Search isn’t what it used to be. In 2025, we’ve moved far beyond typing chopped-up keywords into a browser bar and sifting through a sea of blue links. The way we search (and the way we expect to receive answers) have fundamentally changed.
Today’s search tools are powered by large language models (LLMs) that understand intent, context, and nuance. They don’t just surface relevant pages, they generate answers. This shift has given rise to a new generation of search engines built on generative AI, offering conversational, real-time, and often personalized responses.
Unlike traditional search engines that index and rank content, generative AI search tools use advanced algorithms to deliver synthesized answers, summaries, and even original content on the fly. Whether you’re researching a complex topic, troubleshooting code, or comparing products, these AI-powered platforms are redefining how we find information.
In this post, we’ll explore the best generative AI search tools available in 2025, from Perplexity and ChatGPT to Brave, You.com, and beyond. We’ll break down how they work, what makes them different, and how they’re shaping the future of search.
1. ChatGPT by OpenAI

Your all-in-one AI assistant and evolving search engine
ChatGPT is widely credited with sparking the current generative AI boom, and it’s still leading the pack in 2025. While originally launched as a conversational chatbot, ChatGPT has quickly become a go-to search tool for millions, reshaping how people discover, interpret, and interact with information online.
What the Interface Is Like
ChatGPT’s interface is designed around natural language interaction. It feels more like messaging a very smart assistant than using a traditional search engine. You type a prompt, and ChatGPT responds with a generated answer; sometimes the answer is sourced from its own training data, and other times from the live web (depending on your plan and settings).
The built-in Search feature (available to paying users) allows ChatGPT to browse the internet in real-time to supplement its responses. This can be triggered automatically or manually by the user, and is especially helpful for fact-checking, sourcing recent news, or finding up-to-date information on evolving topics.
Notable Features
- Memory (On by Default for Plus Users & Higher): ChatGPT remembers previous conversations to personalize answers over time.
- Custom GPTs: Users can create tailored AI agents for specific workflows or industries.
- Voice Mode (Beta): On mobile, users can engage in live back-and-forth conversation with the chatbot, no typing required.
- File Uploads: Drop in PDFs, spreadsheets, or images to get summaries, data analysis, or code interpretation.
ChatGPT also integrates with other tools and platforms, including Microsoft Copilot, Slack, and third-party apps via GPTs.
Pricing (as of July 2025)
ChatGPT has five pricing tiers:
- Free: Access to GPT-3.5 with basic chatbot functionality
- Plus: $20 / month; gives access to GPT-4.5 (GPT-4o), memory, custom GPTs, and early feature access
- Pro: $200 / month; enhanced limits, priority performance, and advanced model access
- Team: $25 / month per user; includes admin console, shared GPTs, and private workspaces, excludes data from training
- Enterprise: Contact sales; advanced security, analytics, deployment support, and SSO options
Note: The web browsing feature is available on Plus, Pro, Team, and Enterprise plans.
(Bonus) ChatGPT Search by OpenAI
ChatGPT Search began as SearchGPT, a limited-access prototype in July 2024, and its functionality has since been fully integrated into ChatGPT’s core search experience.
- SearchGPT launched to ~10,000 early testers in July 2024, offering AI-generated answers with clear source citations and follow‑ups
- By October 31, 2024, the feature was renamed ChatGPT Search and made available to Plus and Team users. Free access rolled out in December 2024, and as of June 2025, all ChatGPT users (including Free) have access.
Interface & Features
- Conversational Search: Built right into ChatGPT, just click the Search option, or let it trigger automatically when needed
- Live Web-Based Answers: Sourced with citations and annotated inline, with links for deeper exploration
- Context-Aware Follow-Up: ChatGPT understands prior prompts and conversations, enabling natural follow-up queries.
Note: The web browsing feature is available on Plus, Pro, Team, and Enterprise plans.
2. Perplexity AI

Built for search, powered by AI from the ground up
Perplexity AI isn’t just another chatbot with web access; it was purpose-built as an AI-native search engine, blending conversational interaction with reliable source citations. It gained a strong following in 2025 for its fast, clean interface and transparency in how it pulls information.
