Marketers and web designers have been dropped right smack in the middle of a search revolution. It’s been a long time coming, though; Google’s Core Web Vitals, AI search assistants, and zero-click results continue to blur the lines between previously divided marketing principles. Ranking well is no longer about slapping keywords onto an HTML page. It’s a more existential, holistic question of “how does your brand show up across digital surfaces.”
We can analyze the changing relationships between all these disciplines of search marketing until the cows come home, but today’s culprit is SXO: the fusion of SEO and UX.
Now, while I personally think that SEO is already naturally imbued with the behavioral sciences (after all, the goal is to give real humans real answers to real questions), SXO is an offshoot of SEO that adds even more focus to optimizing for intent, curiosity, and conversion.
What Is Search Experience Optimization (SXO)?
Search Experience Optimization (SXO) merges the visibility driven by SEO with the usability driven by UX design. When these two get together, the goal is to design, write, and build websites (or organic landing pages) that not only perform well in search results, but also make sure users stick around once they arrive.
SXO is much more than just keywords and meta tags we SEOs love so much. It looks at how users behave once they land on your site (things like scroll depth, engagement, conversions) and uses that behavior to tell search engines, “Yes, this is actually useful.” In 2026, those signals will continuously carry more weight than ever.
In short, SXO accounts for technical performance, content quality, design elements, and human behavioral signals.
The New Frontier: AI-Driven SXO
At the same time that the marketing space lurches towards extreme humanity as a way to counter the AI revolution, AI chatbots and search platforms are rewriting discovery as we know it. The top organic spot on Google’s SERP is no longer the promised land; brands are fighting tooth and nail to be as much as included in AI-generated responses.
While NoGood and Goodie have enough AEO guides to keep you busy reading for months, we’ll keep it short here. To stay visible, your site needs to:
- Be semantically structured so AI models can interpret it accurately.
- Provide clear, concise answers to questions AI might surface.
- Build recognizable expertise and trust so your brand becomes a noticed (or, ideally, cited) source.
All of this to say: since AEO is being interpreted as an extension of SEO, it’s also an extension of SXO. Marketers must acknowledge how users now interact with both search engines and AI assistants interchangeably.
The Core Principles of UX SEO (or UXO, or User Experience SEO; You Get It)
Core Web Vitals: The Technical Backbone of UX SEO
A big point of intersection with SEO, AEO, and UX is Core Web Vitals. If we’re talking about being discoverable on the web, you better believe that your website’s technical performance is gonna play a major role. Core Web Vitals track how fast your page loads, how stable it feels, and how quickly it responds to user input.
There are three major Core Web Vitals that you should keep an eye on:
- LCP (Largest Contentful Paint): How fast your main content appears (no plain white screens here, guys. C’mon).
- CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift): How visually stable your layout is while loading. If your homepage is glitching right and left before loading completely, you’re in trouble.
- INP (Interaction to Next Paint): How quickly your site reacts when users interact. As big a proponent of beautiful web design as I am, it doesn’t mean jack if your users can’t do what they need to do on it.
Slow sites and unstable layouts aren’t just annoying; they tank engagement. When that happens, search engines (and users) take note. In fact, 47% of users expect websites to load in under 2 seconds.
