If you were paying for a billboard in Times Square, you wouldn’t design something dull, generic, or totally off-brand, right?
Well, when you post a link on social media, and it generates a sad, empty preview like this:
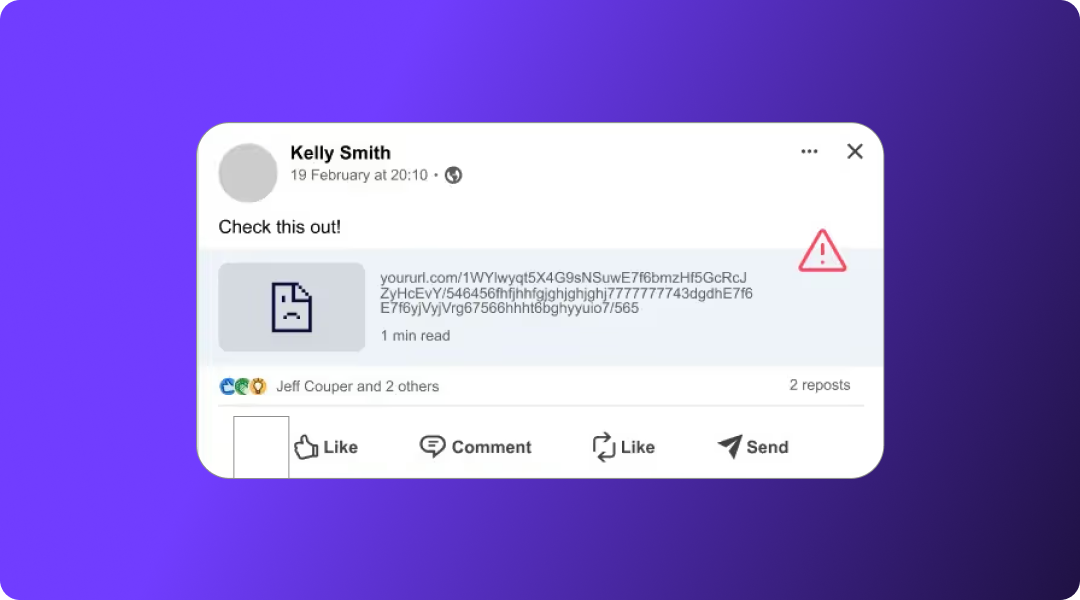
…that’s basically the digital equivalent.
Your link preview is your billboard; and when it’s unoptimized, you’re throwing away attention, clicks, and credibility.
The entire practice of “prettifying” your social posts comes down to one thing: Open Graph SEO. That means optimizing the OG tags in your page’s HTML so every platform, LinkedIn, Facebook, X, Slack, iMessage, Discord, WhatsApp, can generate a rich, compelling link preview that actually gets clicked.
What is Open Graph in SEO?
Open Graph (OG) is a metadata protocol originally created by Facebook in 2010 that tells social platforms exactly how your content should appear when someone shares your link. These OG meta tags live in your page’s HTML and control the preview image, title, description, and other elements users see in their feeds.
Here’s what that looks like in practice:

Instead of showing a plain, unbranded URL, Open Graph tags allow your link to appear as a rich, clickable preview; complete with an image, caption, and headline. This makes your content more engaging, more trustworthy, and significantly more likely to earn clicks and shares.
Is Open Graph Still Used?
Absolutely! And arguably, it matters more now than ever. Social feeds are overflowing with content (and a growing amount of low-quality, bot-generated posts), which means your link preview needs to work harder to stand out. Open Graph tags ensure your content appears polished, branded, and credible the moment it’s shared.
OG isn’t just “still used”; it’s a default standard across most major platforms. Facebook, LinkedIn, X, Slack, Discord, iMessage, and even many AI crawlers rely on OG metadata to understand what your page is about and how it should be represented. Without it, your content looks broken, untrustworthy, or easy to scroll past.
When you implement OG correctly, you’re not just improving aesthetics; you’re signaling to users (and platforms) that your brand understands how content is consumed, previewed, and shared today.
Before we dive into how to optimize OG SEO, here are the key benefits you should know.
1. Increases Brand Awareness
Open Graph tags give you full creative control over how your content appears when shared; from the headline to the description to the preview image. Instead of relying on whatever text or image a platform “guesses,” OG lets you intentionally design a branded, eye-catching link preview.
Use this to your advantage: choose visuals that reflect your identity, write social-optimized headlines, and craft descriptions designed specifically to stop the scroll. A well-designed OG preview makes your content instantly recognizable and builds brand recall over time.
2. Leads to Higher Social Media CTR
A strong OG setup directly impacts click-through rate. When your link shows up with a bold image, clear headline, and compelling description, you dramatically increase the chances that users pause and click.
Just make sure your OG metadata accurately reflects the content it promotes. Misleading images or descriptions might earn the click, but they’ll tank engagement metrics and increase bounce rates (which hurts your trust signals across platforms).
3. Unifies Brand Appearance & Visual Assets
Because OG metadata dictates how your content appears everywhere (Facebook, LinkedIn, X, Slack, Discord, iMessage, WhatsApp) it becomes a powerful tool for ensuring brand consistency.
Consistent visual assets and messaging help users instantly recognize your posts, even if your brand is still growing. For smaller brands especially, OG provides a low-effort, high-impact way to look polished and professional across every social channel.
4. Improves Indexing & Platform-Specific SEO
While Open Graph is not a Google ranking factor, it is a major signal for social crawlers. Platforms like Facebook, LinkedIn, Slack, and Discord use OG tags to understand:
- What the content is
- What type of object it represents (e.g., article, product, website)
- How it should be displayed
- Which users may find it relevant
Clear OG metadata helps these platforms properly index, categorize, and distribute your content, which increases your chances of being shown to the right audience at the right time.
And with AI models increasingly pulling structured metadata (including OG tags) to build previews and summaries, a clean OG implementation also supports AEO, not just social SEO.
