Even though the underlying mechanisms of Google’s algorithms remain largely unknown, we can make assumptions about users’ search behavior based on the data we do have, such as traffic, click-through rates (CTR), and search volume.
And if you thought that SEO was fading into obscurity in favor of Answer Engine Optimization (AEO), think again. While AI is becoming the search solution for many, our in-depth research suggests that strong SEO is the foundation for strong AEO. Therefore, the goal of this article is to outline which traditional (and non-traditional) ranking factors we believe will be vital to creating an effective SEO strategy, in 2026 and beyond.
How Does Google Rank Content in 2026?
Google’s ranking system in 2026 is a complex, interconnected web driven by AI and a deeper understanding of user intent. The “secret sauce” lies in providing a truly valuable and trustworthy experience that satisfies both humans and machines.
The New SEO Strategy
Generative AI is the new name of the game. Your website now has two primary audiences: the human user, and the AI that may summarize your content directly on the search results page (SERP) or in LLMs like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity. This means your content must be structured to serve both. It should be:
- Human-First: Engaging, well-written, and authoritative, with a clear focus on Helpfulness, Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (H-E-E-A-T).
- Machine-Readable: Organized with clear headings, lists, and schema so algorithms can easily extract and cite your information.
Success hinges on creating content that is not only relevant, but also acts as a definitive source that AI can confidently use (but a human can still easily comprehend and trust).
The Top 8 SEO Ranking Factors of 2026
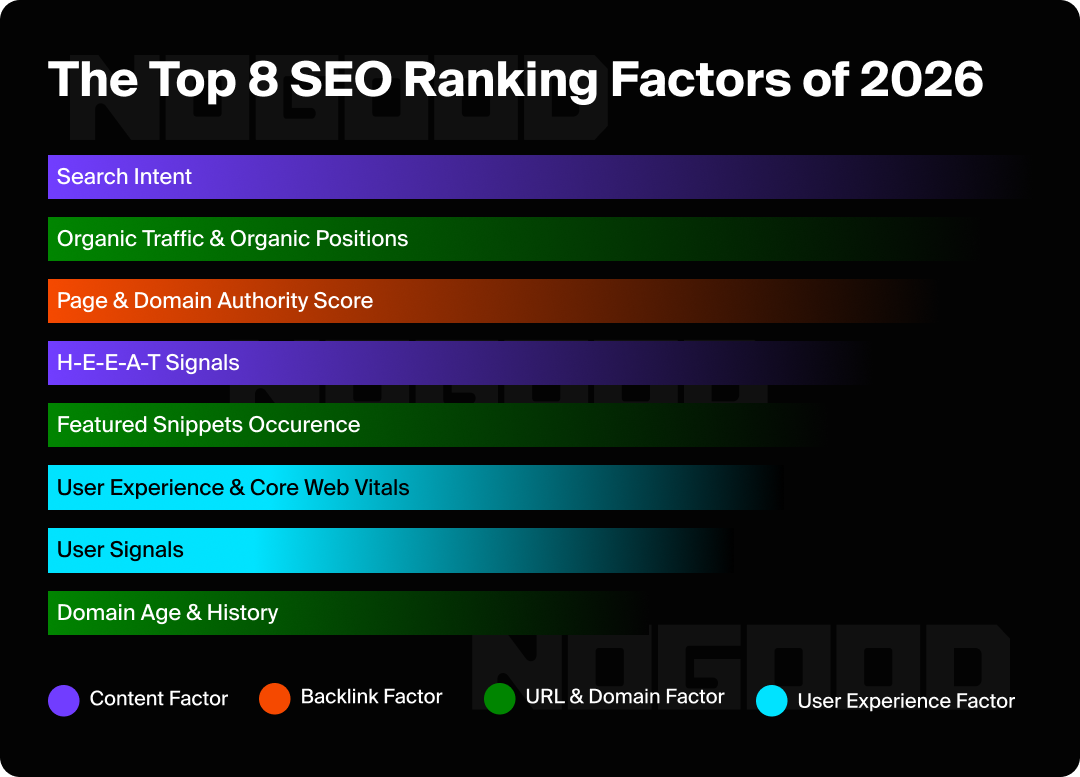
1. Search Intent
According to Google, it makes sense that search intent, or text relevance, is at the top of our list. To put it simply: the more relevant your content is, the more likely it is to rank on Google.