What the Interface Is Like
Perplexity’s homepage offers a clean search bar, similar to a traditional search engine, but with AI-enhanced features. As soon as you click in, it presents suggested questions based on trending topics or your recent history (if signed in).
Once you submit a query, Perplexity responds with:
- A generated answer written in natural language
- Inline citations linking directly to the sources it used
- A “related” questions section for follow-up queries (similar to Google’s “People Also Ask”)
- A right-hand panel with options to Search Images, Search Videos, or even Generate Images
You can also set Perplexity as your default search engine via its browser extension.
Notable Features
- Pro Search: A more in-depth response mode available to paid users that conducts expanded research, summarizes sources, interprets code, and solves complex problems—ideal for professionals or academics
- LLM Selection: Choose from models like GPT-4o, Claude, and others for different types of tasks
- File Uploads: Upload PDFs or documents for analysis or summarization
- Perplexity Pages (NEW): Users can now publish long-form, citation-supported content using Perplexity’s engine, turning your searches into shareable, AI-generated articles
Pricing (as of July 2025)
- Free: Basic access, with or without an account
- Pro: $20 / month; Includes Pro Search, file uploads, LLM selection, faster responses, and Perplexity Pages
3. Google Gemini

Google Gemini is Google’s flagship generative AI product, replacing Bard in early 2024. It integrates tightly across Google products (Search, Gmail, Docs, Android, and more) offering a conversational experience powered by Google’s in-house Gemini language models (formerly known as PaLM 2 and now Gemini 1.5 Pro). While it’s still evolving as a “search tool,” Gemini represents Google’s AI-forward vision of how users find, explore, and generate information.
What the Interface Is Like
Gemini is available as a standalone chatbot at gemini.google.com, and it’s also embedded across other Google services:
- In the Gemini interface, users input queries or prompts into a chat box and receive conversational, multi-modal answers, often with images, links, or code.
- In Google Search, Gemini powers AI Overviews, which surface short summaries at the top of the results page for eligible queries.
- In Google Workspace, Gemini is embedded as a side panel (“Help me write”) in Docs, Gmail, and Sheets.
Responses can be expanded, shortened, or rephrased, and Gemini often shows the sources it’s drawing from (although citations are sometimes vague or missing).
Additional Features
- Multimodal Input: Gemini can process text, images, and code, and understands complex mixed inputs.
- Integration With Google Workspace: You can generate emails, summarize documents, draft spreadsheets, and more.
- AI Overviews in Search: Gemini summarizes top search results for quick info consumption (currently rolling out globally).
- Notebook Mode (Experimental): For more structured interactions like step-by-step reasoning or planning.
- Mobile App & Android Integration: Gemini replaces Google Assistant on some Android devices, giving users an on-call AI assistant.
Pricing
- Gemini (Free): Available with a standard Google account.
- Gemini Advanced: $19.99/month via the Google One AI Premium plan, which unlocks access to Gemini 1.5 Pro, longer context windows, and deeper Workspace integration.
4. Claude

Claude is Anthropic’s conversational AI, positioned as a more “harmless, honest, and helpful” chatbot. Named after Claude Shannon, it’s trained with a focus on constitutional AI, meaning it follows a set of ethical guidelines built into its reasoning. Claude is used widely in both individual productivity and enterprise AI workflows.
The most recent release, Claude 3, includes three models: Claude 3 Haiku (lightweight), Claude 3 Sonnet (balanced), and Claude 3 Opus (most powerful). Claude is known for being fast, smart, and incredibly good at summarizing and reasoning over long documents.
What the Interface Is Like
The main interface for Claude is at claude.ai, which provides a clean, minimalist chat window where users can type or upload files for Claude to analyze. Compared to other AI search tools, Claude is less focused on web results and more on helping users work with their own documents, ideas, or research.
Claude responds in a clear, human-like tone and can handle complex questions or tasks like coding, brainstorming, or summarization. Users can also organize chats into folders and create “Projects” to manage longer conversations across a theme.
Additional Features
- File Uploads: Claude can accept and analyze PDFs, CSVs, and other documents (with very large context windows).
- Long Memory (Beta): Available to some users, Claude can “remember” information across sessions for more personalized responses.