To track Core Web Vitals, here are a few tools to keep handy:
- Google PageSpeed Insights (for quick diagnostics, my personal favorite)
- Lighthouse (for more in-depth technical audits)
- Screaming Frog or Ahrefs (both solid site auditors)
- Hotjar or Microsoft Clarity (for heatmaps and session replays)
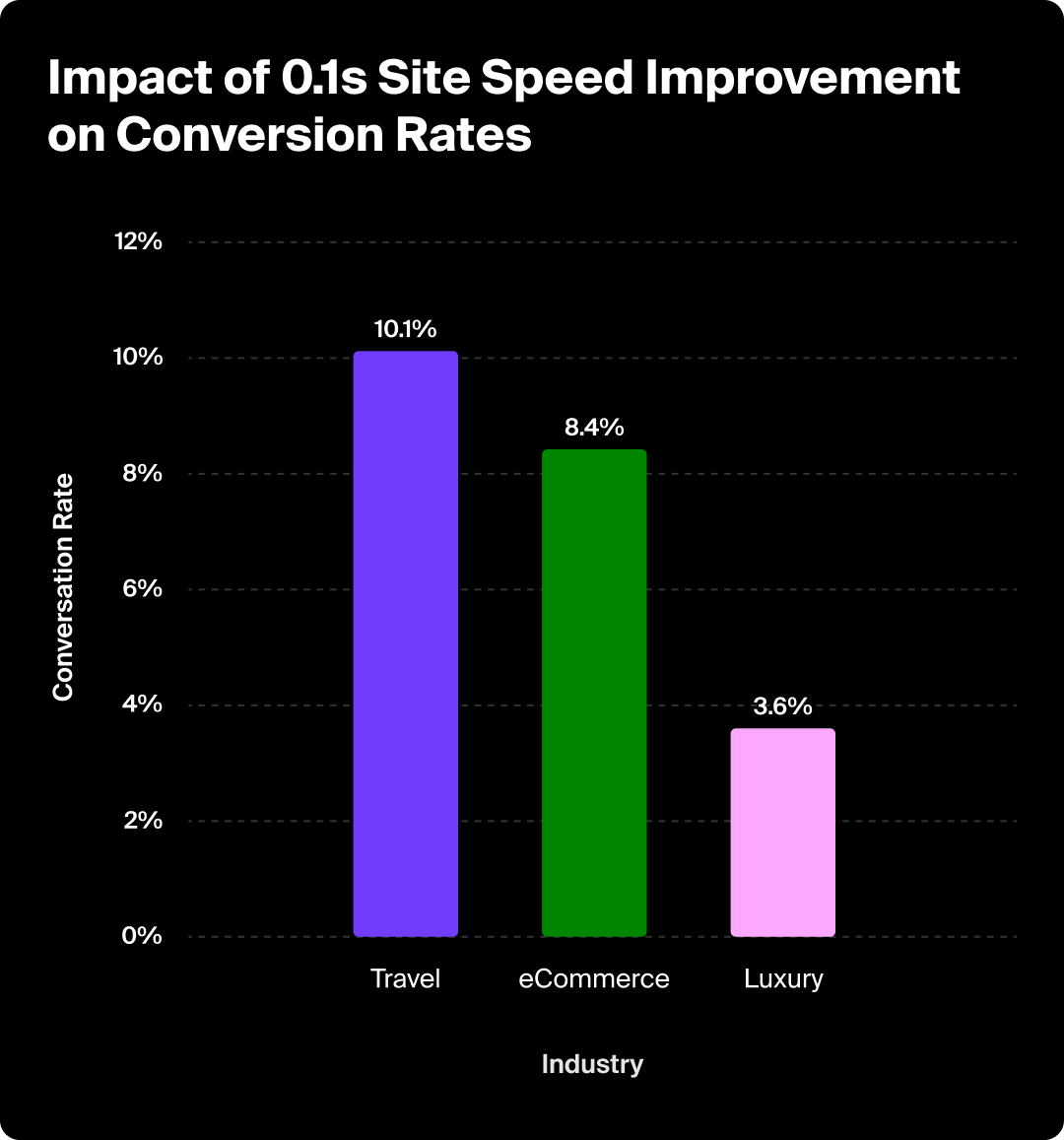
To illustrate the importance of keeping your website technically sound, even shaving a second off load time can lift both your rankings and your conversion rate. In 2024, Nitropack collaborated with Google on a study that found the result of a 0.1s improvement in load time leads to some pretty significant results:
- A 10.1% increase in conversions in the travel industry
- An 8.4% increase in conversions for eCommerce websites
- A 3.6% increase in online purchases in the luxury sector
Content Experience: Writing for Users & Search Engines
Where technical performance represents the intersection of UX and SEO that users can’t necessarily see, the content experience is where UX and SEO most visibly meet. Between the rise of AI search and emphasis on re-humanizing marketing, it’s no longer enough to publish keyword-optimized text. Your words need to feel intuitive, relevant, and human.