Google’s algorithms are now sophisticated enough to evaluate whether your page’s content, format, and depth match the user’s expectations. However, let’s dive deeper into actionable items to improve search intent.
Decoding Intent
When determining the intent of a query, our best advice would be to focus less on keywords for a second. While keywords are still important, it’s even more important to cover a topic comprehensively, with user needs at the top of mind.
Before you start writing, analyze the top-ranking pages for your target keyword. Ask yourself, “What is the user’s underlying goal? Are they looking to buy something, learn a concept, find a location, or get a quick answer?”
For more in-depth guidance on search intent and how it relates to your SEO strategy, check out our work on the keyword matrix.
Quantifiable Signals
Google looks at quantifiable signals, noting that if you looked up “dogs”, you probably aren’t looking for a webpage that simply says the word “dogs” a million times. Instead, Google algorithms work to identify other relevant content that goes beyond the keyword “dogs”, such as photos, videos, or a list of breeds.
As a first step, you can analyze how the top results are formatted; If they’re listicles, guides, or video tutorials, your content should follow a similar format to meet user expectations.
More quantifiable signals include URL and target keyword similarity, so make sure you add your primary keyword in the URL and H1 of your page.
Ensure a Comprehensive Answer
A comprehensive answer provides a complete solution to the user’s query, leaving no need for them to return to the search results. This signals to Google that your content is a high-quality resource. To make your content comprehensive, anticipate and address all possible sub-questions (this is where FAQs come in handy, too), which you can do by using clear headings, bullet points, and a mix of text and visuals.
2. Organic Traffic & Overall Visibility
There is no surprise here; high organic rankings are still the goal, including rich results and Featured Snippets. A domain that ranks for a wide range of relevant keywords and attracts a high share of traffic in its niche signals authority and relevance to search engines.
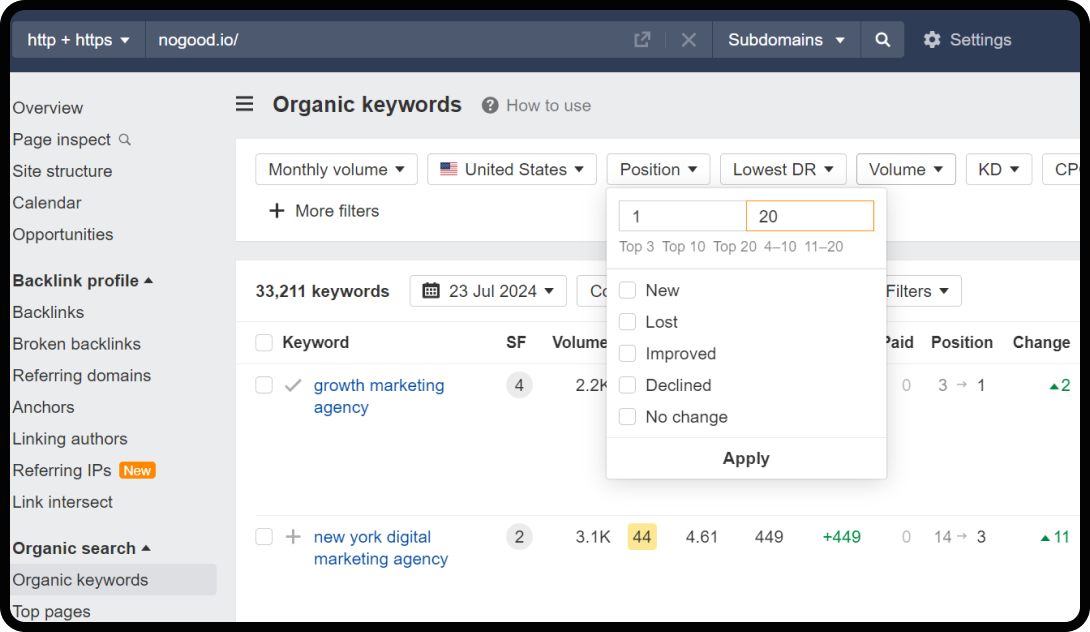
You can filter for these keywords of yours by heading to Ahrefs, and filtering for positions 1 – 20.
Alongside this, another factor influencing your organic positions is your general domain traffic share. Your domain traffic share is the percentage of visits that your website gets out of the total visits to all sites in your category or niche. To calculate your domain traffic share, you can use the following formula:

Here is an actionable tip to secure organic rankings:
Pillar & Cluster Pages
We’re going back to old-school SEO strategies with this. Instead of creating isolated articles, group your content around central pillar topics. This creates a network of interconnected pages that establishes your website as an authority on a subject.