7 Open Graph Meta Tag Types to Optimize For
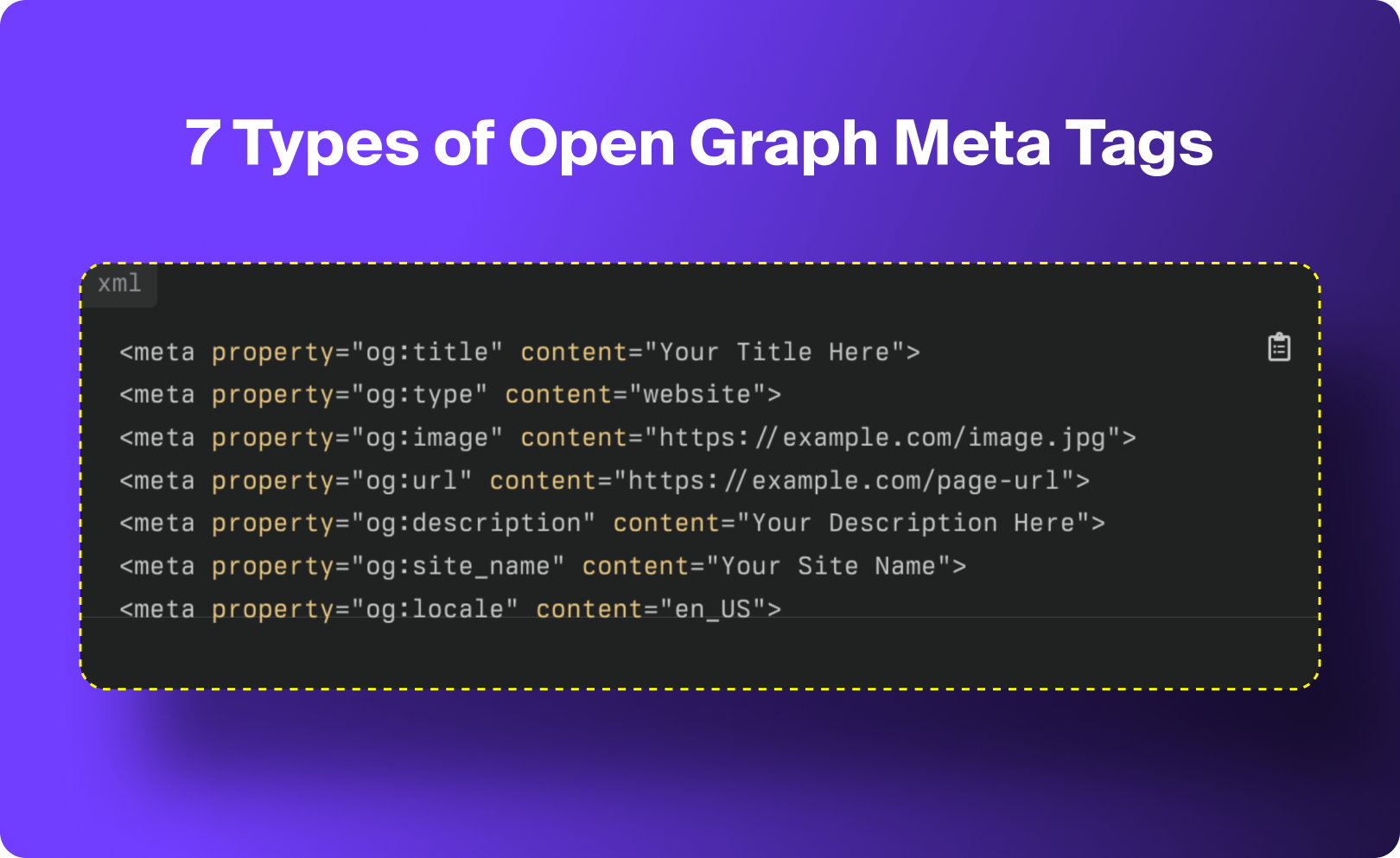
1. og:title
og:title defines the headline that appears in your social link preview. It can match your SEO meta title, but it doesn’t have to, and in many cases, it shouldn’t. Your OG title should be written specifically for social audiences, where space is limited, and attention is scarce.
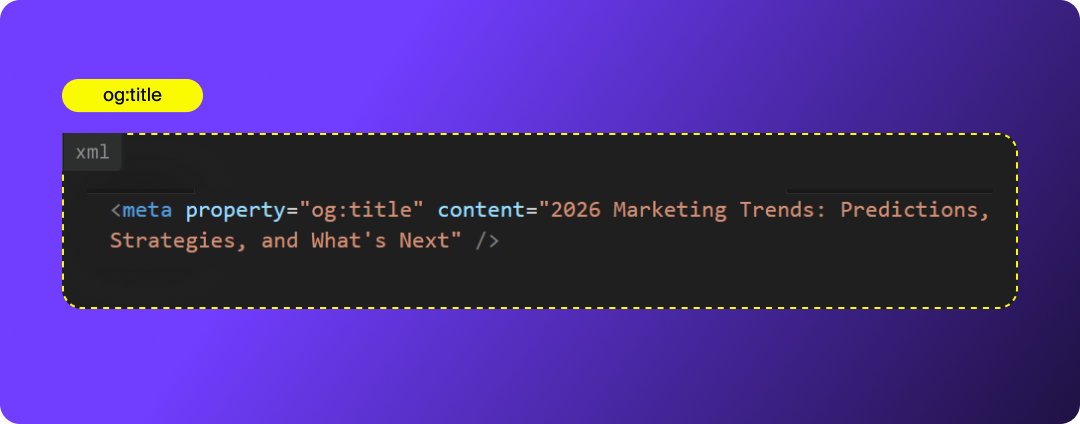
How to Optimize og:title:
- Keep It Concise (Ideally Under 60 Characters): Most social platforms truncate long headlines, so aim for ~60 characters to ensure your full title appears cleanly in the preview.
- Write for Humans, Not Robots: On social, your job is to stop the scroll. Make your OG title conversational, curiosity-driven, or benefit-focused while still accurately reflecting the content.
- Use Title Case for Readability: All caps can feel aggressive, and all lowercase can look unpolished. Title case (Capitalizing Key Words) improves clarity and helps your OG previews look more consistent across platforms.
- Avoid Clickbait or Mismatched Titles: Your OG title should closely align with the on-page content. Misleading titles may boost clicks temporarily, but will increase bounce rates and erode trust (both with users and with platform algorithms).
2. og:description
og:description provides the short summary that appears beneath your OG title in a social link preview. It works similarly to a meta description, but it’s written specifically for social audiences, meaning it should be clearer, more engaging, and tuned to what will make someone click in a social feed.
Use this space to highlight the key takeaway or value of the page, and tailor it to the platform where the link will be shared.
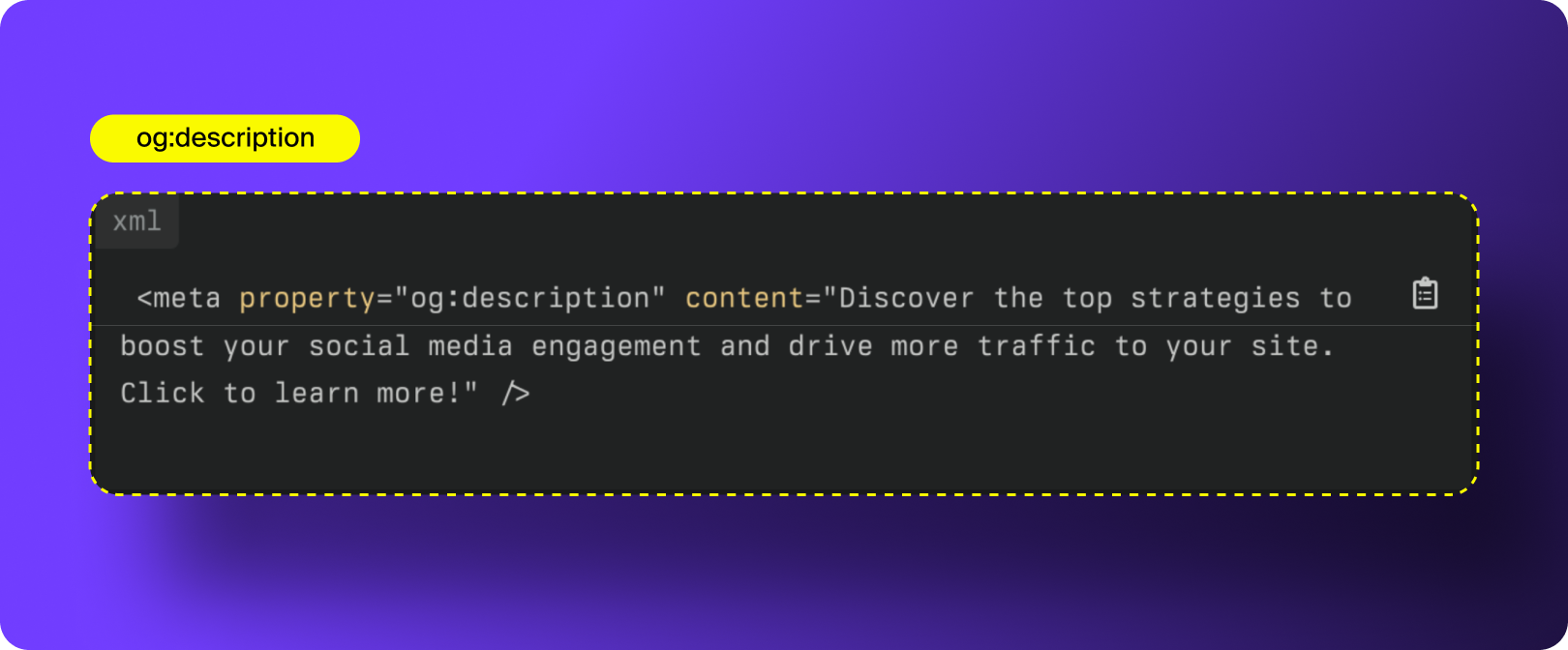
How to Optimize og:description:
- Match Your Social Tone: Your OG description only appears on social platforms, so it should align with the tone you use on LinkedIn, Facebook, X, etc. Keep it conversational, direct, and user-first, but always accurate to the content.
