Have you ever seen a piece of content, immediately thought of someone, and sent them the link in a Slack message, DM, or text? If you answered yes, then you’ve used dark social. The term may sound ominous, but dark social actually has immense opportunities for brand growth and visibility that many are leaving untapped. According to recent insights, it’s estimated that 95% of content sharing happens on dark social; brands that aren’t paying attention to this hidden layer of internet sharing suffer from a major blind spot behind what’s actually driving their content reach.
What Is Dark Social?
“Dark social” is a term used to describe web traffic generated by social sharing channels that cannot be accurately tracked by traditional analytics platforms. These channels include social media DMs, private messaging apps, and online communities. Other variations you may have heard include dark social Media, Dark Traffic, or Dark Funnel, which all mean that brands and marketers are left in the dark without trackable referral data.
Powered by community interaction and closed communities, dark social is the silent audience that goes beyond your known brand advocates, social media followers, and newsletter subscribers. When users share links directly with others via private messaging apps like WhatsApp, iMessage, or Slack, the traffic is attributed as “Direct” even if the discovery happened through socials, meaning that the original, accurate referral data is lost. Even with UTM links, tracking can still be lost if something is shared as a screenshot or if someone searches for the brand on a separate browser instead of clicking on a direct link.
The Influence Iceberg
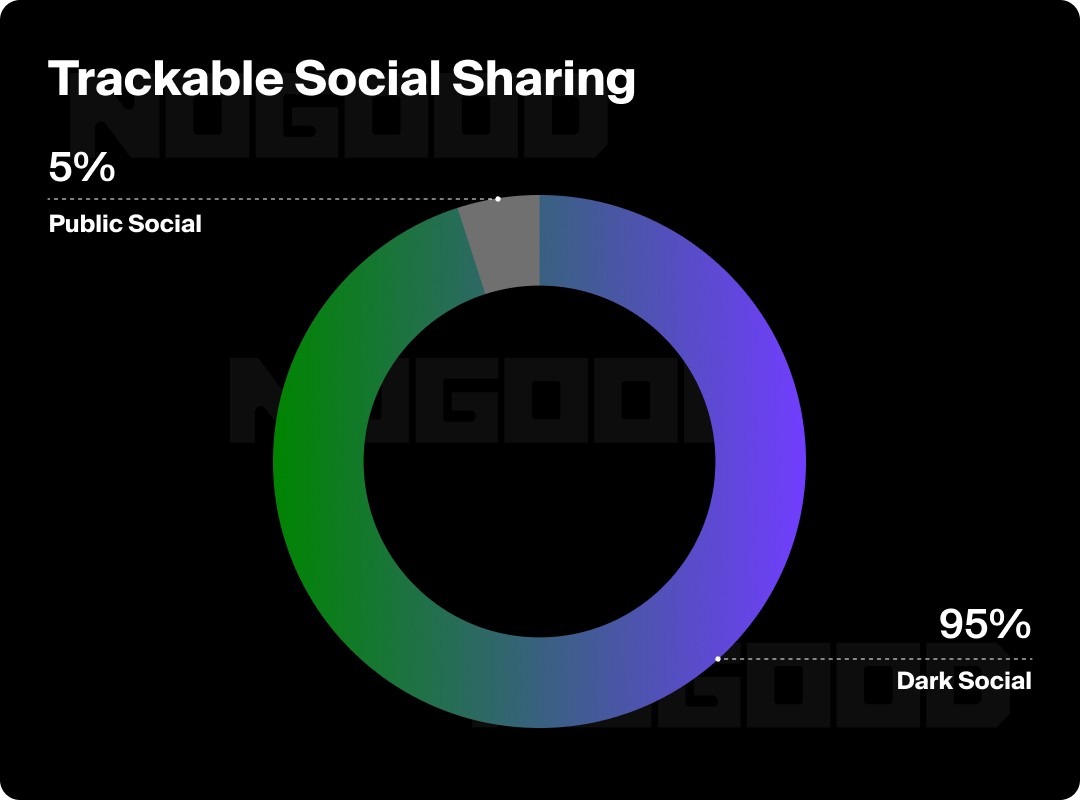
The ecosystem of influence is not a simple linear path of content discovery → awareness → conversion. The prevalence of dark social means that we should be thinking of influence more as an iceberg, with trackable social sharing above the waterline, and an ecosystem of hidden interactions below.