To help with this, you can plan your content quarter by quarter, taking external ranking signals into account. For example, if your DR is 35 in Q1 of 2026, it won’t make sense for you to write about a general topic that’s hard to rank for. Starting with easier-to-rank content and adjusting this as your external signals change is the most efficient way to improve organic traffic and organic positions.
Here are some steps you can take to achieve this:
- Research Keywords: Use keyword research tools like Ahrefs to find and create content for all relevant long-tail and short-tail keywords in your niche. This will help you identify the core topics you want to address.
- Audit Content: Review your existing content and adapt your strategy after you’ve identified gaps and opportunities for improvement.
- Leverage internal links: Execute an internal linking audit and strategy after completing the above-mentioned steps. This will also pass along the authority to your target pages while prioritizing user needs by making navigation easier for them.
- Track Overall Traffic Share: Monitor your website’s share of organic traffic within your industry. This broader metric provides a clearer picture of your competitive position than just tracking a few keyword rankings.
3. Page & Domain Authority Score
After Google identifies if the search intent matches the users’ query, its systems prioritize the content that seems most helpful. One of the main ways Google’s algorithms do this is by establishing whether other prominent websites refer to or link to the content, measuring its authority.
Authority is a reflection of a site’s credibility and trustworthiness. Google’s algorithms rely on external signals, such as links from other prominent websites, to determine this. Authority is built over time and is a key indicator that a website is a reliable source of information.
Let’s take a look at how you can get this specific ranking signal right:
Earn High-Quality Backlinks
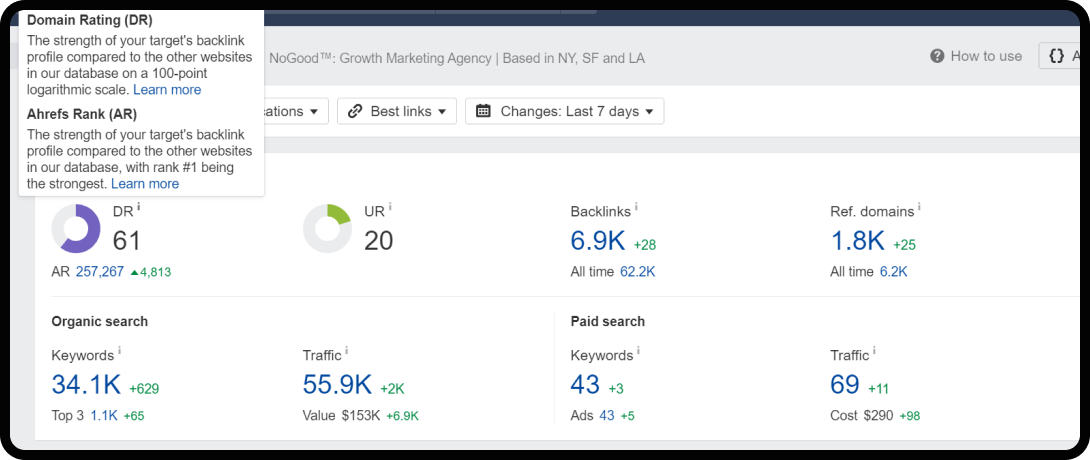
Focus your link-building efforts on earning links from authoritative, relevant websites in your industry. A single, high-quality link from a respected source is far more valuable than dozens of low-quality links.
Create Linkable Content
One of the best ways to build organic, high-quality backlinks is to create great content, which you can do by creating content that comprehensively solves the issues users might experience.
Also, unique content is a plus! This can include original research, detailed guides, or original data (like what we have going on over at Goodie).
Build Your Brand
A strong brand presence outside of search (through social media, word-of-mouth, and industry recognition) can also contribute to your authority signals. Think of SEO as a type of digital PR play in this sense.
