If you haven’t noticed already, generative AI is reshaping the way we work. Tools like OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini are now becoming integral to the workflow, from content ideation to customer service.
You might use these tools every day, but do you truly understand how they work? The reality is, even for experts, an LLM is characterized as a “black box“; a system whose inner workings are incredibly difficult to fully understand. While we understand the general principles, the sheer number of parameters means we can’t trace the exact path that leads to a specific response.
This guide will demystify Large Language Models (LLMs) and reveal how they can be leveraged as strategic assets in marketing. By understanding the core mechanics, you’ll gain a competitive edge in content, SEO, and beyond.

What Are LLMs?
LLMs are a type of AI, built on a massive neural network that has been trained on an enormous dataset of text and code. Functionally, they are highly advanced predictive engines designed to generate human-like text by predicting the next most probable word in a sequence. This core capability allows them to perform a wide variety of tasks, including content creation, summarization, and answering questions, making them a foundational component of modern AI.
The Training Process
An LLM gets its “intelligence” by consuming copious amounts of training data, including books, articles, and code. This process not only teaches the model facts; it teaches it the complex patterns and relationships of human language. This gives the model the background knowledge to handle any topic, from customer service to market analysis.
Understanding the Basics
The breakthrough that made LLMs possible is the Transformer Architecture. Before this, AI models processed language sequentially, which made it hard to understand the full context of a sentence. The transformer model changed this by allowing the model to process vast amounts of text simultaneously, understanding how words relate to each other regardless of their position. This ability to grasp the entire context is why LLMs can create long-form content without losing their focus.
The Role of Language
For an LLM to process language, it first has to translate words into a numerical format. This is a two-step process:
- Tokenization: The first step is breaking down raw text into smaller, manageable pieces called tokens. A token isn’t always a full word; it can be a part of a word, a single character, or a punctuation mark. For example, the phrase “unbelievable” might be broken into three tokens: “un,” “believ,” and “able.” The model then learns the meaning and context of these smaller units.
- Word Embedding: Next, each token is converted into a numerical representation called a vector. These vectors are a list of numbers that capture a token’s meaning and its relationship to other tokens, and allow the model to understand the semantic relationships between words. This is why an LLM knows “king” and “queen” are more closely related than “king” and “car,” a crucial concept for producing relevant content for SEO and powering tools like semantic search.