- Keep It Short (Ideal: 90–110 Characters): Most platforms cut off long descriptions, and shorter summaries tend to perform better. As a rule of thumb:
- Keep it under ~110 characters for LinkedIn and Facebook
- Keep it even shorter (~90 characters) for Slack, X, and Discord
- Concise = more readable = more clickable.
- Lead With the Value: Start with the takeaway: what the user will learn, gain, or understand by clicking. Avoid fluffy intros or generic statements.
- Use Natural, Semantically Relevant Keywords: While OG descriptions don’t directly influence “SEO rankings,” they do help with social discovery and with how platforms categorize content. Include 1-2 natural, important keywords that help describe the topic (NOT keyword stuffing). This also helps LLMs better understand your page when generating previews, summaries, or citations.
- Avoid Repeating the Title: Many sites repeat the headline in the OG description, which wastes valuable space. Your description should expand on, complement, or clarify your title.
3. og:image
og:image defines the preview image that appears when your link is shared, and it’s arguably the most important Open Graph tag. Social platforms are visual-first, and the image you choose does most of the heavy lifting when it comes to stopping the scroll, signaling brand identity, and driving clicks.
Your og:image tag tells platforms which image to use, how to display it, and what the image represents.
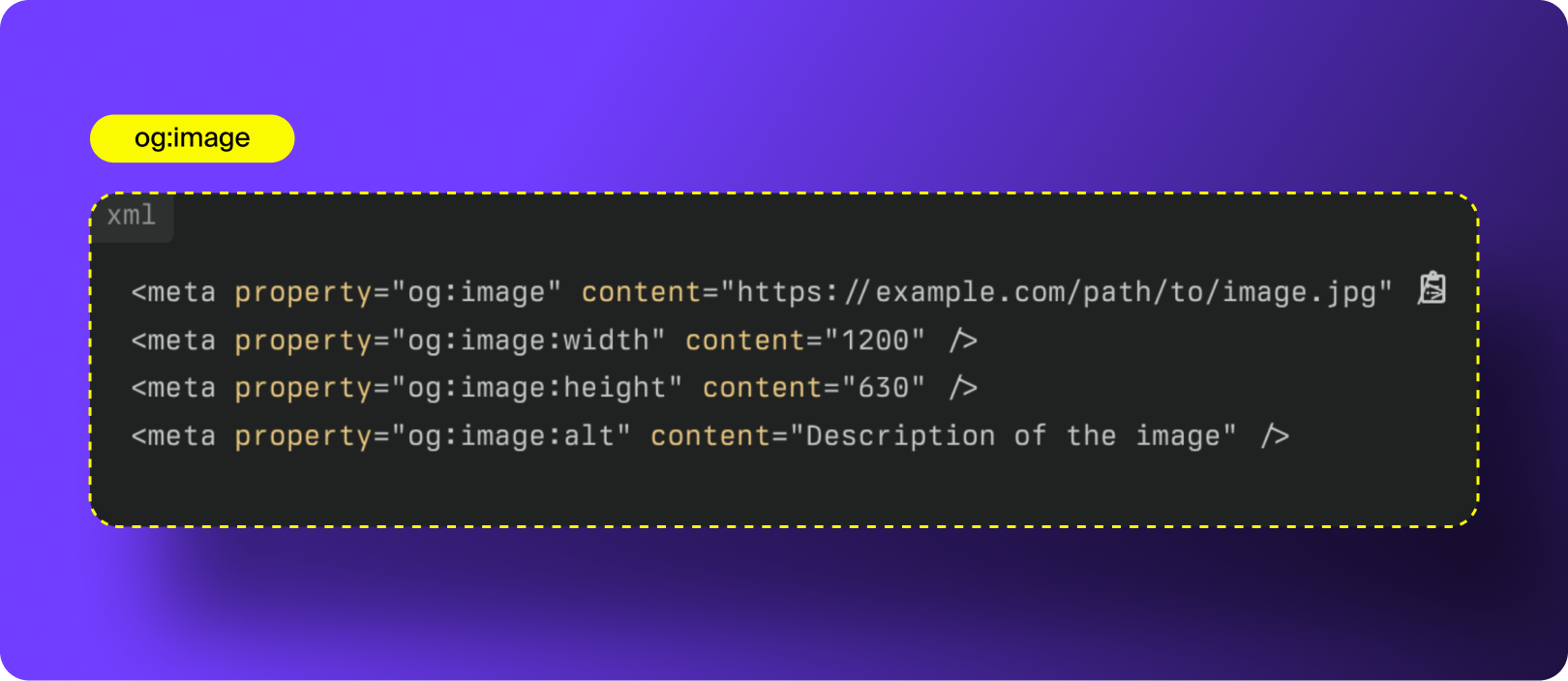
How to Optimize og:image:
- Use High-Quality, High-Resolution Images: Your OG image should be crisp on both desktop and mobile. Low-quality or pixelated previews instantly reduce credibility and engagement.
- Incorporate Branding (Logo, Colors, Typography): A branded OG image is a huge advantage for recognition and recall. Even if users don’t click, they start to associate your colors and design language with your content.
- Use the Correct Dimensions (1200 × 630 px): This is the ideal aspect ratio (1.91:1) for most platforms. Anything smaller risks cropping, stretching, or fuzzy rendering.
- Choose the Right Format (JPEG or PNG): These formats are universally supported, compress well, and maintain quality across platforms. Avoid WebP here, as many social scrapers still struggle with it.
- A/B Test Your Visuals: Experiment with different templates, photography vs. illustrations, text overlays, or color palettes. Track CTR and engagement to learn which styles resonate most with your audience.
- Set a Fallback Image: If your page doesn’t have a featured image (or something breaks during scraping), define a branded default og:image to ensure your preview never renders as a sad gray box.
Here are a few additional Image-related Open Graph tags to use:
- Og:image:width: Tells platforms the intended width so the image loads at the correct dimensions without resizing delays.
- og:image:height: Does the same for height. Supplying both width and height prevents platforms from guessing, improving load speed and rendering accuracy.
- og:image:alt: Provides descriptive alt text for the image. This improves accessibility and helps social platforms and AI models understand what your image represents. It’s also increasingly important for AEO since LLMs rely on alt text to interpret image context.
4. og:url
og:url defines the canonical URL associated with your Open Graph data. It acts as the permanent identifier for the content and helps social platforms understand which version of a page is the “official” one when multiple URLs point to the same content. Using og:url correctly also consolidates engagement signals and ensures analytics reflect activity across duplicate or parameterized links.