The influence iceberg essentially implies that there is more to influence than what meets the eye; the majority of what affects your brand sentiment lies beneath the surface of what’s publicly trackable. To close this measurement gap, we’re seeing the rise of brand sentiment tracking and social listening tools that are built to capture insights beyond traditional public metrics. Social listening analyzes conversations about your brand and industry across both public and private channels, helping marketers uncover actionable insights for strategic decisions.
Importantly, this approach shifts the mindset from simply counting likes, shares, and comments to interpreting influence as a networked ecosystem. A single DM or message in a private Discord server may reach fewer people than a viral Tweet, but it can carry disproportionately high trust and persuasive power because it comes from a trusted source.
Brands that leverage this perspective can:
- Spot early trends: Dark social often surfaces emerging product preferences or cultural movements before they hit public platforms.
- Measure true sentiment: By tapping into private discussions, brands gain a more accurate picture of customer perceptions, complaints, and enthusiasm.
- Refine content strategy: Understanding which messages travel in private channels allows marketers to craft more resonant, shareable content that thrives both above and below the surface.
Ultimately, thinking of influence as an iceberg encourages brands to look beneath the surface and invest in tools and strategies that reveal the hidden interactions shaping perception, trust, and purchasing behavior. Brands that integrate social listening, dark social tracking, and AI-powered analytics can uncover the conversations driving sentiment, identify hidden advocates, and optimize content strategies based on how influence actually spreads.
Taking Advantage of Dark Social
Though tracking can be a major concern for marketers married to GA4, there are ways to take advantage of dark social that can tap into the trust and authenticity inherent in this method of social sharing. Recent data highlights a significant erosion of trust between consumers and brands, emphasizing a critical need for transparency and ongoing engagement.
This is a big reason why social search is experiencing such high adoption rates, as users look to get unfiltered recommendations and information from real people rather than brands. Consumers today actively seek validation from trusted communities and peers, making the word-of-mouth marketing and peer recommendations within dark social particularly important for driving brand influence.
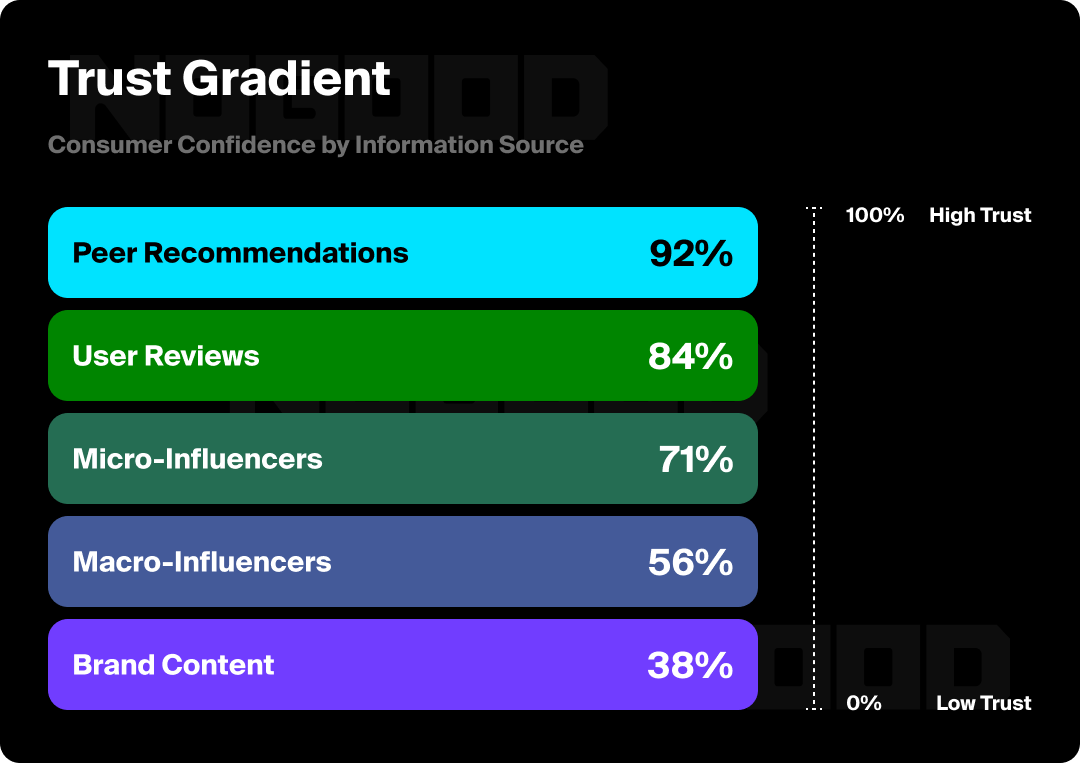
The psychology of dark social and closed communities is rooted in peer-to-peer trust and selective sharing. We all want public engagement on our content, but it is almost a higher compliment (and even better conversion) if the content gets shared privately. This reflects the genuine nature and quality of said content that stirs a user’s behavior to specifically share with someone in particular, not just push a post out to their entire audience.