4. H-E-E-A-T Signals
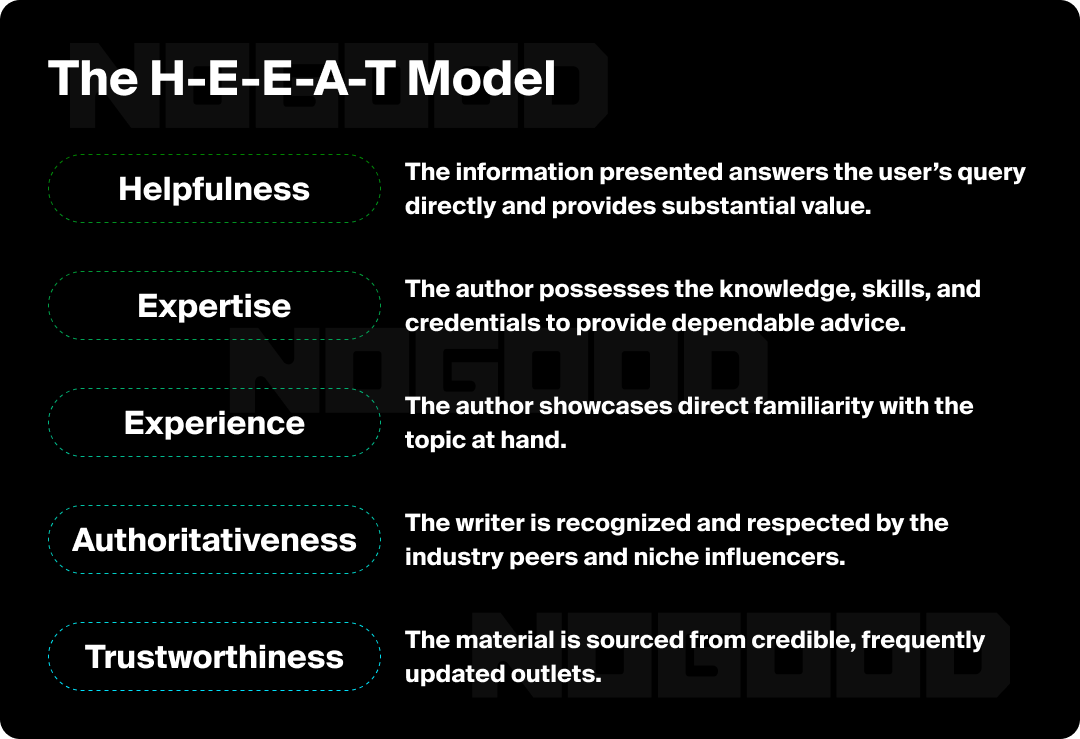
H-E-E-A-T (Helpfulness, Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) is Google’s framework for evaluating content quality. A high H-E-E-A-T score indicates that your content provides genuine value to users, which is a critical ranking signal. It’s no longer enough to simply have keywords on a page; you must demonstrate a deep understanding of the topic and prove that your information is reliable.
Helpfulness
Helpfulness is now at the core of Google’s ranking systems. It’s no longer enough for content to simply exist; it must benefit the user by providing a unique and valuable solution to their query. A truly helpful page is one that leaves the user with no need to return to the search results to find more information. You can make your content more helpful by:
- Answer the Core Question Immediately: Get to the point. Start your content with a concise, direct answer to the user’s query, and then provide more detailed context.
- Provide Unique Value: As previously mentioned, create content that offers a unique perspective or original insights that can’t easily be found on other websites.
- Structure Your Content Logically: Use clear, descriptive subheadings (H2, H3, etc.) to guide the user through the content. Use bullet points and lists to make complex information easy to digest.
Expertise
When it comes to expertise, a successful strategy focuses on comprehensive keyword coverage rather than density. While keywords still matter, search engines penalize content that uses them excessively or unnaturally.
Your goal is to show a deep level of expertise on a topic, which means using a variety of keywords and related terms that demonstrate your comprehensive knowledge. This natural use of language is a signal that your content is created by an expert.
If you want to include a wide breadth of keywords, in Frase, you can view a heatmap of keywords top-ranking content has included in their articles to see which keywords you might be missing in order to better portray what your article is about to Google.
You should also avoid cloaking, a deceptive practice where different content is presented to search engine crawlers than to human users. This is a violation of search engine guidelines and is considered a black-hat SEO tactic.
For example, a website might show a user a page about “professional consulting services,” while simultaneously showing the Googlebot a completely different page about “online gambling” that is stuffed with keywords. The goal is to deceive the search engine into ranking the page for a high-traffic, irrelevant keyword.
Experience
Experience is about demonstrating first-hand knowledge of a topic. Distinct from expertise, it proves that you have personally used a product, visited a location, or gone through a process you are writing about. This experience adds a layer of authenticity that is difficult for AI-generated content to replicate, which you can do by:
- Use Original Multimedia: Include original photos, videos, and audio that you have created. A photo of you testing a product or a video walkthrough of a process is powerful evidence of your experience.