- Projects: Helps group conversations and files under a topic (ideal for long-term work).
- Enterprise Use: Claude powers AI tools at companies like Slack, Notion, and Quora’s Poe.
- Privacy-Focused: Anthropic emphasizes user data privacy and avoids using customer prompts to retrain its models.
Pricing
- Free Tier: Access to Claude 3 Sonnet with limited usage.
- Claude Pro: $20/month for access to Claude 3 Opus (comparable to GPT-4 Turbo) and faster response times.
- Enterprise Pricing: Custom rates available for API and team integrations via Anthropic’s developer platform.
5. Microsoft Copilot

Microsoft Copilot Search integrates generative AI directly into the Bing search engine and across the Microsoft ecosystem, including Edge, Windows, and Microsoft 365. Built on OpenAI’s GPT‑4, it aims to transform how users discover and interact with information by blending traditional search with conversational, real-time AI responses.
What the Interface Is Like
The Copilot interface is available via Bing.com, the Edge sidebar, Windows Copilot, and Microsoft apps like Word and Excel. The experience feels like a cross between a classic search engine and an AI assistant:
- You enter a query into a chat-style box.
- Copilot returns a summarized answer along with clickable citations, suggested follow-up questions, and related content.
- You can interact with the answer in real-time, refine your query, or explore visual/web results alongside the AI response.
In Edge, the Copilot sidebar remains accessible as you browse, allowing you to summarize web pages, compare product listings, or generate text on the fly.
Additional Features
- Web Citations: Each response includes sourced links, often from trusted or authoritative sites.
- Image & Video Generation (Edge): Powered by DALL-E and integrated into the sidebar experience.
- Contextual Browsing: Copilot can summarize or analyze the page you’re currently viewing.
- Microsoft 365 Integration: With Copilot in apps like Word and Excel, users can ask questions about documents or auto-generate content using enterprise data.
- Custom GPTs (Experimental): Microsoft has begun testing user-built Copilots for specific tasks or knowledge bases.
Pricing
Microsoft Copilot Search is free to use via Bing and Edge.
- Bing + Copilot: Free with a Microsoft account.
- Copilot in Microsoft 365 Apps: Included with Microsoft 365 Copilot subscriptions (starting at $30/month per user for business plans).
- No separate payment is required for standard Copilot Search on the web.
6. You.com

You.com offers an AI, search-enabled chatbot platform designed to balance general search with business and creative use cases. It aims to provide users with a customizable and privacy-conscious alternative to traditional search engines.
What the Interface Is Like
You.com features a clean text input box where users can enter any query and receive a conversational AI response enriched with real-time web results shown as clickable footnotes. The interface sometimes adds relevant images alongside answers. Like Google’s “People Also Ask,” You.com displays related questions below responses to guide deeper exploration. The platform also offers a “private mode,” similar to incognito browsing, to enhance user privacy.
Before starting a search, users can select from four modes tailored to different tasks:
- Research: Detailed fact-finding and data exploration
- Creative: Assisting with visual generation and brainstorming
- Genius: Solving complex, multi-step problems
- Build Your Own: Create custom AI agents for personalized workflows
Users can specify their industry to help You.com tailor search results; common categories include Marketing, Sales, Engineering, Product, Data Analysis, and Finance. You.com also supports mobile apps, WhatsApp chatbot integration, and desktop browser extensions, enhancing accessibility across devices.