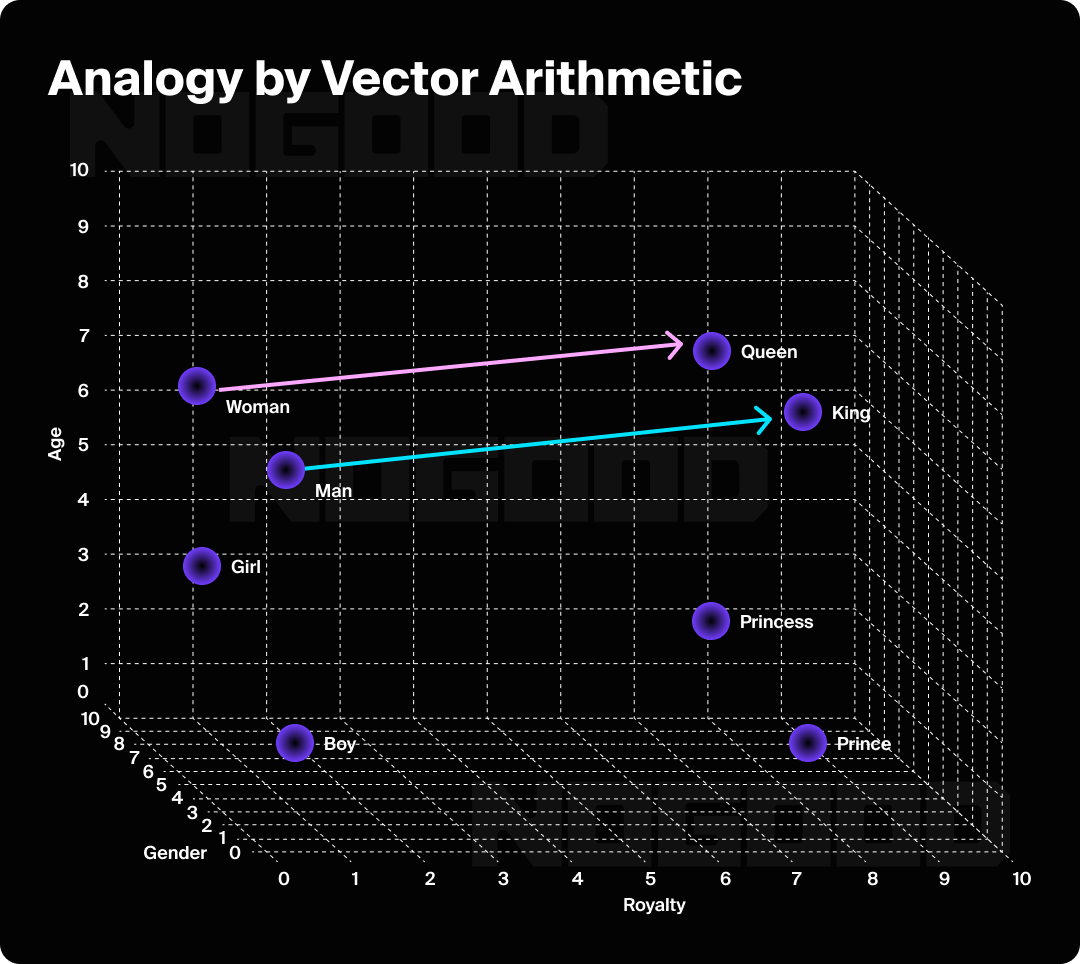
How Exactly Do LLMs Work?
Now that we’ve covered what an LLM is and its purpose, it’s time to pull back the curtain. Understanding the core technical principles isn’t just for data scientists; If you’re in marketing, this information you need to know. The more you know about LLMs and how they work, the better you can craft prompts and leverage these models to their full potential.
Focusing on the Context: The Attention Mechanism
The attention mechanism is the LLM’s superpower. Think of it as the model’s ability to selectively “focus” on the most relevant words in a given piece of text. When you feed it a long article to summarize, the attention mechanism is what allows the model to prioritize keywords, relationships, and key phrases from the beginning of the text all the way to the end.
This is why LLMs can generate long, coherent articles without losing the plot; and it’s what makes them so effective at tasks like content summarization or writing a detailed email from a few bullet points. It’s also the reason LLMs can handle a large context window and produce a relevant, in-depth response.

From Model to Marketing Assistant
While the attention mechanism is the powerhouse of the LLM, two fine-tuning processes turn it into a usable tool for marketing.
Instruction Tuning
This is the process of training the model to follow specific directions. It’s what transforms a general-purpose language model into a valuable assistant that understands and acts on clear commands.
This is where the model learns to follow instructions like, “Write an ad for a new running shoe targeting young professionals in a witty tone,” instead of simply generating something generic.
Reinforcement Learning From Human Feedback (RLHF)
After instruction tuning, the model can follow directions, but it might not always give the response you want. This is where humans come in. In RLHF, human reviewers rank a series of model responses for helpfulness, safety, and quality. This feedback loop teaches the model what a “good” response looks like from a human perspective.
Essentially, this training is how the model learns to write content that’s not just factual, but also on-brand, in the right tone, and free of harmful or biased language.

What’s the Point of Using LLMs for Marketing?
So, what does all of this technical information mean for you as a marketer? Now that you understand the mechanics behind LLMs, from the transformer architecture to RLHF, you’re no longer just a user; you’re a prompt engineer. Knowing how these models learn and reason is your key to getting better results, as the best marketing teams are optimizing their use of AI by understanding its underlying logic.
LLMs go beyond their function as writing tools, acting as a multi-purpose toolkit that can transform your entire marketing workflow. By moving beyond simple text generation, marketers can leverage these models to gain a competitive edge in customer engagement, SEO, content strategy, and more.
