In today’s digital landscape, the success of your online presence hinges on more than just compelling content. Technical SEO, the foundational pillar of search engine optimization, plays a pivotal role in ensuring your website is discoverable and user-friendly. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of technical SEO, empowering you with the knowledge and tools to navigate issues such as website performance, indexation, and user experience.
Whether you’re a seasoned SEO expert or just starting, this guide will unlock the secrets to boost your website’s visibility, drive organic traffic, and deliver a seamless user experience.
Here’s what we’ll explore in our guide
Definition and importance of a technical SEO audit
Why perform a technical SEO audit
Prepping for the audit
Step 1: Website crawl and indexation
Step 2: Finding indexation and crawlability issues
Step 3: Site speed and performance analysis
Step 4: Mobile optimization
Step 5: Technical on-page SEO
Step 6: Analyzing and fixing internal links
Step 7: Addressing and identifying image issues
Step 8: Website architecture and navigation
Step 9: Finding and fixing HTTPS issues
Step 10: Fixing code issues
Step 11: Finding and fixing status codes with issues
Step 12: Reporting and monitoring
So, how long does a technical SEO audit take?
Definition and importance of a technical SEO audit
A technical SEO audit is critical for optimizing your website’s performance, ensuring it’s both search engine and user-friendly. This procedure involves a systematic examination of your website’s underlying infrastructure, identifying and resolving issues that impact its:
1. Search engine ranking: Technical SEO audits ensure your website complies with search engine guidelines, improving its chances of ranking higher in search results.
2. User experience: By identifying and fixing technical issues, you enhance the overall experience of visitors to your website, reducing bounce rates and improving user satisfaction.
3. Accessibility: Audits address issues that might hinder access to your site for people with disabilities, improving accessibility for a broader audience.
4. Site security: Ensuring your website is secure is paramount, as it protects user data and positively influences search engine rankings.
Why perform a technical SEO audit
A technical SEO audit is not just a routine task; it’s a fundamental step toward the success of your online presence. Here’s why you should prioritize it:
The role of technical SEO in search engine marketing
- Search engine rankings: Technical SEO optimizations help search engines understand your website better, leading to improved rankings. This includes factors like XML sitemaps, meta tags, and proper indexing, which guide search engines through your site.
- Crawlability: Search engine bots need to navigate your site efficiently. A technical audit ensures no roadblocks (e.g., broken links or duplicate content) can hinder this process.
- Indexation: Ensuring that search engines index all relevant pages and content on your website is critical to technical SEO. Proper indexation means better visibility in search results.
The impact on user experience and website performance
- Loading speed: Users expect fast-loading pages. Technical SEO addresses issues that may slow down your website, making it more responsive and user-friendly.
- Mobile optimization: With the shift towards mobile-first indexing, ensuring that your website is mobile-friendly is crucial. A technical SEO audit ensures that your site performs well on various devices.
- User satisfaction: Providing a seamless and error-free browsing experience keeps users engaged and reduces bounce rates, contributing to higher rankings.
Real-world examples: The consequences of neglecting technical SEO
Warner Bros.’ SEO lesson

Even industry giants like Warner Bros. can’t ignore the impact of SEO. They learned this the hard way when a movie starring Harley Quinn suffered losses of over $16 million due to a critical SEO oversight.
What happened?
Warner Bros. initially titled the movie “Birds of Prey: The Fantabulous Emancipation of One Harley Quinn.” The problem? Harley Quinn’s name wasn’t upfront, causing confusion in search results. Users looking for ‘Birds of Prey’ ended up elsewhere, akin to releasing a Harry Potter movie titled “The Philosopher’s Stone: The First Year of Hogwarts School for Harry Potter.” It just didn’t make sense.
Realizing their mistake, Warner Bros. rebranded the movie as “Harley Quinn: Birds of Prey.” However, the damage was done. Without Harley Quinn in the spotlight, the movie struggled to rank well in searches, leading to lower box office earnings than expected.
Why did this happen?
