AI crawlers if you want your data included in their training sets or live indexing.
- Optimize Site Speed & Mobile-Friendliness: Real-time AI crawlers assess site performance and may discard or deprioritize slow, clunky pages.
Entity and Brand Authority
LLMs generally rely on an entity-based understanding of content:
- Entity Confirmation: Ensure your brand is defined consistently across platforms, from social media to Wikipedia.
- Authority Cues: Publications, academic references, news mentions, and strong domain-level authority all indicate trustworthiness.
- E-E-A-T Alignment: Google’s emphasis on Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) also extends to how LLMs interpret your site.
Off-Page Signals & Community Mentions
Generative AI training can involve everything from social media posts to discussions on forums. Mentions in these spaces can shape how the model perceives your brand:
- Unlinked Brand Mentions: LLMs can learn about your product even from references without a hyperlink.
- Community Discussions: When your brand is actively recommended or debated in communities like Reddit or Quora, that can surface in AI’s knowledge base.
- Social Proof: High engagement on social posts and user-generated content signals real-world relevance.
Engagement & User Experience
While Google may or may not take bounce rates into account for rankings, AI systems are beginning to incorporate user feedback loops:
- Conversational Flow: If users repeatedly mention or engage with your brand in multi-turn queries, the AI may rank you higher or keep referencing you.
- Positive Sentiment: LLMs can parse sentiment in reviews or discussions to gauge brand favorability and will rank brands with positive sentiment higher than those more negatively regarded.
GEO Implementation Strategies: How to Get it Right?
Many of the most impactful strategies for GEO focus on developing and distributing high-quality content that aligns with and supports the authority of your brand. Think of your content as the backbone of your GEO strategy.
Research & Planning
To create content that resonates with your audience and will be relevant to their queries, you must start with research:
- Discover User Questions: Map the long-tail, question-based queries people ask about your industry. Tools like AnswerThePublic, Semrush’s “Questions” feature, and even direct prompts to ChatGPT or Perplexity can yield potential user phrasing.
- Identify AI Engine Types: Pinpoint whether your audience is more likely to use ChatGPT’s offline data or Bing Chat’s real-time engine. This dictates your approach to content freshness and domain authority.
- Competitor Analysis: Ask generative engines about your competitors. Check how they appear in responses. Identify gaps you can exploit.
- Brand Perception: Dig into how your brand is perceived by those who are searching in your niche. Understand what people are saying about your brand so you can grasp the current sentiment and figure out where you may need to make changes.
Content Creation & Structuring
What you include in your content and how you structure it directly impacts how LLMs are able to understand your relevance to and your expertise on a certain topic. Focus heavily on providing detailed, thoughtful, and original perspectives on important topics in your industry.
When structuring your content, you should:
- Provide Direct Answers: Start content pieces with a concise, “TL;DR”-style summary. AI often lifts these for quick responses.
- Use Clear Headings: Group subtopics with H2/H3 labels so LLMs can easily identify relevant sections.
- Include Original Data & Quotes: Studies show that LLMs prefer referencing content with statistics, quotes, or unique angles.
- Multi-Format Approach: Embed videos, infographics, or tables for depth; advanced models can incorporate them into answers.
- Incorporate FAQ Sections: Build FAQ sections, especially in longer content, to address common questions and make it easy for AI to pull relevant information.
Optimizing for Different Generative AI Engine Types
Training-Based Models (ChatGPT, Claude, Llama) rely on a set library of knowledge, usually with a cut-off date. To optimize for these models, consider long-term and evergreen approaches:
- Get your brand into widely crawled sources (news outlets, authoritative databases).
- Focus on timeless, high-authority content that remains valid well after the model’s training cutoff.
Real-Time & Hybrid Models (Perplexity, Bing Chat, Gemini, ChatGPT with browsing) can browse the internet as they’re processing a query to build the most relevant response. Focus on more immediate fixes and updates to optimize for these models, such as:
- Technical SEO Best Practices: Fresh, indexed content is essential; site speed, structured data, and mobile optimization are also critical for AI to quickly parse and synthesize information on your website.
- Timely Updates: Publish frequent updates, new research, or product info so the real-time crawler picks it up. Consistent and timely content publishing ensures you stay relevant in your particular industry.
Distribution & Community Building
Today with the rise of GEO, community building has become the new link building. Since LLMs are trained on a wide variety of data from all corners of the internet, make sure to amplify and take part into your brand discussions beyond your website:
- Active Forum Participation: Contribute meaningfully on Reddit, Quora, and niche communities.
- Social Media Seeding: Post share-worthy insights on LinkedIn or industry-specific networks.
- Guest Podcasts & Webinars: Voice your expertise in events that might be transcribed and then included in AI training sets.
Testing & Iteration
Many AI models are still being trained, new AI models are being released, and new features are being added to the ones that already exist. Keep close tabs on your GEO strategy implementation and test where necessary to ensure you’re seeing results:
- Prompt Experiments: Regularly ask ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, etc. about your brand or key topics. Track if you appear and in what context.
- Refine & Re-Test: Adjust content structure or brand mentions and test again. This cyclical process is crucial for incremental GEO improvements.
- Collaboration with R&D: If your company has data scientists or partnerships with AI tool providers, collaborate to see how training sets are curated.