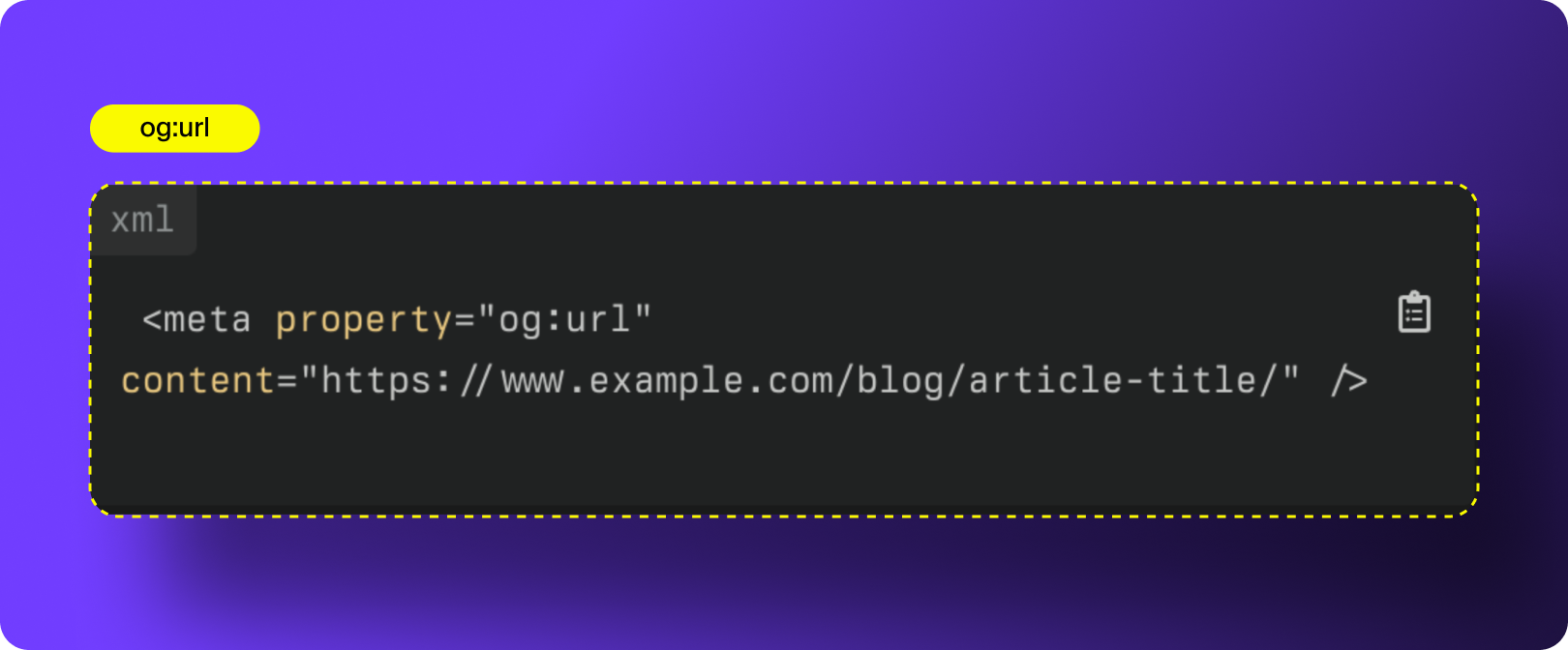
How to Optimize og:url:
- Use the Canonical URL: Always set og:url to the canonical version of the page, the one you want crawlers and users to land on. This prevents platforms from pulling previews from outdated or duplicate URLs and reduces unnecessary redirects.
- Maintain Consistent URL Structure: Use a uniform URL format across your site (e.g., no mixing trailing slashes, inconsistent parameters, or uppercase letters). Your og:url should match the structure used across your website to avoid fragmentation and ensure clean data in your social analytics.
Need help unifying your URL structure across all channels?
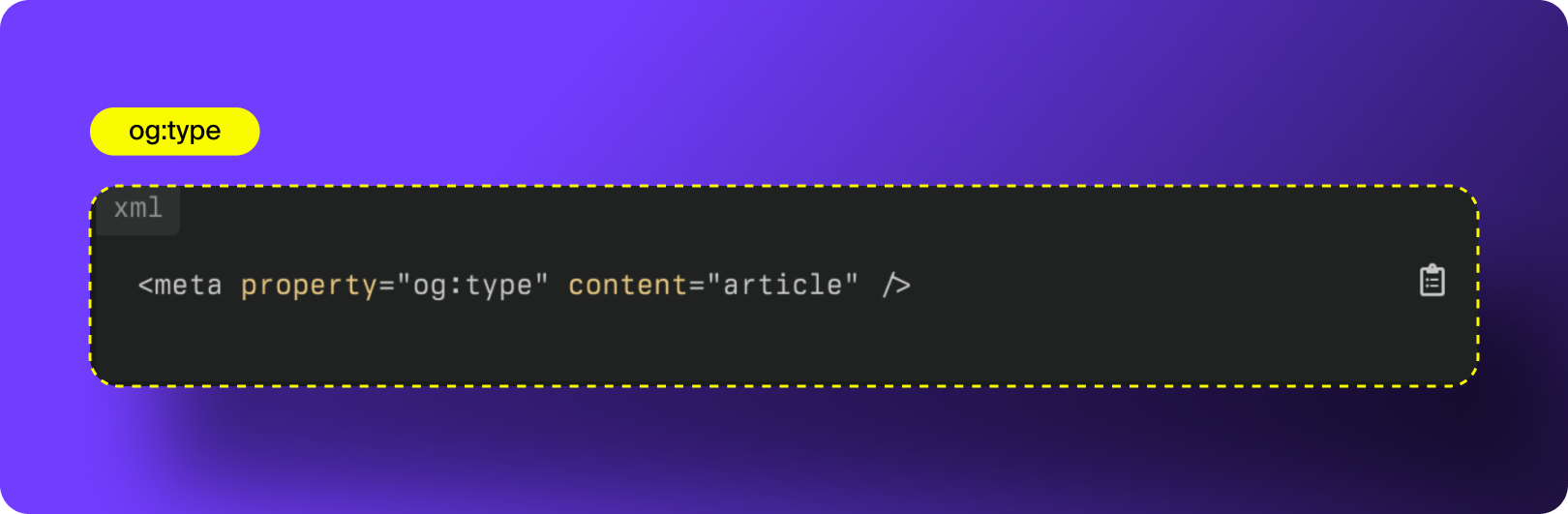
5. og:type
og:type defines what kind of content your page represents. This helps social platforms understand how to categorize your link and which additional metadata fields should apply. Different content types trigger different display behaviors across platforms.
Common og:type values for Open Graph SEO
- website: standard pages (homepages, landing pages, About pages, Contact pages)
- article: blog posts, news articles, editorial content
- product: individual product pages in eCommerce stores
- profile: user or author profile pages
- Video.movie/video.other: long-form videos, media, or motion graphics
How to Optimize og:type:
- Use One Type Per Page: Each page should have a single, clearly defined type. Choose the type that best represents the content to avoid confusion in how platforms display your link preview.
- Use “Website” as a Safe Default: If your content doesn’t fit a specific or specialized type, default to website. This ensures platforms can still process and display your OG data correctly.
- Ensure Accuracy and Consistency: Your selected type must match the page’s actual purpose. Using the wrong type (e.g., marking a blog post as a “product”) can cause incorrect indexing or display issues on social platforms.