This disaster happened because Warner Bros. overlooked crucial SEO steps. They didn’t conduct thorough keyword research or assess their competition. They didn’t check what already ranked for their keywords, leading to a costly mistake.
The lesson
The lesson is clear: SEO matters, even in the film industry. Balancing creativity with optimization is vital. Just like other businesses launching products or services, involving SEO experts is essential to avoid costly blunders.
LinkedIn’s SEO misstep
LinkedIn faced an SEO mystery in May 2020. A large portion of their content disappeared from Google Search, leaving users puzzled.
Why did this happen?
Google’s John Mueller hinted that LinkedIn caused this issue. They tried to switch from HTTP to HTTPS using Google’s tool, which removed all variants, including HTTPS, WWW, and non-WWW versions.
The lesson
The takeaway here is that using Google’s removal tool for domain redirects isn’t the smartest move. It’s useful for blocking outdated content, but it can have unintended consequences. For a smooth transition to HTTPS, 301 redirects are a better choice. They ensure search engines recognize the new version as the permanent one, safeguarding rankings and traffic.
LinkedIn’s incident underscores the importance of careful SEO management and the potential repercussions of misusing tools. Properly handled, businesses can transition seamlessly while protecting their search visibility and user engagement.
Prepping for the audit
Set clear goals and objectives
Preparing for a technical SEO audit is a crucial foundation for success. Before diving into the nitty-gritty details, setting clear goals and objectives is essential. Here’s why:
- Define your purpose: Start by clearly defining why you’re conducting a technical SEO audit. Is it to improve your search engine rankings, enhance user experience, or identify and fix specific issues? Having a precise purpose will guide your audit.
- Establish measurable goals: Determine what success looks like. Are you aiming for higher search rankings, reduced bounce rates, or faster page loading times? Setting measurable goals helps you track your progress.
- Prioritize areas of improvement: Identify the most critical aspects of your website that need attention. This could include issues like page speed, mobile optimization, or security. Prioritizing areas for improvement ensures you allocate resources effectively.
- Align with business objectives: Your technical SEO goals should align with broader business objectives. For instance, if you’re an e-commerce site, improving product page visibility may be a primary goal. Ensure your SEO audit supports your overall business strategy.
- Timeframes and milestones: Set realistic timeframes and milestones for achieving your objectives. This helps keep your audit on track and ensures timely improvements.
When should you perform a technical SEO audit?
Performing a technical SEO audit is not a one-time affair; it’s an ongoing process that plays a pivotal role in maintaining and improving your website’s performance. Here’s when you should consider conducting one:
Initial audit for new sites
- Newly built websites: An initial technical SEO audit is essential whenever you create a new website, whether for your own use or a client’s. It ensures the website starts on the right SEO foot, addressing any early issues.
Regular audits as part of ongoing maintenance
- Quarterly basis: It’s a wise practice to conduct technical SEO audits regularly, ideally every quarter. This consistent approach helps you avoid potential problems, adapt to search engine algorithm changes, and ensure your website’s overall health.
- Continuous content publishing: Regular audits become even more critical if your website frequently publishes new content. Consistent content updates can introduce technical issues that need prompt attention.
When rankings are stagnant or declining
- Stagnant rankings: If you notice that your search engine rankings are not improving or remaining stagnant, it’s a clear signal to perform an SEO audit. It can help identify issues that may be hindering your site’s performance and provide insights into necessary optimizations.
- Declining rankings: A sudden decline in rankings is a red flag. Conducting an SEO audit in such cases is crucial to uncover and address the root causes of the decline, preventing further drops in visibility.
Tools and resources for conducting the audit
A successful technical SEO audit requires the right tools and resources to analyze your website effectively. Here’s a breakdown of the tools needed for each of the three parts of the audit:
1. Technical audit
- Crawl errors and indexing: Google Search Console is an essential tool for identifying crawl errors and monitoring indexing issues. It provides insights into how Googlebot interacts with your site.
- Hosting analysis: Assessing hosting-related issues can be done through web hosting monitoring tools or website performance testing tools like GTmetrix and Pingdom.