In this way, these dark links develop more qualified leads and BOF conversions. When a trusted person messages you a link, you are more likely to open it than if it were to originate from a random stranger or email account. Especially when it comes to putting in your payment information or subscribing to an email list, a user is more likely to complete an action if a trusted source “recommended” it.
One way that brands have been tapping into dark social is by building out their own closed communities for their most loyal users, so that they can control the narrative of dark social and be privy to conversations about their products in ways they may not have been before.
Notion, for example, has private channels on Slack, Discord, and Facebook that are all moderated by community ambassadors known as Notion Pros. These are unpaid brand representatives that assist in answering Q&As, creating educational resources, and helping promote Notion globally.
Dedicated brand communities assist in taking back control of dark social activity by giving users a place to gather and communicate with other users (instead of talking about your product on an untraceable channel). Positive and negative feedback can be shared through these channels, and community members and ambassadors can assist in answering questions and getting the pulse on what’s really being said.
Privacy as Luxury
The rise of dark social is in a large part affected by how consumers today are increasingly viewing and defining privacy as a form of luxury. According to Brand Strategy Consultant Eugene Healy, “the greatest privilege in the current culture of overexposure is to be invisible”. Since major tech players have effectively transformed consumers into products to be harvested for data to feed algorithms, the culture of luxury has shifted toward prioritizing “if you know you know” conversations and more intentional socialization that is consciously guarded from outside influences.
This redefinition of privacy reframes exclusivity: it’s no longer just about material access, but about controlling visibility. Encrypted messaging platforms, private group chats, and closed communities have become the new gated “clubs”; spaces where consumers can share, recommend, and influence without the surveillance of algorithms or the noise of mass platforms.
Privacy as luxury is heavily tied to control, specifically users being able to control the type of content they want to see and consume. Gated Substack newsletters play a big part in this by giving users more control over the creators and brands that they follow, rather than being overwhelmed by trend-chasing algorithms.
For brands, this shift presents both a challenge and an opportunity. Traditional visibility metrics (things such as likes, shares, and impressions) fail to capture the value of these closed conversations. Yet, these spaces often host the most authentic exchanges, where trust is built and purchasing decisions are influenced far more than in public feeds.
Marketers must begin to see dark social as the new arena of cultural capital. Just as luxury once signaled status through scarcity, today’s version signals status through discretion. Brands that understand how to engage with communities without disrupting their guarded nature (by seeding content that is shareable in private contexts, by fostering exclusivity through gated experiences, or by respecting boundaries with privacy-first messaging) stand to gain disproportionate influence.
In essence, the rise of dark social and the elevation of privacy as luxury are not just consumer behaviors; they represent a cultural recalibration. Influence now flows through trust, intimacy, and intentionality, not just reach.
Measuring What (Allegedly) Can’t Be Measured
Let’s talk about the measurement paradox: how do you measure dark social if its very definition is that it is untrackable? The dirty secret of marketing analytics is that there are ways to measure dark social; even if those methods aren’t necessarily perfect, they are useful in painting a picture of brand sentiment or overall influence beyond what shows up in standard dashboards.
1. Google Analytics & Direct Traffic Analysis
- Deep-dive into direct traffic. Visits to obscure or long-tail URLs (like product pages or blog posts) are unlikely to be typed manually, making them strong indicators of dark social shares.
- Segment traffic by page depth, device type, and geography to uncover patterns tied to private sharing.