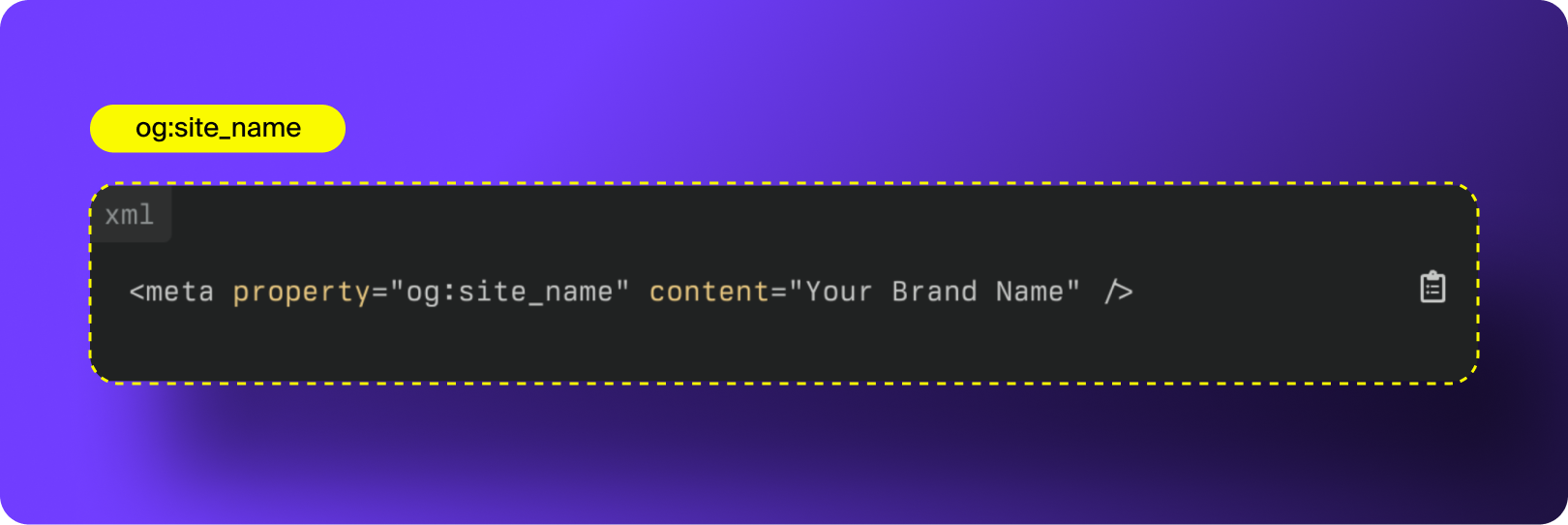
6. og:site_name
og:site_name identifies the name of the website or organization that owns the content. It appears in certain social previews and helps platforms understand the broader entity associated with the page.
How to Optimize og:site_name:
- Avoid Repeating Your Brand Name in og:title: If you’re using og:site_name, you don’t need to include your brand name again in the og:title. Duplicating it can make your preview look cluttered or repetitive.
- Use a Consistent, Official Name: Write your site name exactly as it appears in your branding, no unusual capitalization, emojis, or special characters. Consistency helps platforms correctly identify your entity and avoids mismatches across social previews.
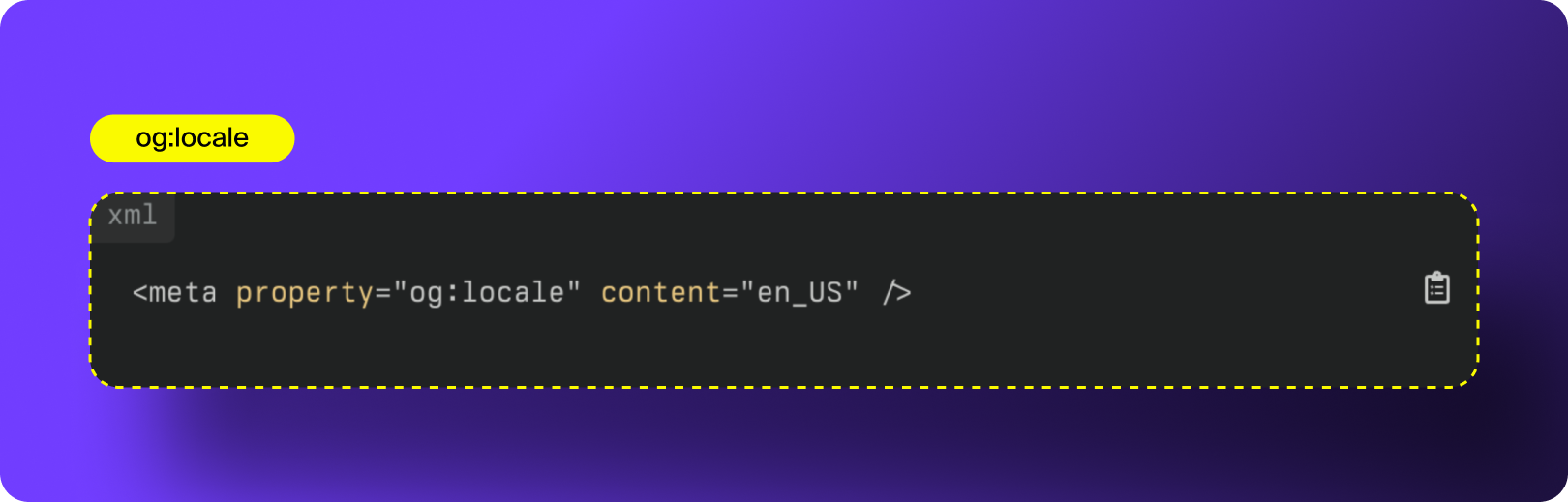
7. og:locale
The og:locale open graph tag specifies which language your content should be displayed in. If you have multiple language options for your content, you can use og:locale defines the language and regional formatting used for your page (for example: en_US for U.S. English or fr_FR for French). This helps social platforms display your content in the correct language and improves how your previews appear to international audiences.
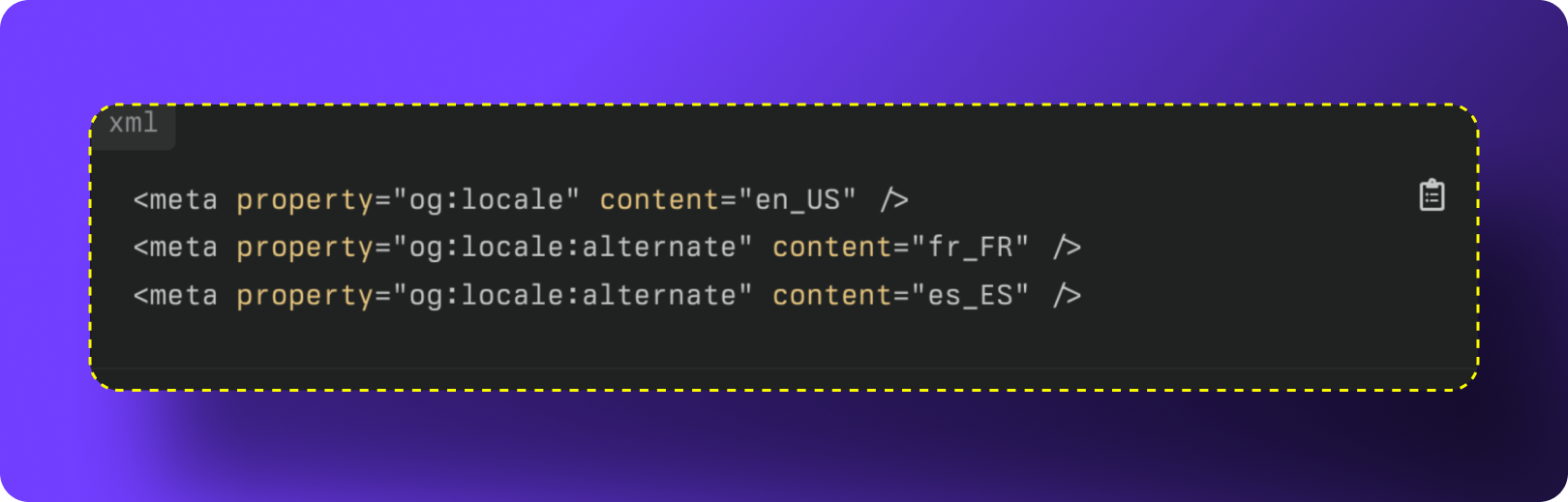
If your website supports multiple languages, you can use og:locale:alternate tags to indicate all additional versions.
Example of Alternate Tags
How to Optimize og:locale:
- Specify the Correct Primary Locale: Use the locale that matches the default language of the page. Examples:
- en_US: English (United States)
- en_GB: English (United Kingdom)
- es_ES: Spanish (Spain)
- Add Alternate Locale Tags for Multilingual Content: If your page is available in multiple languages, include an og:locale:alternate tag for each additional version. This helps platforms serve the right preview to the right audience and prevents mismatches in language display.