Case Studies and Practical Examples
Case Study 1: B2B SaaS Gains AI Mentions
A B2B SaaS company in the project management niche found they rarely appeared in ChatGPT’s offline knowledge. To remedy this, they:
- Partnered with Industry Blogs: They published joint reports with tech sites that had high domain authority.
- Increased Wikipedia Presence: They created a well-cited Wikipedia entry referencing their white papers.
Result: Within the next model update cycle, ChatGPT began including them in the top “best project management tools” references, boosting direct brand searches by 25%.
Case Study 2: eCommerce Brand Optimizes for Perplexity
An eCommerce retailer specializing in eco-friendly lifestyle products noticed Perplexity was growing in popularity among sustainability-minded consumers. To drive inclusion of their brand in Perplexity’s results, they implemented:
- Structured FAQ: They added custom FAQ schema with concise Q&A blocks to their product pages.
- Community Advocacy: They encouraged satisfied customers to share experiences on subreddits like r/ZeroWaste.
Result: In under two months, the brand appeared consistently in Perplexity’s “top eco-friendly stores” suggestions, correlating with an 18% bump in monthly revenue.
Case Study 3: Consultancy & Hybrid Systems
A consultancy wanted to rank in Google Gemini and also appear in ChatGPT’s real-time browsing variant. To achieve this, they focused on:
- Weekly Thought Leadership: They posted in-depth blog posts on trending management topics, ensuring daily crawls by Google.
- Citation Seeds: They proactively commented on Fortune 500 LinkedIn posts, dropping relevant data bites that earned them news coverage.
- Result: Gemini frequently included their quotes, and ChatGPT-with-browsing began citing their blog for “up-to-date leadership insights.”
How to Measure GEO and AI Visibility
Measuring success in GEO can feel elusive if you’re used to the more stable metrics of traditional SEO. While SEO performance may shift on a weekly or monthly basis, GEO is even more inherently dynamic—AI answers can shift from day to day, or even query to query.
Key Metrics
- AI Citation Frequency
- How often does the model mention or source your brand?
- Does it list your domain as a reference or recommended link?
- Brand Visibility in AI Overviews
- Are you recommended in relevant top-tier queries? (e.g., “best enterprise software solutions”)
- Does your brand appear in “buying guide” or “how-to” generative answers?
- Post-AI Direct Traffic
- When AI references your brand, do you see a spike in branded searches or direct visits?
- Do you see an increase in brand + product name queries? This is a solid sign of AI-driven awareness.
- Referral Data
- Some AI chat interfaces provide clickable citations. Monitor referral traffic from these sources.
- User Engagement
- Keep an eye on lead volume, time on site, or newsletter sign-ups. Sometimes, AI references warm up leads before they even arrive.
Monitoring Tools & Methods
A strong GEO strategy requires established methods for measuring performance and impact of optimizations. Consider the following to track visibility:
- Prompt Testing: Manually check responses by asking the AI about your brand or relevant keywords.
- Brand Mention Tools: Invest in a tool from the new wave of software that specifically tracks brand references in generative AI outputs.
- Analytics: Use Google Analytics (and similar) to monitor direct traffic spikes; use Google Search Console to track brand search volume.
- Social Listening: Incorporate a tool that tracks social sentiment and discussions that could feed into AI training sets.
Goodie AI for Visibility Analysis
Goodie AI is an emerging platform that helps brands gain insights into how they show up in generative AI outputs. It offers:
- Real-Time Prompt Testing: The platform automates query testing across multiple AI engines (ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity).
- Citation Tracking: It logs whenever your brand is mentioned, along with the conversation context.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Goodie compares your brand’s generative presence to key competitors.
- Performance Dashboards: The platform includes a consolidated view of impressions, mention frequency, and potential referral traffic.
Integrating a tool like Goodie AI can streamline your entire GEO measurement process, giving you actionable data to refine your strategy over time.
Future of GEO and AI Search: Closing Thoughts
Generative AI is rapidly transforming how people search, research, and make decisions. Far from a temporary hype cycle, LLMs are already mainstream and improving continuously with each iteration. This means:
- Data Quality & Freshness Will Become Essential: AI engines that rely on real-time data will increasingly factor in recency and reliability. Maintaining updated content is critical.
- Deeper Personalization Is on the Horizon: Future AI systems may tailor their responses based on the user’s past interactions, location, or personal preferences. Optimizing for broader “personas” might become as important as keyword targeting once was.
- Voice & Visual Inputs Will Blend With Text: As voice-based and image-based queries increase, GEO strategies will expand to cover multimodal content optimization.
- Ethical & Trust Factors Will Be Increasingly Important: Misinformation and AI “hallucinations” remain hot-button issues. Brands that prove trustworthiness—through robust references, transparency, and verified credentials—will likely earn preferential treatment from AI systems looking to minimize errors.
- Standardization Could Emerge: As generative AI matures, there may be regulations or standard practices for citing sources—akin to how search engines have guidelines for indexing.
The Bottom Line
Generative Engine Optimization isn’t just “SEO with a twist.” It’s a new frontier that intersects branding, content strategy, technical optimization, and community influence. In an era when user queries can be answered entirely within a chat window, ensuring that your brand’s perspective informs that answer can make the difference between winning a new lead or never being discovered at all.
By focusing on quality content, structured data, brand authority, and active community engagement, you position your organization to capitalize on the AI revolution—rather than be sidelined by it. Embrace GEO now to protect and amplify your brand’s digital visibility for the next decade and beyond.