- Share Personal Anecdotes: Tactfully weave personal stories and examples into your writing. A simple phrase like “When I was building my first website…” can add significant credibility.
- Provide Step-by-Step Guides: Create tutorials and guides that show the reader exactly how to do something, as if you were teaching them in person.
Trustworthiness
What Google views as trustworthy can be encompassed by the concept of the perfect click. The perfect click is when a user clicks on a page and is satisfied thereafter, not needing to go to other pages after visiting yours. Not only will obtaining the perfect click help you rank higher, but it will also help you appear in Google AI overviews.
Some factors that influence the perfect click are search intent, content quality, user satisfaction, and brand credibility.
Brand credibility can be improved by having testimonials and awards featured on specific landing pages. However, this can also be improved with schema markup.
Schema is what search engines read to understand the content of pages (think of it like speaking the algorithm’s language). Author schema is a property that can be easily added to inform search engines who wrote an article. The proof is in the pudding, with 72.6% of pages on the first page of Google using author schema markup.
Authoritativeness
Authoritativeness is a measure of your site’s reputation and standing within its industry. While we already covered domain authority, here are some ways to signal to search engines that you’re a trusted leader in your niche:
- Optimize for Entity Recognition: Google’s algorithms now understand entities (people, places, and organizations) and their relationships. To build authority, ensure your brand, key people, and products are clearly defined with consistent information across your site and other web properties. This helps Google build a Knowledge Graph for your brand, signaling its authority.
- Build Relationships: Actively engage with other experts in your niche. Contribute to industry publications, participate in forums, or collaborate on projects to build a strong network that can lead to links and mentions.
5. Featured Snippets & Rich Results
Technically, Featured Snippets are not a direct ranking factor, but they can boost your visibility and traffic. Featured Snippets are highlighted excerpts of text that appear at the top of Google’s search results, which are pulled from the content of a web page.
Instead of Featured Snippets, you may now be seeing AI Overviews more often. However, Featured Snippets still exist, so it’s important to continue to optimize for them. Optimizing for Featured Snippets will also improve your Answer Engine Optimization (AEO), increasing your chances of ranking higher in AI search and its SERP features.

Here are some ways you can optimize for Featured Snippets:
Answer Questions Directly
- Identify commonly asked questions in your niche using tools like AnswerThePublic, the “People Also Ask” section on Google, or Frase.io’s SERP analysis tool.
- Answer these questions concisely in your content, preferably within the first 100 words of your article or the related section.
Use Structured Data
- Add schema markup to help Google better understand the structure of your content. This can include Q&A, HowTo, and other relevant schema types.
Format With Lists & Tables
- Google often pulls from lists, tables, and bullet points for Featured Snippets. Ensure your content includes these elements to increase your chances of being featured.
6. User Experience & Core Web Vitals
User experience (UX) is a critical ranking factor that measures how users interact with your website. Core Web Vitals, including page speed, interactivity, and visual stability, impact UX. A fast, mobile-friendly, and easy-to-navigate site signals a good user experience to Google, which in turn can lead to higher rankings.
Optimize for Mobile
With the majority of searches now on mobile devices, a responsive and well-designed mobile experience is non-negotiable. Here are some tips on how to optimize for mobile:
- Design for Mobile Interaction: Use a thumb-friendly layout with large, well-spaced buttons.
- Prioritize Speed and Legibility: Optimize images for quick loading and ensure font sizes are readable. Avoid intrusive pop-ups that block content.
- Ensure Content Parity: Make sure all content on your desktop site is also present on your mobile version, as Google’s Mobile-First Indexing primarily crawls the mobile site.
Improve Site Speed
Use tools to identify and fix issues that slow down your website, such as large images, unoptimized code, and slow servers. You can do this by:
- Optimize Code & Images: Minify CSS and JavaScript, and as mentioned, compress images to under 150kb in webp format.
- Use Caching & a CDN: Leverage browser caching and a Content Delivery Network to serve content faster.
- Eliminate Render-Blocking Resources: Prioritize essential code to speed up above-the-fold content.
- Upgrade Your Hosting: Choose a fast, high-quality web host to improve server response time.
Ensure Easy Navigation
A logical site structure and clear internal linking help users find what they’re looking for and encourage them to explore more of your content.