Additional Open Graph Tags to Consider
While the core Open Graph tags cover most use cases, adding a few advanced tags can improve how your content is categorized, displayed, and refreshed across different platforms. These tags aren’t required, but they can enhance visibility, accuracy, and consistency, especially for brands publishing content at scale.
og:image:type
Specifies the MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) type of your OG image (e.g., image/jpeg). This helps platforms render your image correctly, especially when using nonstandard file formats.
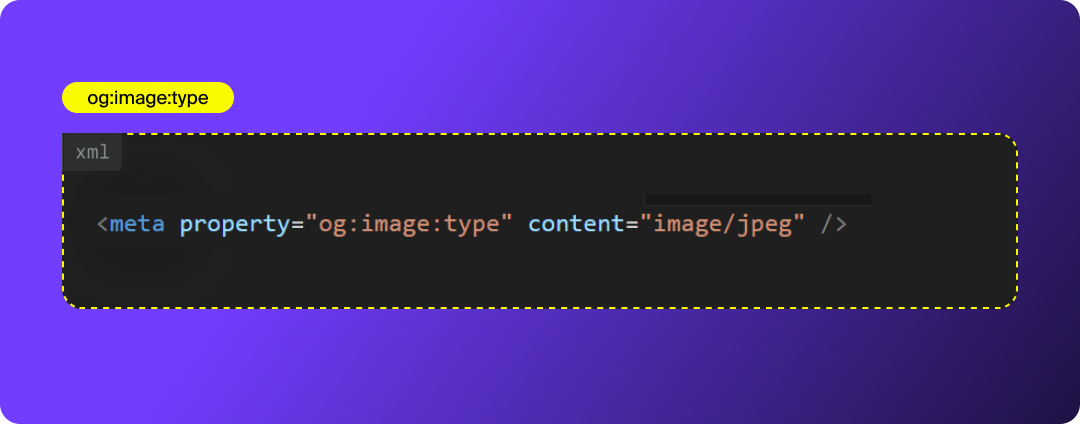
og:image:secure_url
Provides the HTTPS version of your OG image. Some platforms require secure URLs to display images, so including this tag ensures consistent cross-platform support.
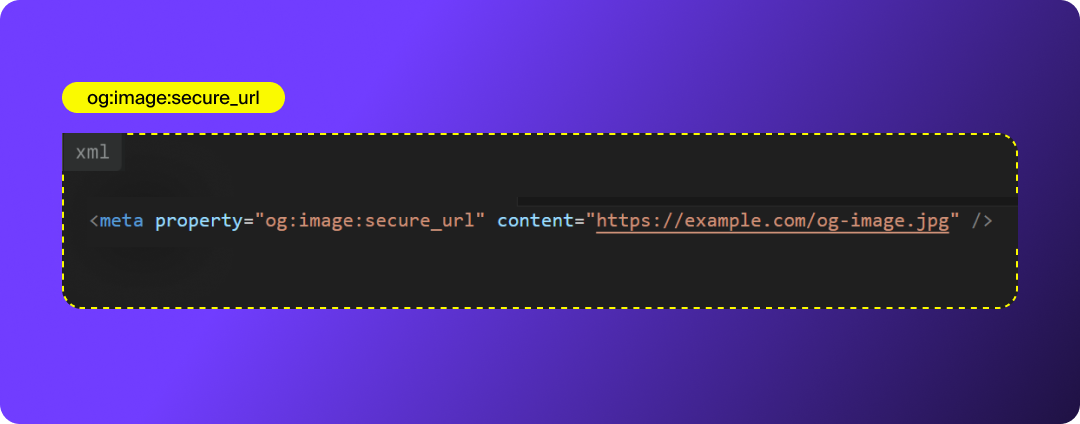
og:updated_time
Indicates the last time the page content was updated. This helps social platforms refresh old link previews and pull in your latest image, title, or description.
Why it matters: Freshness signals are increasingly important for both social crawlers and AI models.
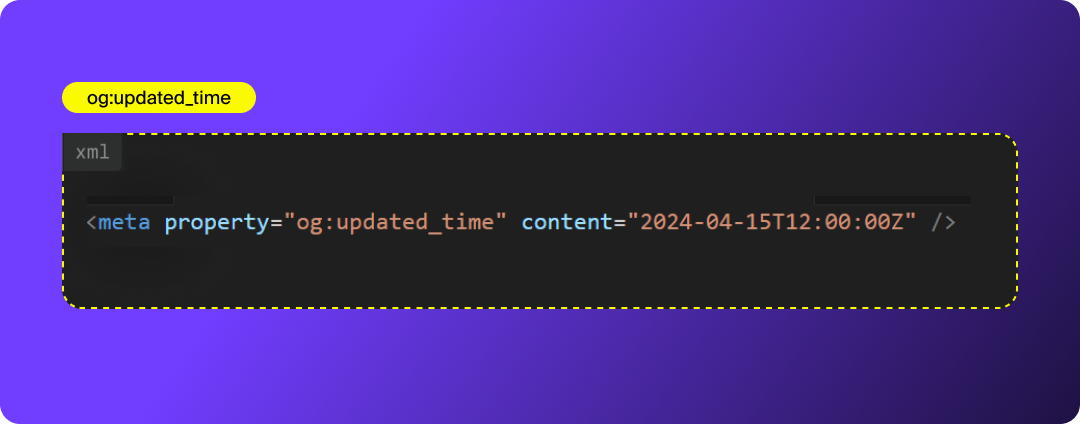
article:author (for blog posts)
Links the content to an author entity, which helps platforms associate expertise with your content and improves credibility.
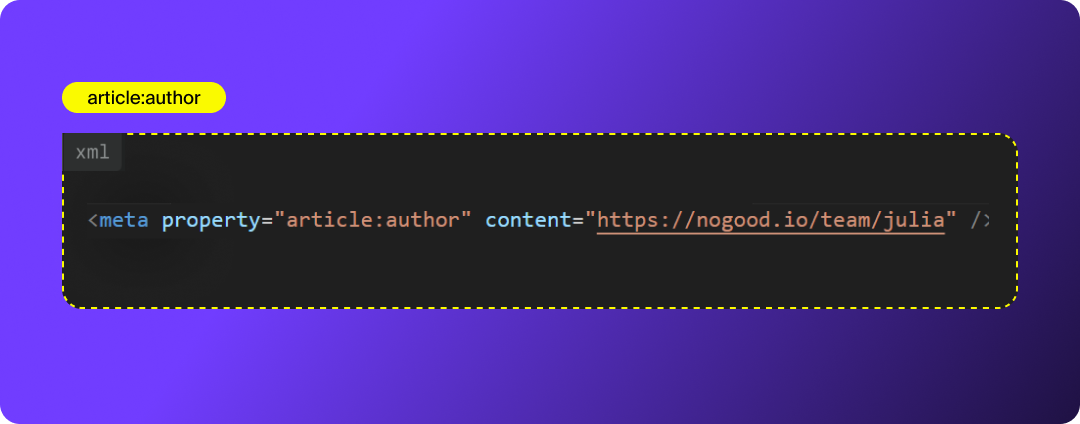
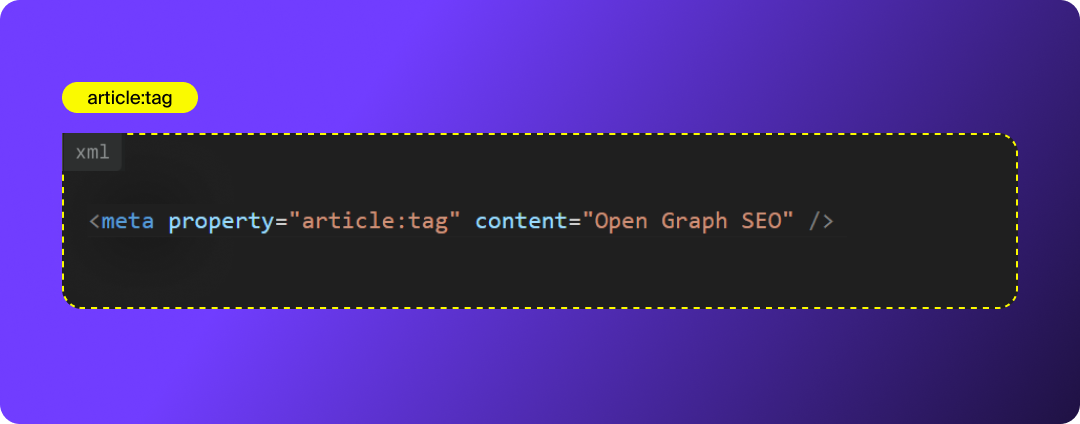
article:tag
Allows you to attach topic tags to your article. Platforms use these tags to categorize and match content to user interests.