- Use cohort analysis to connect spikes in direct traffic with campaign launches, PR hits, or social events that may have sparked private sharing.
2. On-Site Prompts & Qualitative Attribution
- Add “How did you hear about us?” prompts in checkout flows, sign-up forms, or exit surveys.
- Keep answers lightweight and open-ended (“Friend,” “DM,” “Text”) to surface private sharing sources.
- Use pop-up intercept surveys to ask visitors what motivated them to click a link. This qualitative layer captures data invisible to analytics tools.
3. Social Buttons, Share Tracking & Referral Incentives
- Embed “copy link” or “share to WhatsApp” buttons directly into articles, product pages, or apps.
- Tag and track these buttons so you can differentiate intentional private shares from public ones.
- Launch referral programs where users are rewarded for bringing others in; these programs often rely on unique links that give visibility into what would otherwise be dark.
4. UTMs, Short Links & Custom Tracking Infrastructure
- Seed links with UTM parameters across channels, even in influencer seeding kits or email outreach.
- Use branded short links (e.g., Bitly, Rebrandly) to see where links resurface across private groups.
- Set up unique UTMs for campaign variations (e.g., one for WhatsApp vs. one for Telegram) to infer which dark channels drive engagement.
5. Social Listening & AI-Driven Sentiment Tools
- Tools like Sprinklr, Brandwatch, Meltwater, and Talkwalker go beyond mentions to analyze conversation clusters, sentiment, and thematic shifts, even across semi-private forums.
- While they can’t crawl encrypted DMs, they triangulate signals from adjacent spaces (forums, gated newsletters, niche communities) to approximate what’s happening below the surface.
- AI-powered categorization turns messy, unstructured chatter into actionable insights on perception, customer needs, and potential crises.
6. Search & Alert Systems
- Google Alerts or tools like Mention and Talkwalker Alerts notify you when your brand or keywords are mentioned, even outside major platforms.
- This helps capture early signals of brand conversations, especially when those conversations are sparked in private groups but eventually surface publicly.
7. Community Monitoring & Ethnographic Research
- Keep a presence (or build brand ambassadors) within Discord servers, Slack groups, private Facebook groups, and niche forums.
- Direct observation or ambassador feedback can provide qualitative insights into how your brand or category is discussed behind closed doors.
- Treat this less as “data scraping” and more as digital ethnography; a way to understand tone, trust, and cultural context.
8. Attribution Modeling & Incrementality Testing
- Dark social often shows up as unattributed direct traffic. By running incrementality tests, you can isolate lift that likely originated from private sharing.
- Multi-touch attribution models, while imperfect, can help assign some credit to dark social activity by analyzing indirect correlations between awareness and conversion spikes.
Are You Afraid of the Dark?
Dark social represents a structural shift in how influence and information flow online. The key challenge for brands lies in operating in a world where visibility is partial, trust is private, and influence is decentralized.
Moving forward, marketers need to rethink relationship building, experience design, and measurement. Influence in dark social requires seeding trust into the right spaces, respecting privacy, and providing content that consumers are motivated to share within their personal networks.
Brands that succeed will combine advanced measurement tools with deep understanding of community dynamics and cultural context. Growth in this environment comes from engaging authentically, fostering credibility, and capturing insights from conversations that are often invisible to traditional analytics.
Dark Social FAQs
What is the difference between dark social and regular social media?
Regular social media is public and trackable, whereas dark social occurs in private, untracked channels that aren’t visible to standard analytics.
What are dark social media apps?
These are apps and platforms that facilitate private sharing and conversations, such as WhatsApp, iMessage, Telegram, Signal, Discord, Slack, Facebook Messenger, and private Instagram or TikTok DMs.
Why does dark social matter for brands?
It drives a significant portion of content sharing, often with higher trust and engagement, influencing brand perception and purchase decisions beyond what is visible publicly.
Can dark social be measured?
While full measurement is impossible, tools like social listening platforms, UTMs, link shorteners, referral programs, and qualitative surveys can help approximate its impact.
How can brands leverage dark social?
Brands can create shareable content for private channels, foster closed communities, and engage influencers or ambassadors who participate in these hidden networks.
How does privacy affect dark social?
As consumers increasingly value privacy, they share and engage in closed channels, making dark social a reflection of intentional, trust-based communication rather than broad visibility.