What Are SEO Landing Pages & Why Do They Matter?
SEO landing pages are conversion-focused pages on your website that are optimized to rank highly for a specific target keyword. SEO landing pages are important for gaining organic visibility in the SERP for queries being conducted by your target audience. These landing pages generate attention, interest, desire, and action (AIDA). Search Engine Optimization landing pages focus on serving users based on each user’s search intent.
Need Help Building, Launching & Optimizing Landing Pages?
Understanding Search Intent & Keyword Research
An effective landing page is created and optimized based on the user search intent. Understanding the user’s intent will help you decide what type of content to create and the conversion path you should implement on your landing page.
When conducting relevant keyword research for your landing page, keep in mind that there are 4 different types of search intent.
1. Navigational
Keywords are navigational if the user is trying to find a specific destination. Typically, these are users looking for login pages, specific company information, or “near me” searches for local businesses. It is unlikely that you will be utilizing navigational keywords when optimizing website landing pages.
2. Informational
Informational keywords are the most common for educational landing pages targeting top-of-funnel (TOF) users. These users want to learn more about a specific topic or problem they are experiencing. These queries often contain who, what, when, where, and why directives and are most commonly utilized for blogs.
3. Transactional
Users conducting searches with transactional-related keywords are looking to complete a conversion action. These queries may contain specific product or service names or “buy” directives. These keywords are most often used to optimize product/service landing pages.
4. Commercial
Commercial keywords are typically users who are problem and solution-aware and are likely to convert but want more information first. These keywords may be comparing two companies or products or questions about a specific product or service. It is common to use commercial intent keywords to optimize competitor landing pages.
Now that you’ve identified your user’s search intent and the type of content you should create, you can effectively optimize your landing page to meet their needs.
Challenges of Ranking Landing Pages in Search
Optimizing landing pages for organic search comes with specific inherent difficulties. Understanding these challenges is key to developing an effective SEO strategy.
Here are the primary hurdles landing pages face in achieving organic visibility:
Limited Content Depth
Unlike extensive blog posts or articles, landing pages are designed to be concise and hyper-focused on a single conversion goal, meaning less overall text.
Reduced content provides fewer contextual clues for search engines to understand the page’s breadth of topics. It also offers fewer opportunities to naturally integrate a wide range of relevant keywords, potentially hindering ranking for broader search queries or featured snippets.
High Keyword Competition
Landing pages frequently target high-intent, transactional keywords (e.g., “buy [product],” “sign up for [service]”), which are typically the most competitive in any industry.
Ranking for these keywords requires significant domain authority and highly precise optimization to stand out against established competitors, making it difficult to secure top positions or direct answers for commercial queries.
Technical Optimization Hurdles
Various technical issues can impede a landing page’s search performance. This includes critical factors like slow page loading speeds, improper indexing, crawlability issues, or a lack of mobile responsiveness. Any of these can lead to lower rankings and diminished organic visibility.
Balancing Conversion Goals With SEO Demands
There’s an inherent tension between a landing page’s primary goal (driving a specific user action) and traditional SEO requirements.
Conversion-focused design often favors minimalistic layouts, minimal text, and few internal/external links to reduce distractions. However, SEO often benefits from richer content, robust internal linking, and comprehensive information. Striking this balance is essential for satisfying user intent for conversion and search engine algorithms for ranking.
Optimizing Landing Pages for Search Intent
The foundation of any effective landing page starts with an AIDA design framework, high-quality, and shareable content, and then a well-optimized conversion funnel. Google’s helpful content guidelines will help ensure your users receive value while increasing your chances of ranking highly in the SERP. Lastly, a conversion funnel can include things like downloadable content offers, calculators, audits, tools, and more.