AEO benefit: These tags help LLMs understand entity relationships and topics more accurately.
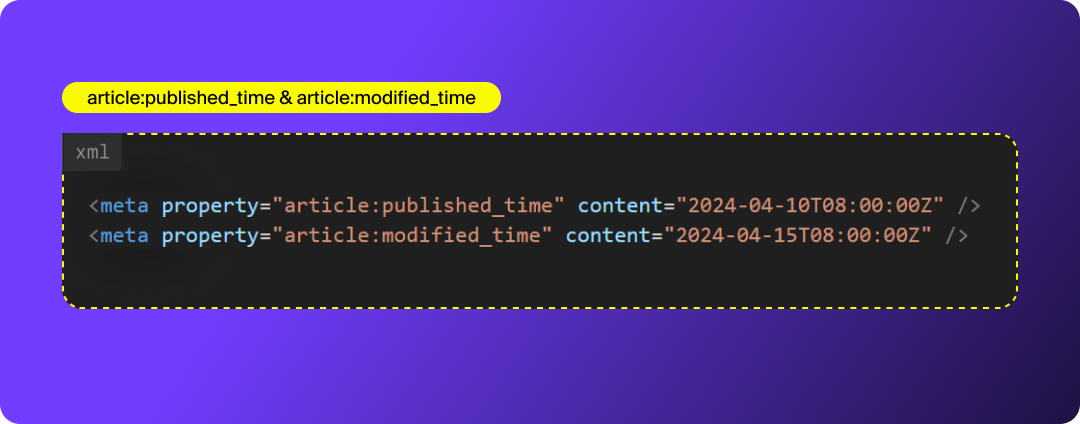
article:published_time & article:modified_time
These timestamps communicate when the article was originally published and last updated. They’re especially helpful for time-sensitive content and ensure social previews reflect the most current version.
Twitter Card Tags (twitter:card, twitter:image:alt)
Although X uses its own metadata format, it falls back on OG tags if Twitter Card tags aren’t provided. It’s best practice to include both for full coverage.
- twitter:card defines the layout (use summary_large_image for blog posts).
- twitter:image:alt adds accessibility and improves context for AI systems.

Why These Additional Tags Matter
Adding these supplemental tags helps:
- Improve consistency across social platforms
- Ensure correct image rendering
- Strengthen metadata clarity for LLMs (AEO)
- Improve accuracy for multilingual or global audiences
- Help platforms refresh previews with updated content
- Reinforce entity relationships (author, topic, etc.)
They’re small additions with outsized impact, especially for brands that rely heavily on content distribution, social amplification, or AI visibility.
How to Implement Open Graph Tags
Now that you know the core Open Graph tags and how each one works, the next step is implementation. You can add OG tags manually, through your CMS, or with an SEO plugin, but regardless of method, the goal is the same: place clean, structured metadata in your site’s <head> so every platform can read it correctly.
Implementing Open Graph Tags Manually
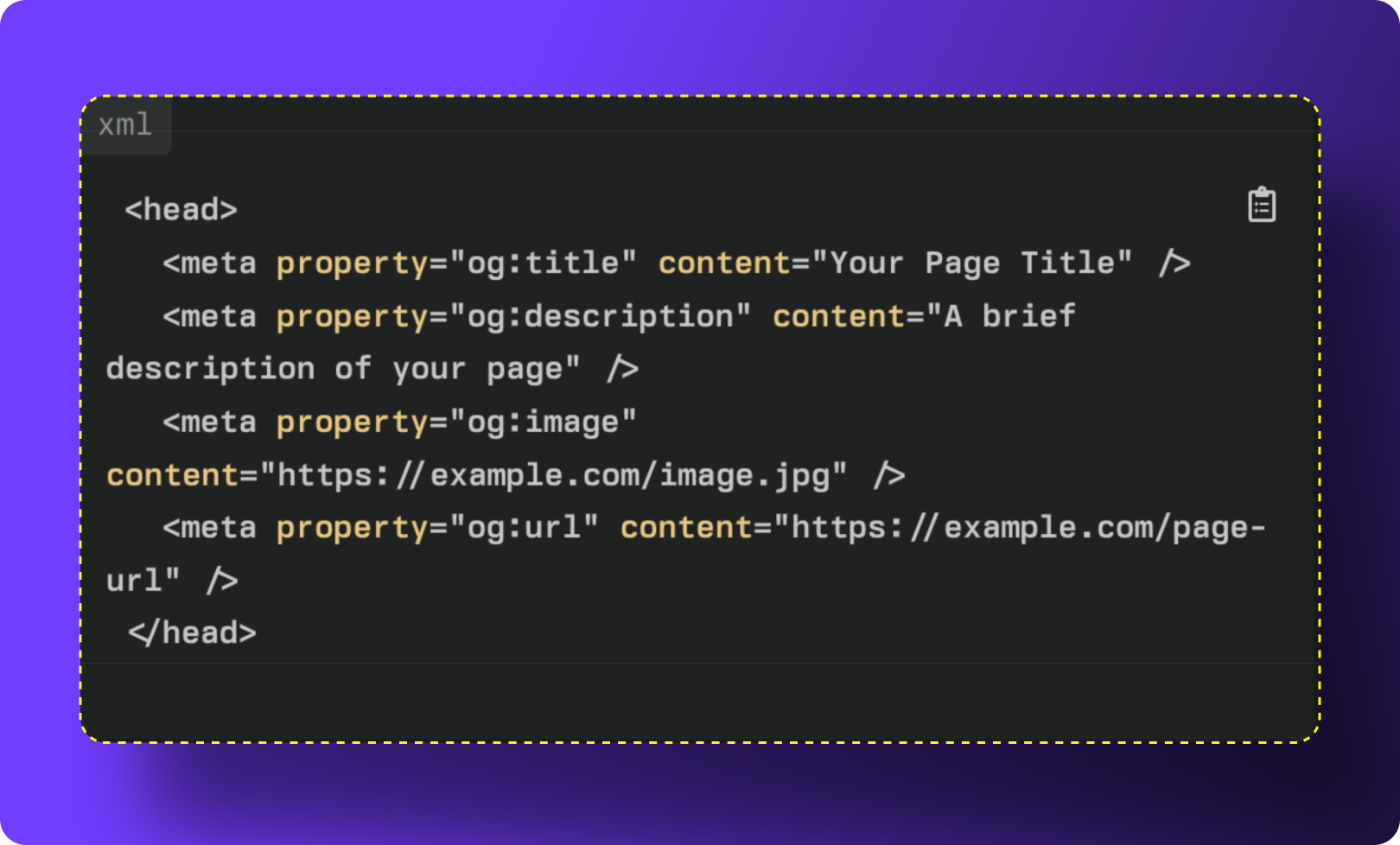
If you prefer full control, you can add Open Graph tags directly to your site’s HTML. All OG tags should be placed inside the <head> section of your webpage so social crawlers can detect them immediately.