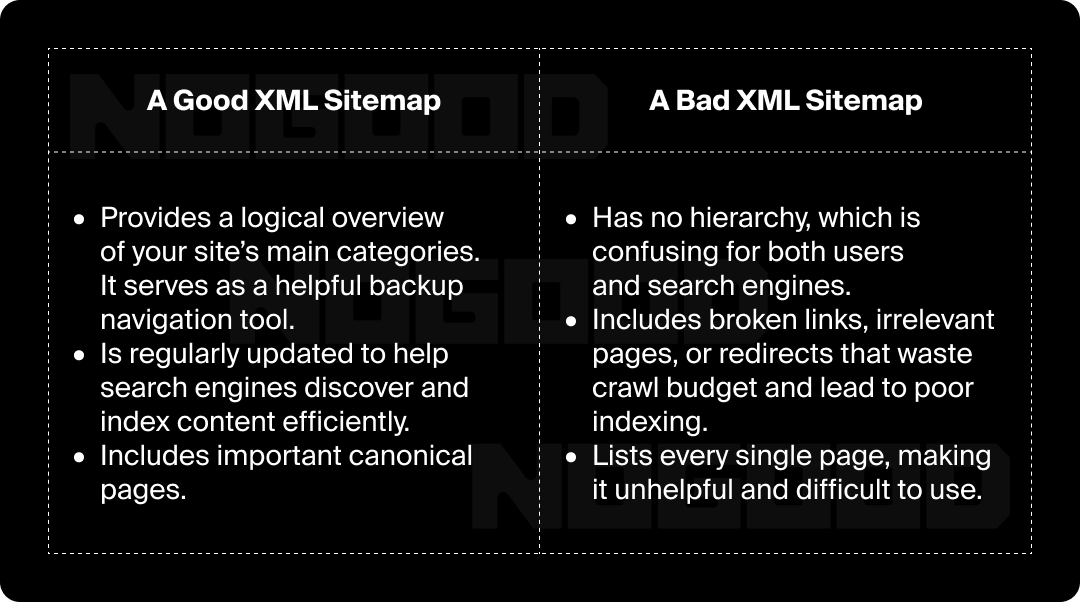
You can do this by creating and implementing a well-structured XML sitemap, which is a roadmap for both search engines and users.
7. User Signals
User signals provide insights into how users interact with your website, influencing its ranking on search engines. These signals include direct traffic share, time on site, engaged sessions, and more.
Increase Time on Site
- Create engaging, high-quality content that keeps users on your site longer. Use multimedia elements like videos, infographics, and interactive content to boost engagement.
- Pro Tip: Think about how you’re portraying the information on your page. Consider immediately satisfying the user with what they came for on the page instead of having a 1,000-word introduction and FAQs at the start of the page.
- Strategically place internal links to guide users to other relevant pages on your site.
Increase Engaged Sessions
Ensure your content is a perfect match for the user’s search intent. When users find what they’re looking for immediately, they are more likely to stay on your site and engage with it meaningfully.
Build a Loyal Audience
High levels of direct traffic and branded searches tell Google that users find your website so valuable they return to it directly, which indirectly boosts your rankings. Use email marketing, push notifications, and social media to keep users coming back.
8. Domain Age & History
An older, established domain with a clean history has an advantage in search rankings as it represents a long-term track record of trust with search engines. While a new site can certainly rank well, an old domain that has consistently provided value and is free of past penalties is a powerful signal of credibility.
Also, beware of using expired domains to try and boost the ranking of low-quality content. Google will view this as misleading users into thinking new content is part of the older site.
Maintain a Clean History
Avoid using a domain that has a history of spam or manipulative practices. For example, do a deep dive into keywords for which you rank organically. If articles rank because they were stuffed with keywords, you may want to consider optimizing them or removing them entirely.
Build Domain Authority
Continuously work on improving your domain’s authority through quality content, backlinks, and engagement.
Keep Content Fresh
Even with an old domain, it’s important to regularly update your content to maintain relevance and show that your information is current and accurate.
The factors discussed are what we deem to be the most important for ranking on Google in 2026, but we realize that this list isn’t exhaustive and that there are plenty of other factors you can take into consideration for SEO.






Well written Ryan! This must have taken you a long time to put together and it’s a great list. I wonder how long it will be until you have to update it but I guess that’s part of of the fun in this industry; constantly changing.
I suppose you can also use this page as an example of high quality content too 😉