Automated Content at Scale
One of the most impactful uses of LLMs is their ability to generate high-quality content at scale. Marketing teams can use these tools to create a steady stream of blog posts, social media updates, email newsletters, and ad copy in minutes.
For example, instead of a copywriter spending hours creating 15 headline variations for a Google responsive search ad, an LLM can generate dozens of on-brand options in seconds, allowing the human expert to focus on refining the best ones. This strategic partnership frees up your team to focus on creative oversight rather than manual production.
Customer Engagement
The LLM’s ability to understand context and generate human-like responses makes it the ideal technology to power proactive customer engagement tools. Traditional chatbots were often rigid, limited by a simple set of predefined rules. LLM chatbots, however, can provide personalized support 24/7.
They can analyze a customer’s query, understand their intent, and respond in a natural way that feels genuinely helpful. These AI assistants can also handle a wide variety of tasks, from answering frequently asked questions to providing personalized product recommendations, leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
SEO & Content Strategy
As search engines like Google incorporate generative AI to provide direct answers, the focus of SEO is shifting. Now, it’s about becoming a credible authority that AI trusts and cites.
- Focus on Authority & Expertise: LLMs prioritize trustworthy sources. Creating in-depth, expert-created content is more important than ever.
- Optimize for Citations: The new goal is to have your content cited in AI-generated answers. This requires writing factual, well-structured content that AI can easily ingest.
- Use Structured Data: Implementing schema helps AI models understand and extract key information from your website, increasing the chances of your content being used in an AI summary.
Multimodal Marketing
Beyond text, multimodal models are starting to roll out. These models are trained on more than one type of data (such as text and images) and can understand and generate content that blends these modalities, unlocking a new level of creative freedom for marketers.
- Generate Ad Creative: Give the LLM an image of a product and a short description, and it can create a variety of unique ad visuals and copy to match.
- Automate E-Commerce: Feed a multimodal model an image of a product, and it can automatically generate a compelling product description, complete with keywords and a brand-specific tone.
- Personalize Experiences: AI can analyze a customer’s previous purchases and browsing history alongside product photos they’ve lingered on to provide hyper-personalized recommendations that feel intuitive.

How Do Agents Work With LLMs in Marketing?