Additional Features
- Customizable AI agents and workflows
- Multiple AI model options available for Pro users
- Industry-specific tuning for more relevant results
- Privacy-focused design with a “private mode” option
- Integration with popular platforms like WhatsApp
Pricing
- Free: Access to You.com’s proprietary large language model (LLM) with standard features
- Pro: $20 / month; unlocks additional LLM models, file uploads, and the ability to create and use custom AI agents
- Team: $30 / month per user; includes unlimited queries with custom agents and ensures all user data is excluded from AI training
- Enterprise: Custom pricing with expanded team features and support
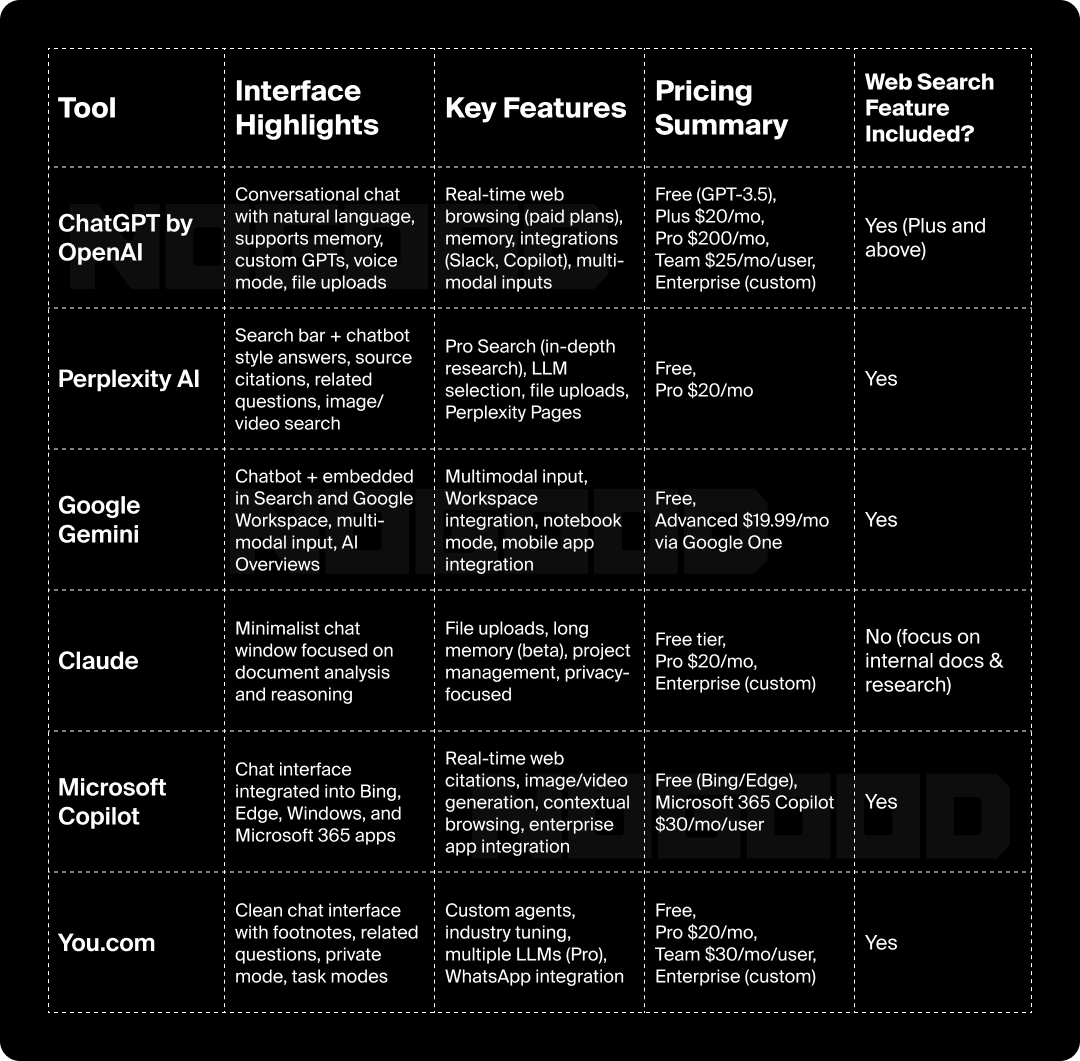
AI Search Tools Comparison
Level Up Your Organic Strategy: Own Your Visibility in Generative AI Search
Generative AI search tools are revolutionizing how people find, consume, and interact with information online. From accelerating research to powering personalized content discovery, these AI-driven platforms are reshaping the entire search landscape.
As adoption of these tools grows, brands and content creators face a new reality: traditional SEO alone isn’t enough. To stay visible and competitive, you need to evolve your strategy and optimize for AI-powered answer engines.
That’s where Goodie comes in.