AIDA Landing Page Design Framework
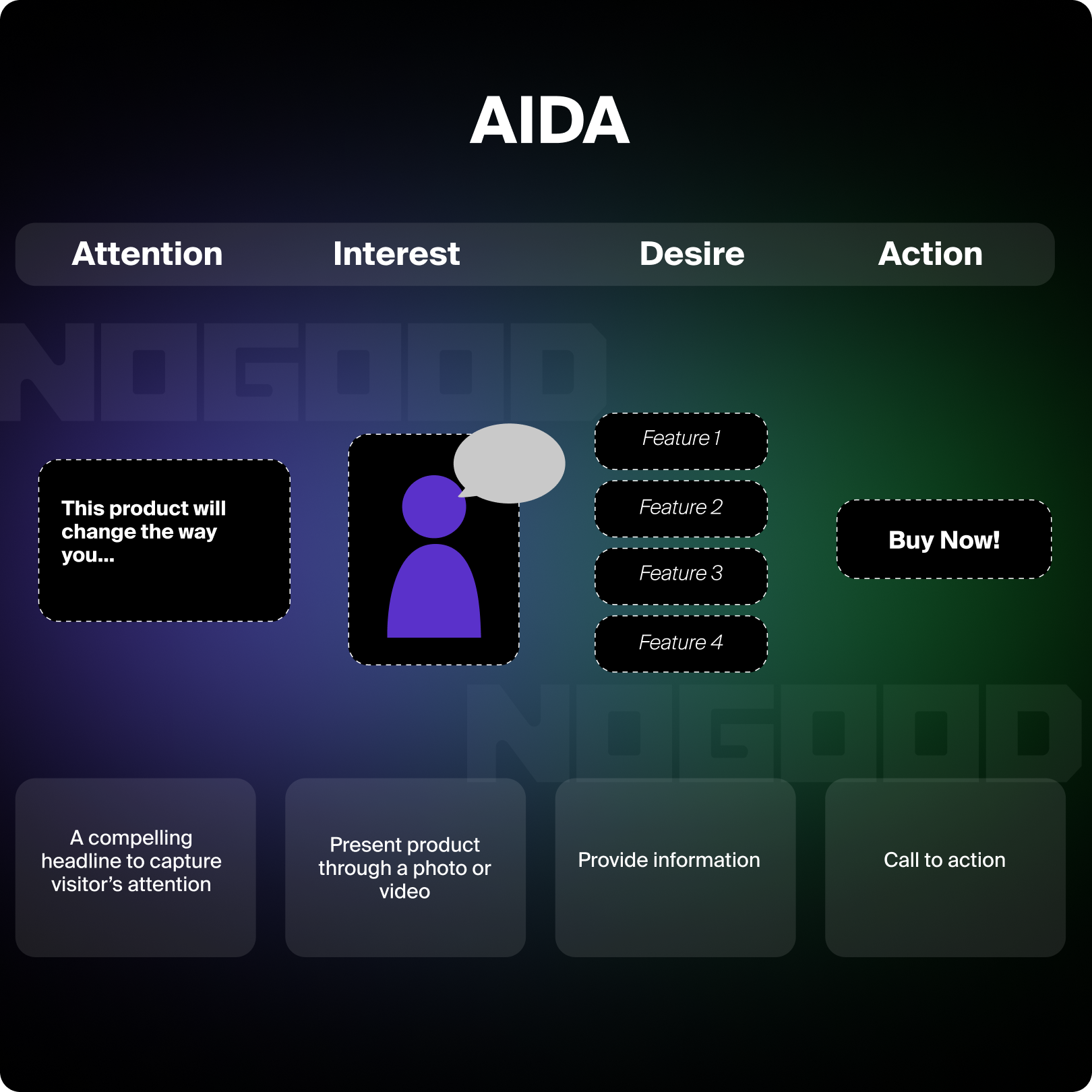
Attention
You have under 8 seconds to capture someone’s attention once they land on your website. Use your landing page hero section and H1 tag like you would a hook to an essay. Once you have a user’s attention, they are more likely to continue to read, which is the first step in minimizing your bounce rate. You can capture someone’s attention through hero section design elements and strong messaging.
For example, you can utilize font types, styles, and colors to make your headline stand out. You can also implement captivating images.
If you have returning users who are logged into an account, you can also utilize zero and first-party data to customize the messaging for each individual person. When focusing on the messaging, essay guidelines around hooks can be helpful. Hooks that are thought-provoking, funny, factual, or novel can help draw readers in.
Now that you’ve captured the reader’s attention, it’s important to keep them engaged.