While LLMs can be a powerful asset to your marketing efforts, their main limitation is that they are “reactive” tools; they only respond to your prompt and can’t take action on their own. This is where LLM agents come in. An agent is a proactive, autonomous assistant that uses an LLM as its “brain” to perform complex, multi-step tasks.
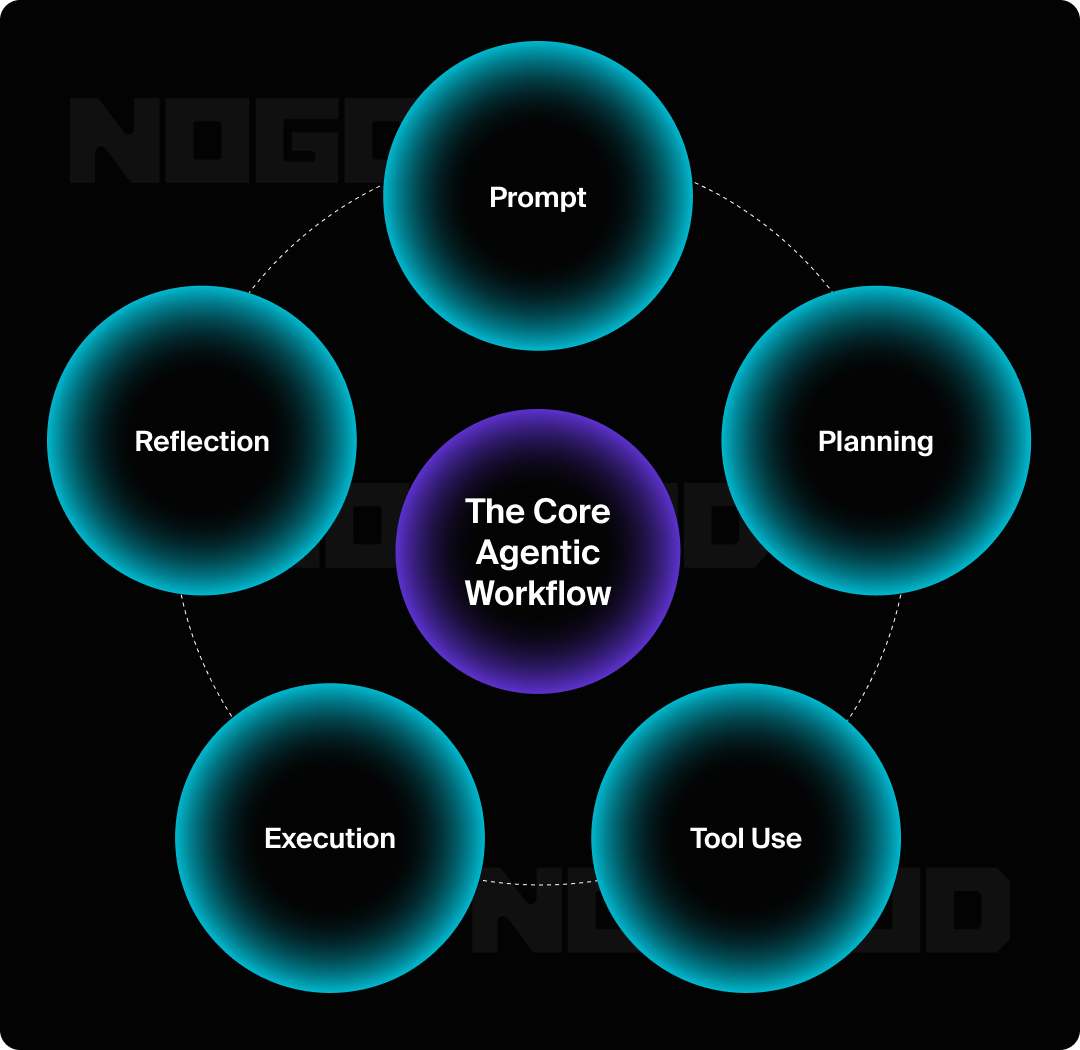
The Core Agentic Workflow
An LLM agent operates by following a continuous, multi-step process that allows it to reason, plan, and take action to achieve a goal. Let’s use the high-level command, “Launch a marketing campaign for our new product,” as a practical example.
- Planning: The agent receives your request and, using an LLM, creates a step-by-step plan. It might decide it needs to: 1) research competitor campaigns, 2) write social media posts, 3) schedule the posts, and 4) analyze performance. This is the first step where the agent transforms a simple command into a series of actionable tasks.
- Tool Use: The agent then identifies and uses the necessary tools to execute each step. This is what differentiates an agent from a chatbot. It might use a web-scraping tool to research competitors, access your brand guidelines from a cloud-based storage system, and use your social media management platform’s API to schedule posts.
- Execution & Reflection: The agent executes the plan, performing each action in the sequence. But the process doesn’t end there. After writing and scheduling the posts, it might “reflect” on the initial results. If it notices that posts with certain emojis or headlines are performing better, it will adjust its plan and strategy to favor those elements in future posts, creating a self-correcting workflow.
The Strategic Advantage
LLM agents are poised to be the next big leap in marketing automation, providing a host of strategic benefits:
- Hyper-Personalization at Scale: An LLM agent can analyze an individual customer’s data, like purchase history and browsing behavior, and automatically generate and send a personalized email with a custom product recommendation and an on-the-spot discount.
- Increased Efficiency and Focus: By automating complex workflows like campaign launches, LLM agents free up marketers from repetitive tasks. This allows your team to focus on creative work that only humans can do—like defining brand strategy, building relationships, and thinking critically about marketing trends.
Conclusion
The ability to understand and effectively use LLMs will soon be a core competency for any marketer who wants to succeed. By moving beyond simple prompting and grasping these core mechanics, you can transform these tools from a simple shortcut into a powerful strategic partner. The future of marketing isn’t about working against AI, but working with it. By embracing these tools responsibly and understanding their full capabilities, you can unlock new levels of efficiency, creativity, and strategic insight for your brand.