Goodie is an AI search visibility and answer engine optimization (AEO) platform designed to help your brand stand out across the biggest large language models (LLMs) driving this new search era, including ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Perplexity, and Meta.
With Goodie’s intuitive dashboards and actionable insights, your team can:
- Understand exactly how AI search tools interpret queries related to your brand
- Track your visibility and performance across multiple AI platforms
- Identify new optimization opportunities to capture high-value, AI-driven traffic
Put simply: Goodie helps you own your presence in AI-powered search and future-proof your organic strategy.
Generative AI Search Tools: FAQs
What are the main benefits of generative AI search?
Generative AI search offers a smarter, more conversational way to find information. Instead of just listing links, these tools generate concise, tailored answers that save you time and effort. They can:
- Understand complex or natural language questions, making searches feel more intuitive
- Provide detailed summaries and explanations rather than just raw data
- Pull information from multiple sources and synthesize it into one response
- Offer personalized and context-aware follow-ups for deeper exploration
- Assist with creative tasks, problem-solving, coding, and more—all within the search experience
Together, these benefits make generative AI search a powerful tool for faster, clearer, and more productive information discovery.
How up-to-date are generative AI search engines?
The freshness of information in generative AI search tools varies by platform and model. Some, like ChatGPT with web browsing enabled, Perplexity, and Microsoft Copilot, actively retrieve real-time data from the internet to provide current answers. Others rely primarily on their training data, which may only be updated periodically.
While many generative AI tools can access recent news, trends, and evolving topics, there’s often a slight delay compared to traditional search engines that index the web continuously. For time-sensitive or breaking news queries, it’s a good idea to verify information with trusted sources.
Overall, these tools are improving rapidly in real-time access, but understanding each platform’s update frequency helps set accurate expectations.
How does RAG help generative AI search tools produce the most accurate information?
RAG, or Retrieval-Augmented Generation, combines the power of large language models (LLMs) with real-time access to external data sources. Instead of relying solely on pre-trained knowledge, RAG enables AI to fetch relevant documents or facts from trusted databases or the web during a query. The AI then uses this fresh, retrieved information to generate more accurate, contextually relevant, and up-to-date responses.
This approach reduces hallucinations (inaccurate or made-up answers) by grounding AI-generated content in verified sources, improving trustworthiness and precision in generative AI search results.
What are the best ways to use AI search engines?
- Asking natural language questions, i.e. typing out your thought process exactly as it occurs to you, so you don’t have to edit your query before searching.
- Using specialized modes offered by different tools. Some models offer a research mode, for example, which is a great tool to use for specific projects and queries.
- Using AI-generated summaries for responses or search results with a wide range of complex information.
- Solving complex problems or equations. Many of these tools can reason through complicated issues and provide solutions, and they can also generate and/or debug code.
- Performing competitive research. By inputting queries that are relevant to your brand, product, or service, you can better understand the context you’re operating in. Does your brand come up for these searches, or do your competitors?
What are the challenges of AI search engines?
AI-powered search engines are still a relatively new technology, and many of them are still being developed. Many of these programs have not had all issues solved for, and there’s often still a lot of room for improvement in certain areas.
For example, AI search engines need data inputs in order to train their algorithms. This data isn’t always available, or the models may be trained inconsistently. Additionally, since these AI tools are learning from the data inputs, they may pick up on certain biases or inaccuracies if they were present in the original data. This could harm the quality of accuracy of the results they generate and deliver to users.
On a similar note, some people also have concerns about data privacy. Some of these platforms retain user data and may or may not use it to train their AI models.
Lastly, some generative search AI platforms can still be subject to producing inaccurate information.
What’s the difference between generative AI and a large-language model (LLM)?
AI-powered search engines are still a relatively new technology, and many of them are still being developed. Many of these programs have not had aGenerative AI and LLMs are related, but they’re still separate concepts within the overarching umbrella of artificial intelligence. In many of the tool;s we discussed above, LLMs were a key component of these generative AI search platforms, but each platform had features and capabilities beyond the LLM component.
LLMs are a specific subset of generative AI that are focused primarily on natural language processing and text generation. Generative AI can speak to additional content generation tasks, going beyond text to include images, audio, and video.