Interest
Generating interest involves understanding your audience’s needs, and the search intent can help. For example, you can generate interest by showing readers empathy and understanding. Readers need to be able to resonate with your messaging and feel like you can provide a potential solution to their problem.
Imagine you’re writing a blog post about retirement and savings. If you wrote something like:
“Retirement planning requires consistent contributions to a diversified portfolio. Consult with a financial advisor to determine your risk tolerance and allocate assets appropriately. Start early to maximize the benefits of compounding.”
Your audience might feel alienated. They won’t necessarily resonate with messaging that is so technical and matter-of-fact. However, if you pivoted to something like this:
“Feeling like retirement planning is an uphill battle? You’re not alone. Many feel swamped by the endless options and complex advice. We understand that confusion and the urge to just put it off. The good news? It doesn’t have to be so hard. We’re here to cut through the noise and give you a clear, manageable path forward.”
Your audience might be more receptive to your message.
Desire
Creating desire takes empathy and understanding a step further. Readers likely will have objections and questions at this stage. The desired section of your landing page should address these objections and questions by focusing on the features and benefits of your product or service. This is also the section where you can create urgency by implementing limited-time offers, countdowns, or time-sensitive factual claims.
Action
Action is the art of persuasion. This section is your call to action that encourages users to enter your conversion funnel. Depending on the search intent of a page this action may be asking the users to schedule a demo, book an appointment, or download additional content.
For example, a landing page that is targeting an informational intent keyword could be more effective with a downloadable content offer. High-quality content offers like eBooks, guides, or checklists give the user something tangible to take with them and enable you to collect emails for re-marketing. A commercial intent page may prompt users to request a free audit or consultation. Transactional intent landing pages should always reduce friction toward the purchase action.
Search Experience Optimization: How UX & SEO Work Together
Google’s Helpful Content Guidelines
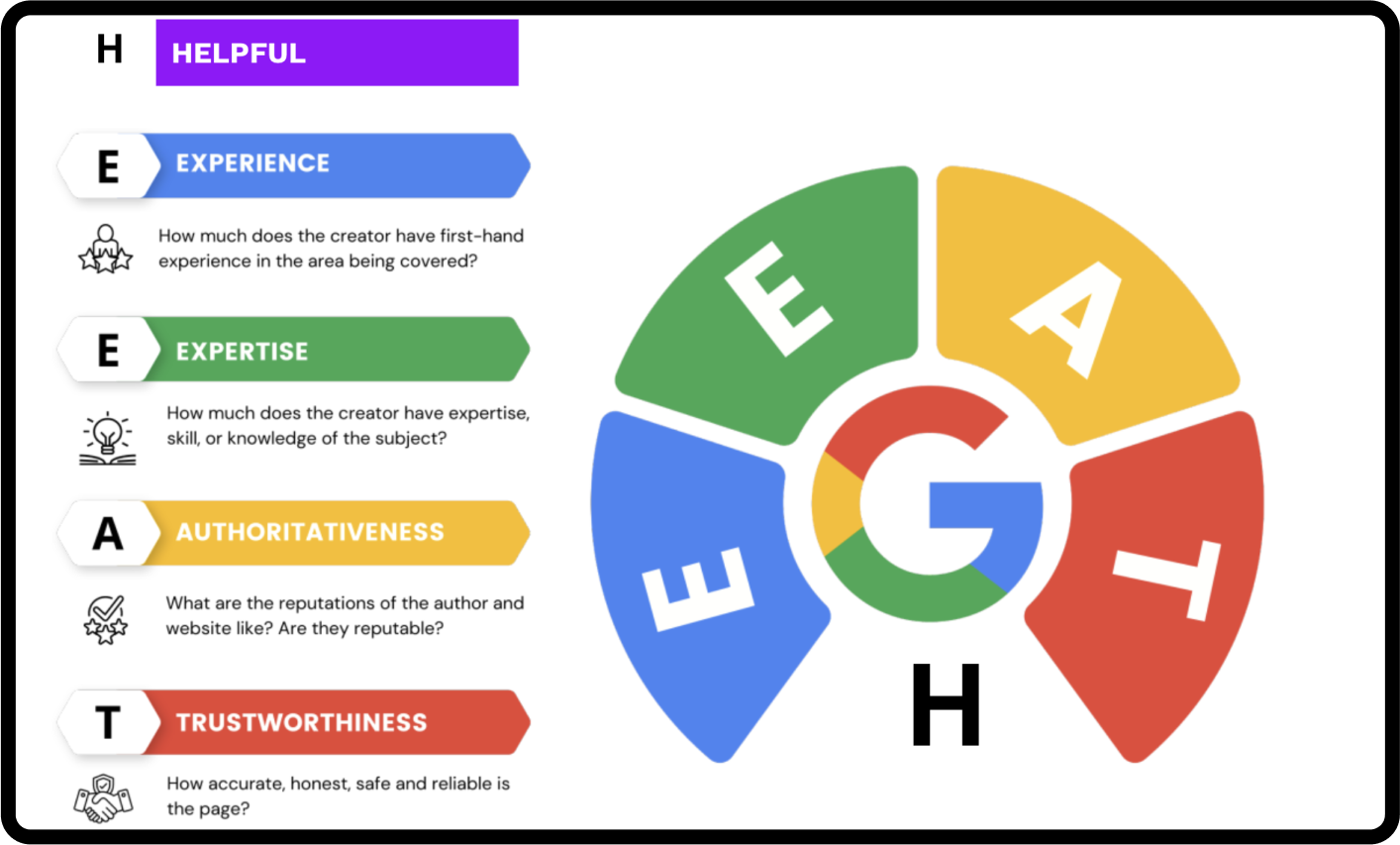
Focusing on people-first content is the key to an effective landing page. Google provides official guidelines, colloquially known as E-E-A-T, that can help lead your content in the right direction. However, these guidelines should also include helpfulness, as the main goal of landing pages is to ensure users receive the answers they need to make a decision.
- Helpful: Does the content satisfy the user’s search query or need for information?