Pro Tip: If you’re using WordPress, always add custom code inside a child theme or a custom code snippet plugin. This prevents your OG tags from being overwritten when your theme updates.
Example Code:
Implementing Open Graph Tags on WordPress
You can add Open Graph tags to WordPress manually by placing them in the <head> via a child theme, but in most cases, it’s safer and faster to use a dedicated SEO plugin. Plugins handle the markup for you, prevent syntax errors, and automatically generate OG tags for every post and page.
If you still want to implement OG tags manually, add them using:
- A child theme (never the parent theme), or
- A code snippet plugin like WPCode or Code Snippets (the safer modern method)
Avoid editing functions.php directly in the parent theme — it’s risky and gets overwritten during updates.
Recommended SEO Plugins for Open Graph Implementation:
- Yoast SEO:
- Path: Yoast > Settings > Site Representation > Social Profiles
- Then: Yoast > Settings > Content Types > Social Appearance
- Make sure “Open Graph” is enabled.
- Yoast automatically adds OG tags for titles, descriptions, and images, and lets you customize them per page.
- All-in-one-SEO:
- Path: AIOSEO > Social Networks
- AIOSEO gives you full control over your OG images, titles, descriptions, and default settings for each content type.
- Rank Math:
- Path: Rank Math > Titles & Meta > Global Meta
- Rank Math includes built-in OG controls and dynamic templates so you can set consistent defaults for blog posts, pages, and custom post types.
Using any of these plugins ensures your OG tags are properly implemented without manually touching HTML or PHP. They also provide preview tools so you can see exactly how your link will appear on platforms like Facebook, LinkedIn, and X before you publish.
Implementing Open Graph Tags on Shopify
Most modern Shopify themes include built-in Open Graph tags by default. To confirm whether your theme already supports OG, check the social-meta-tags.liquid snippet inside your theme files; this is where Shopify typically defines the logic for OG titles, descriptions, and images.
When OG tags are included in the theme, Shopify will automatically pull your preview image, page title, and description from your on-page metadata and featured image. This ensures link previews look consistent across social platforms without requiring manual code changes.
Customizing Open Graph Tags in Shopify (Step-by-Step)
If you want more control over how your content appears when shared, you can customize these OG tags by editing your Liquid template files.
- Go to: Online Store > Themes > … > Edit Code
- Open the Snippets folder.
- Locate and open social-meta-tags.liquid.
- Modify the existing logic or replace default tags with your own custom OG code.
Always duplicate your theme or create a backup before editing Liquid files. Shopify does not autosave previous versions of custom snippets.
How to Validate Open Graph Tags On Social Platforms
Once your Open Graph tags are implemented, you should always validate them to ensure your link previews render correctly across platforms. Social networks often cache old OG data, so using their debugging tools helps you preview your metadata, identify issues, and force a cache refresh if needed.
Below are the main tools for testing and troubleshooting OG tags on each platform:
LinkedIn ↔ Sharing Debugger
- Enter your URL.
- Click Inspect.
- LinkedIn will fetch your OG tags, show the preview, and highlight any missing or invalid metadata.
- It will also refresh the cached version of your link.
Facebook ↔ Meta for Developers
- Paste your URL into the debugger.
- Click Debug.
- Review the preview and OG data for errors or warnings.
- Click Scrape Again to refresh Facebook’s cache and pull in your updated OG tags.
X (Formerly Twitter) ↔ Card Validator
- Paste your URL.
- Click Preview Card.
- Ensure the image, title, description, and card type render correctly.
- Fix any flagged issues in your OG or Twitter Card metadata.
How to Audit Your Open Graph
Once your Open Graph tags are implemented, the next step is to run a site-wide audit to ensure there are no missing tags, duplicates, broken images, or conflicting metadata. A proper audit helps you validate that OG tags are consistent across all templates and content types, not just the pages you manually checked.
You can use tools like Ahrefs, Sitebulb, Screaming Frog, or Semrush to crawl your site and surface Open Graph issues.
- Set up or run a Site Audit on your domain.
- After the crawl completes, navigate to the “Social Tags” section.
- Review the breakdown of OG-related issues such as:
- Missing og:title, og:description, or og:image
- Incorrect or missing image dimensions
- Multiple conflicting OG tags on the same page
- Non-secure (HTTP) image URLs
- Missing fallback OG images
- Click into each issue to see the URLs affected and the exact tag(s) you need to fix.
Ahrefs makes it easy to identify patterns across templates; for example, if all your blog posts are missing og:image:alt, or if your product pages are using the same default image.
Other Tools to Consider
Screaming Frog
- Crawl your site
- Go to Custom Extraction or Social tab
- Export OG data and diagnose inconsistencies at scale
Sitebulb
- Offers detailed OG reports and flags missing tags, incorrect MIME types, and caching issues
Semrush Site Audit
- Surfaces high-level OG issues under the “Markup” and “Social Tags” categories
Why This Matters
A clean Open Graph implementation ensures your content renders correctly every time it’s shared, and keeps your previews consistent across platforms. Regular audits help you catch template issues early, prevent broken previews, and maintain a professional, click-worthy presence across the social graph.
Measuring the Impact of Your Open Graph Optimization Efforts
Like any marketing initiative, you’ll want to understand whether your Open Graph SEO work is actually making a difference. While OG performance isn’t always straightforward to measure (since OG tags primarily impact pre-click behavior), there are several reliable indicators you can use to track effectiveness and optimize over time.
1. Click-Through Rate (CTR)
CTR is one of the strongest signals that your Open Graph previews are performing well. A noticeable increase in CTR from social platforms typically means your OG image, title, and description are compelling enough to stop users mid-scroll.
If CTR is low, run controlled A/B tests on:
- OG image styles
- Headlines and title tone
- Description length and clarity
- Branding elements (colors, overlays, typography)
Testing will help surface the formats that resonate most with your audience.
2. Engagement Metrics (Likes, Comments, Shares, Saves)
High engagement on posts containing your links often indicates that your preview is visually appealing, informative, or relevant enough for users to interact with.
Engagement matters because:
- More interaction = more algorithmic reach
- Shares and saves signal strong content value
- Comments and clicks together reflect deeper user intent
While OG tags don’t directly influence engagement after the click, they significantly impact the decision to click, and that’s where they provide the most leverage.
3. Bounce Rate & Time on Page
If OG previews accurately reflect your content, users who click should stick around. A high bounce rate might mean your OG title or image oversells or misrepresents the content.
4. Social Referral Traffic
In GA4, review Traffic Acquisition → Session Source/Medium to track whether traffic from social channels grows over time.
5. Image Load Errors or Scraper Warnings
Platforms like Facebook’s Debugger and LinkedIn Post Inspector flag:
- Broken image URLs
- Incorrect file formats
- Wrong dimensions
- Missing metadata
Fixing these issues improves consistency and CTR.
6. Direct Feedback from Debrief Tools (Validators)
If you’re using Debuggers or Inspectors regularly, monitor whether your OG tags are being cached, pulled correctly, or blocked by robots.txt directives.
Want to learn more about how to measure success on social media?
Maximizing Engagement Through Open Graph SEO
Open Graph SEO gives you something increasingly rare in today’s crowded digital landscape: control. By defining exactly how your content appears across social platforms, you’re no longer at the mercy of auto-generated previews or mismatched images. Instead, you get to decide how your brand shows up: visually, contextually, and strategically.
Strong OG implementation doesn’t just make your posts look better. It increases clarity, builds credibility, reinforces brand identity, and, most importantly, drives higher CTR through scroll-stopping visuals and clear, value-driven copy. When done well, OG tags turn every link share into a mini-landing page designed for engagement.
Of course, getting your OG setup right requires a bit of technical finesse, and small mistakes can lead to broken previews or inconsistent branding. If you want support implementing or auditing your Open Graph strategy, our team is here to help you get it right the first time.