Google’s E-E-A-T framework rewards content that demonstrates both credibility and empathy. UX writing (concise, user-focused, and conversational) also reinforces those signals.
|
SEO Copy |
UX SEO Copy |
UX + SEO + AEO Copy |
|---|---|---|
|
Keyword-heavy paragraphs |
Natural, conversational flow |
Conversational and intent-based copy geared towards both humans and AI |
|
Generic CTAs (“Learn More”) |
Contextual CTAs (“Learn How to Scale Your Marketing”) |
Predictive, intent-driven CTAs that extend the reader’s journey |
|
Long intros |
Clear takeaways up top |
Answering main question up top followed by context, examples, and sub-answers mirroring conversational search flow |
Adding UX considerations into your writing process increases readability, encourages engagement, and reduces bounce, improving the behavioral metrics that search algorithms monitor. Writer to writer, I like to sit back and read the things I write out loud. If I have trouble understanding the flow of my own writing, there’s no shot that a random user will.
UX Principles That Directly Impact SEO Performance
The same way that there are principles of SEO that play nicely with UX, the opposite is also true. Speaking from personal experience, there’s always a component of my work with clients where the recommendations I give are not based on any hard SEO best practices; rather, they’re design, layout, user journey, or usability-related.
To review a few:
1. User Personas
If you’ve ever read a marketing-related article before, you know just how important knowing your audience is. It’s a vital part of any marketing strategy, and the same goes for UXO. Understand what your audience wants, what frustrates them, and how they navigate online.
- Why It Matters: Relevance to user intent improves engagement time and rankings.
- How to Do It: Use analytics, GA4 reports, or AI persona generators to personalize site flows.
2. User Journey
Visualize how users move through your site, from entry point to conversion.
- Why It Matters: A frictionless flow reduces drop-offs and increases session duration.
- How to Do It: Walk through the flow yourself or run user testing. Note where the friction happens and simplify where possible; every extra step is a chance for a user to drop off.
3. User Testing
A/B testing, click tracking, and behavioral analytics tools show how real users interact with your site.
- Why It Matters: Small design or content changes can lead to major gains in engagement and conversion rates.
- How to Do It: Use tools like Microsoft Clarity or Hotjar to get insight into user journeys. Or, just send the website to friends, family, colleagues, and anyone else you can think of (we all do it sometimes).
4. User Interests
User personas are a living thing, ever-evolving. Monitoring social trends, search queries, and search behavior to continuously improve the UX on your site keeps your UXO strategy agile and consistently meeting user intent.
- Why It Matters: Meeting user interests signals to search engines that your site satisfies intent, driving organic traffic and backlinks.
- How to Do It: Watch how your audience’s interests evolve. Monitor internal search queries, social mentions, and feedback.
How UX & SEO Work Together: Design, Structure & Performance
We’ve reviewed ways that SEO and UX intersect, but how do they work together? After all, a well-planned UXO strategy must act as the bridge between the best practices of SEO, the human behavior sciences of UX, the creativity of content, and the beauty of design.
Responsive Web Design
Mobile-first design is still gospel; 64% of website traffic in 2025 comes from mobile devices. Responsive layouts adapt to various devices and screen sizes while also improving your Cumulative Layout Shift and ensuring accessibility across platforms.
I found a pretty fun example of non-responsive web design if you need a visual for how terrible it makes the browsing experience (it sends chills down my spine).
Intuitive Navigation
Navigation is the Yellow Brick Road leading your user to the Emerald City, also known as the contact form or checkout page. Use clean hierarchies, internal linking, and descriptive labels to guide users (and help crawlers map relevance).
💡 Pro Tip: For larger-scale eCommerce brands, faceted navigation might be a good solution from a UX perspective; however, it must be implemented and managed properly in order to preserve SEO performance. Luckily for you, I’ve whipped up an article about that already 👀
Site Speed Optimization
The general (and easier) technical fixes that I keep my eyes on are image formatting and sizing (150kb in webp or svg formats preferred), script minification, and CDN usage. If I haven’t drilled it into your head already, I’ll repeat it here: fast load times reduce abandonment and directly improve LCP scores.
Remember to play nice with your dev team; they’re likely poking around in the backend just like you are. Try to avoid being that pesky extra cook in the kitchen.