- Experience: How much first-hand experience does the creator have with the subject?
- Expertise: How much expertise, skill, or knowledge does the creator have on the subject?
- Authoritativeness: What is the reputation of the author and the website? Are they reputable sources for information on the subject?
- Trustworthiness: How accurate, honest, safe, and reliable is the page?
On-Page SEO Landing Page Strategies
Title Tags
Title tags are a part of Google’s SEO ranking factors and should always contain your target keyword. These will appear in search results, link previews, and browser tabs. Title tags should be between 50-60 characters to avoid being truncated in SERPs. Using the most important words first can ensure that you’re able to effectively deliver your message to readers.
Typically, your title tag should either exactly match or be closely aligned to your H1 tag for consistency. Users read title tags to understand the contents of a landing page, and if the title tag and H1 contain significant variation, it can confuse the reader and cause a high bounce rate. It can be helpful to review the existing SERP for your target keyword to understand what title tags Google is deeming as the most effective. However, don’t simply copy and paste the #1 position’s title tag. You should ensure your title tag is unique to make your landing page stand out.
Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions are not a ranking factor but can help improve the click-through rate of your landing page. Even though they’re not a ranking factor, they should still include primary or secondary keywords, as Google will sometimes highlight meta description words that match a user’s query.
Meta descriptions should provide initial value to users before they even land on your page by calling out features, benefits, or key facts. Considering user intent can help you provide users with an answer to their questions before landing on your page. Additionally, including a call-to-action at the end of your meta description can encourage users to take the next step toward visiting your page.
Headings
Implementing a proper heading structure can create a better user experience by making the content more digestible and easier to navigate. Additionally, including primary and secondary keywords, as well as clear and concise answers directly below each section heading, can help improve your SERP ranking. Clear and concise answers directly below section headings can optimize your landing page for featured snippets, which will increase your organic visibility.
Alt Text
Image alt text is important for accessibility, user experience, and image organic traffic. Alt text is a specific description of images that can help the visually impaired, provide additional context, or provide information if the image does not load. Alt text can also help images rank in Google image results by including keywords. You do not need to apply alt text to icons or images that are purely decorative or described with an existing caption.

Internal Linking
Internal links are important for indexability and passing link equity between pages. They can also keep a user on your website longer by providing them with additional helpful information on the same or similar topic. It’s important to use keyword-rich anchor text but to avoid using the same anchor text for two different pages.
When positioning internal links, placing them closer to the top of your page can help reduce bounce rate and improve dwell time. Additionally, it is important to be aware of tap targets being too close on mobile devices. This happens when two or more internal links are too close together and could result in the user accidentally clicking the wrong link.
Schema
Implementing structured data can improve your organic rankings and increase the chance of being featured in rich snippets. Depending on the schema you implement, it can add additional elements to your SERP ranking that can improve your landing page CTR. For example, AggregateRating schema for product pages displays a star rating in search results based on user reviews of your product.
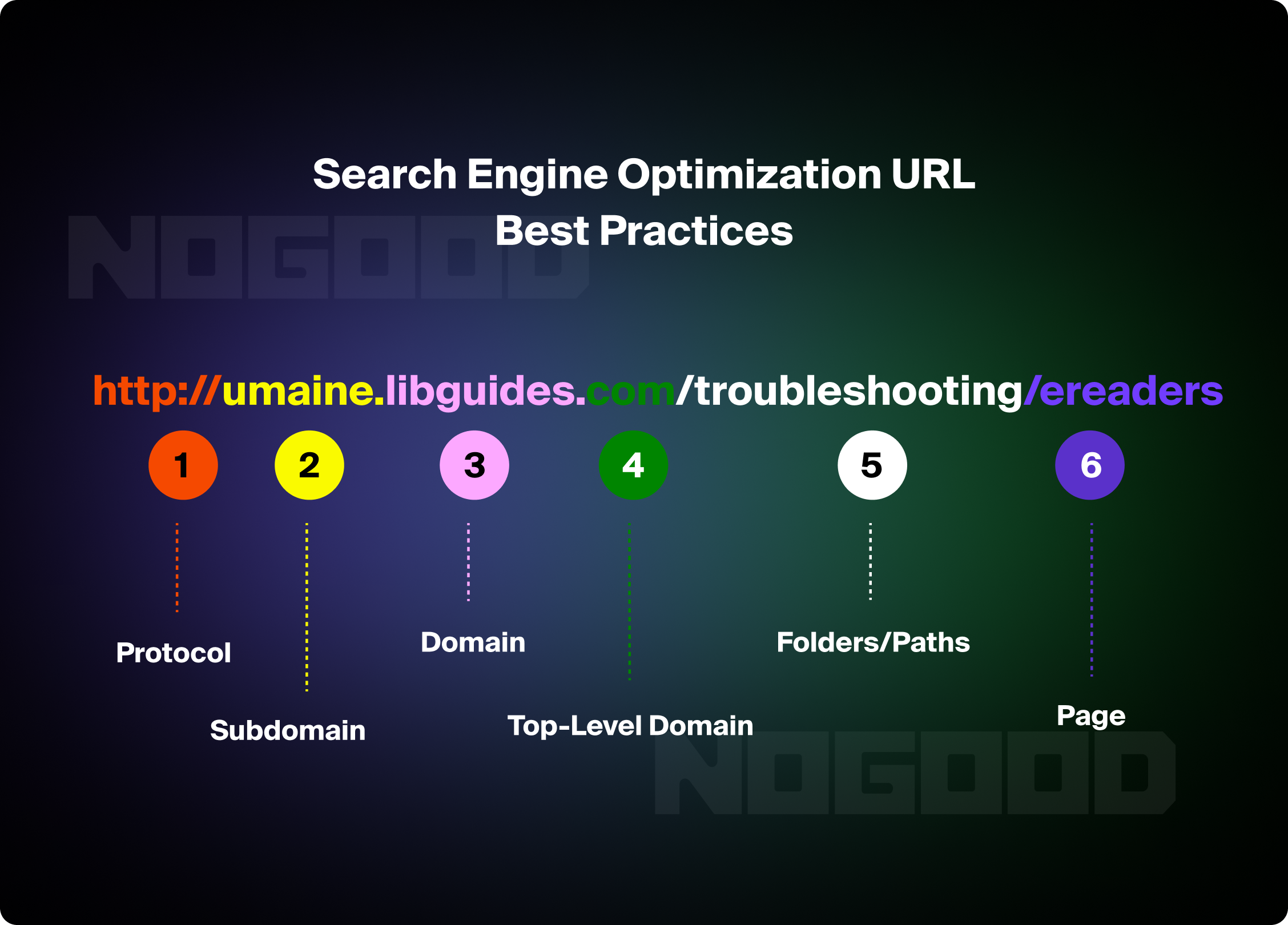
URL Optimization
URLs are a ranking factor and should be simple, descriptive, and include relevant keywords. A well-optimized URL can improve the user experience by indicating where a user is located within your website. Landing page URLs should also be limited to three hierarchical levels, as pages that live deeper in this hierarchy may not be seen as important when Google crawls and indexes your website.