Interactive Elements
Interaction via dynamic content (quizzes, sliders, chat widgets, etc.) is great for driving traffic and engagement, but it can be a pain in your SEO team’s ass. Keep interactivity optimized, purposeful, and fast.
This is a component where user testing is key; if you’re consistently getting feedback that a widget is annoying or distracting, or that the quiz is glitchy and slow, it might be smart to forego interactivity until its performance can be optimized.
The Role of AI in UX & SEO Integration
AEO, SEO, UX… our acronym soup is missing one crucial ingredient: AI. Artificial intelligence has a way of sneaking its tendrils into everything these days, and UXO is no exception.
Search engines are increasingly relying on machine learning models to interpret UX signals like engagement rate, click behavior, and return visits. At the same time, marketers are also using AI tools to improve personalization and relevance in real time.
To bring the abstract into reality, let’s look at a few examples of UX SEO, enhanced by AI:
- Generative Design Testing: AI tools A/B test page layouts for conversion optimization.
- Though this is a legitimate use case that I felt the need to list, I’d like to make a point that I personally don’t recommend relying on AI for tests that are centered around human behavior. Maybe for preliminary testing, but it’s been pretty well established that the best way to market to humans is by being, well, human.
- Predictive Search: AI autocompletes and ranks content likely to satisfy user intent.
- Voice & Multimodal UX: Optimizing for voice commands, image-based search, and video transcriptions enhances accessibility and ranking visibility.
- This is yet another thing I don’t necessarily recommend AI for. While AI can gather recommendations, I think the actual work is best left to our beautiful fleshy human brains.
Key Metrics for Search Experience Optimization
Being that SXO adds an even more prominent human element to traditional SEO, our metrics also shift to become more organic. Traditional metrics like bounce rate or average position give way to behavioral and engagement signals.
|
SEO Metric |
SXO Metric |
|---|---|
|
Bounce rate |
Engagement rate |
|
Ranking position |
Visibility across AI and SERPs |
|
Organic clicks |
Dwell time and scroll depth |
|
CTR |
Conversion completion rate |
|
Pageview |
User journey completion metrics |
Because some of these metrics are less data-focused, I’ll go ahead and review them here:
- Engagement Rate: A GA4 metric combining clicks, scrolls, and interaction time.
- Conversion Rate: Measures how UX clarity drives tangible results.
- Dwell Time: Indicates perceived content value.
- CTR: Still important for testing meta titles and snippets.
- Scroll Depth & Return Visits: New behavior-focused KPIs that reveal ongoing user trust.
Keep in mind that these metrics also require some additional layers of interpretation to connect them back to SXO performance.
How to Conduct a UX SEO Audit
Because there are so many components to UX SEO, the auditing process is longer and multifaceted. It’s comparable to an SEO audit, just with additional human psychology considerations layered on top. Like some sort of weird trifle.
- Technical SEO & Core Web Vitals Audit: Use tools like PageSpeed Insights, Screaming Frog, or Goodie to benchmark speed, CLS, and crawlability.
- UX Audit: Evaluate design consistency, accessibility, and navigation patterns. Use heatmaps (Hotjar, Clarity) and session recordings to find bottlenecks.
- Content Audit: Assess readability, intent alignment, and E-E-A-T signals. Identify underperforming or high-bounce pages and rewrite them with a user intent lens.
- Behavior Analytics Audit: Analyze GA4 engagement metrics, conversion paths, and drop-off points.
- AI Readiness Check: Ensure structured data, schema markup, and multimodal assets (video, images, FAQs) are in place for AI visibility. You can use Goodie for this, too; what am I gonna do, stop you?
Final Thoughts: UX & SEO as a Continuous Feedback Loop
Now, parts of this article got pretty cut and dry and technical, but I urge you to keep one thing in mind throughout the entire process: the “U” in UXO stands for User.
Everything you’re doing—every color you change, every paragraph you rewrite, every image you compress—is supposed to make the experience better for the user. You can science-ify it all you want, but the beautiful thing about all of this is that it’s human. And that makes it fluid, unpredictable even. People are going to be people, and you can’t always find meaning in their actions. So just have fun with it; experiment, try new things, fail, and start over. UXO is an art.