Now that you have a strategically designed landing page with on-page SEO implemented, you should focus on optimizing your landing page speed.
Off-Page SEO Considerations
Backlinks
Backlinks, also known as inbound links, are links from other websites that point to your landing page. They are a critical off-page SEO factor that signals to search engines the authority and trustworthiness of your content. When high-quality websites link to your page, it acts as a “vote of confidence,” boosting your landing page’s credibility in the eyes of search algorithms.
This can improve your organic rankings and drive more referral traffic. Focus on earning links from authoritative and topically relevant domains. Quality over quantity is key; a few strong backlinks are more valuable than many low-quality ones.
Social Proof & Testimonials
Social proof and testimonials are powerful elements for building trust and credibility on your landing page. They demonstrate to potential customers that others have benefited from your product or service, making your offer more appealing.
Strong social proof can lead to lower bounce rates and higher engagement, signaling to search engines that your page provides value. Include authentic customer reviews, star ratings, case studies, or trust badges to encourage conversions.
Optimizing Page Loading Speed & Core Web Vitals
Google Core Web Vitals provide a quantifiable way to measure user experience. There are three main Core Web Vital metrics that should be monitored and optimized:
Largest Contentful Paint
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) measures how quickly the largest element on your page loads. A “good” LCP is typically 2.5 seconds or less. Studies have shown that websites with one-second LCPs have up to 3x higher conversion rates than sites with five-second LCPs. A fast LCP can improve your conversion rate, lower your bounce rate, and improve your organic ranking.

The most common reason for a slow LCP is “slow resource load times,” often relating to a website’s hero image. Unlike images below the fold that can be lazy loaded, hero images are one of the first elements to load.
A well-optimized hero image should be in a WebP format and contain specific size attributes based on device type. Avoid videos or gifs in your hero sections (unless necessary) as they can create significant negative impacts on your LCP if not properly implemented or managed.
Interaction to Next Paint (INP)
Interaction to Next Paid (INP) measures how quickly your page responds to each user interaction. INP replaced First Input Delay (FID) as a Core Web Vital; FID measured how quickly your page responds to the first interaction only.INP is measured based on the interaction that takes the longest; a “good” INP is under 200ms.

The easiest way to reduce your INP is by reducing your page size through optimizing landing page images.
This can mean converting to WebP formats, adding size attributes, and compressing your images as much as possible (without sacrificing quality). A Google case study revealed that The Economic Times saw a 50% reduction in bounce rate after improving their INP. Improving your INP can lower your bounce rate, increase your conversion rate, and improve your organic search engine rankings.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) measures unexpected shifts in layout above the fold on your landing page. This can create a frustrating user experience; imagine a user intends to click a specific button, and that button suddenly shifts.This can result in disruptions in your conversion funnel and higher bounce rates. A “good” CLS score is under 0.1.

Similar to LCP and INP, image optimization can help improve your CLS score. Adding dimensions to your images will indicate how much space the browser should reserve for each element when the page loads.
Increased Organic Visibility With Essential Landing Page SEO
If you have implemented the AIDA design framework, H-E-E-A-T quality content guidelines, on-page SEO optimizations, and improved your Core Web Vitals, you should see increased organic visibility for your landing page.
As a result, you may also experience higher CTRs and should see an improvement in your CVR. The number one takeaway here should be to always keep the user at the forefront and the search engines second; this will set you up for success.