- Comprehensive site analysis: To perform an in-depth analysis of your website’s technical aspects, tools like SEMrush’s Site Audit and Ahrefs Site Audit can identify issues such as broken links, duplicate content, and other technical errors.
2. Content audit
- Keyword research: Keyword research tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, and Ahrefs help you identify relevant keywords to target in your content.
- Competitor analysis: SEMrush and Ahrefs provide valuable insights into your competitors’ content strategies, helping you identify gaps and opportunities.
- Content maps: Creating content maps can be streamlined using content planning and management tools like Frase, which use AI to generate content briefs and maps.
- Meta data optimization: SEO plugins like Yoast or All in One SEO for WordPress can help you optimize metadata.
3. Links Audit
- Backlink profile analysis: Tools like Ahrefs and SEMrush are excellent for analyzing your backlink profile, helping you identify the quality and quantity of backlinks pointing to your site.
- Backlink growth tactics: To strategize for backlink growth, tools like Ahrefs and SEMrush offer insights into link-building opportunities, competitor backlink analysis, and outreach tactics.
* Note: We’ll be using these tools as examples in our steps to conduct a technical SEO audit.
What you need from clients to perform a technical SEO audit
Conducting a technical SEO audit effectively requires collaboration and access to critical data from your clients. Here’s what you need from them to ensure a comprehensive audit:
Google Analytics (GA) access
- Traffic and engagement data: Access to Google Analytics is invaluable as it provides insight into your website’s traffic sources, user engagement, bounce rates, and more. This data is crucial for producing client reports, especially for those involved in referral campaigns or looking to track specific page performance.
- CTA click tracking: In GA4, you can track click rates on specific Call-to-Action (CTA) elements, helping measure the effectiveness of CTAs placed on different pages. This information aids in optimizing user interactions.
Google Search Console (GSC) access
- Impressions and clicks: GSC, or Google Search Console, is indispensable for understanding impressions and clicks on a per-query and per-page basis. With GSC access, a variety of tools can be leveraged to steer content marketing projects effectively.
- Frase content analytics: This tool relies on GSC access to function optimally. It identifies content upgrade and refresh opportunities, uncovers keyword prospects, and pinpoints potential topic clusters based on real click and impressions data.
- Supermetrics integration: GSC data plays a vital role in client reports. It facilitates insights into ‘keyword movement’ without the need for Ahrefs. This means you can track how your client’s blog is performing concerning specific keywords, whether they are on an upward or downward trend, and present this data to them regularly using Google Data Studio.
By obtaining GA and GSC access from your clients, you empower your SEO audit with essential data to gauge website performance and formulate data-driven strategies for improvement. This access ensures a more accurate and comprehensive assessment of the website’s technical and content aspects.
Step 1: Website crawl and indexation
What is a website crawl?
A website crawl, often performed by search engine bots or web crawlers, systematically scans and analyzes a website’s content and structure. It involves following links from one web page to another, collecting data about each page, and indexing the information for search engines to retrieve and display in search results. The crawl helps search engines understand web pages’ content, structure, and relevance, which is essential for ranking them in search results.
Importance of proper indexing
Proper indexing is crucial because it ensures that web pages are accurately and efficiently included in a search engine’s database. It enables search engines to understand the content and context of web pages, making them more discoverable to users searching for relevant information. Proper indexing helps improve a website’s visibility in search results, vital for attracting organic traffic and ensuring that the right pages appear when users search for specific queries. Accurate indexing enhances the overall user experience and is fundamental to effective SEO.
Crawling your website
To initiate a website crawl and gain valuable insights into your site’s health and performance, you can use tools like Ahrefs’ Site Audit, accessible for free as part of Ahrefs Webmaster Tools.
Running an audit with Ahrefs’ site audit
1. Set up a project: The first step is to set up a project in Ahrefs’ Site Audit. Ensure your website is connected to your Ahrefs account as a project. Verification can be done via Google Search Console or by adding a DNS record or HTML file.
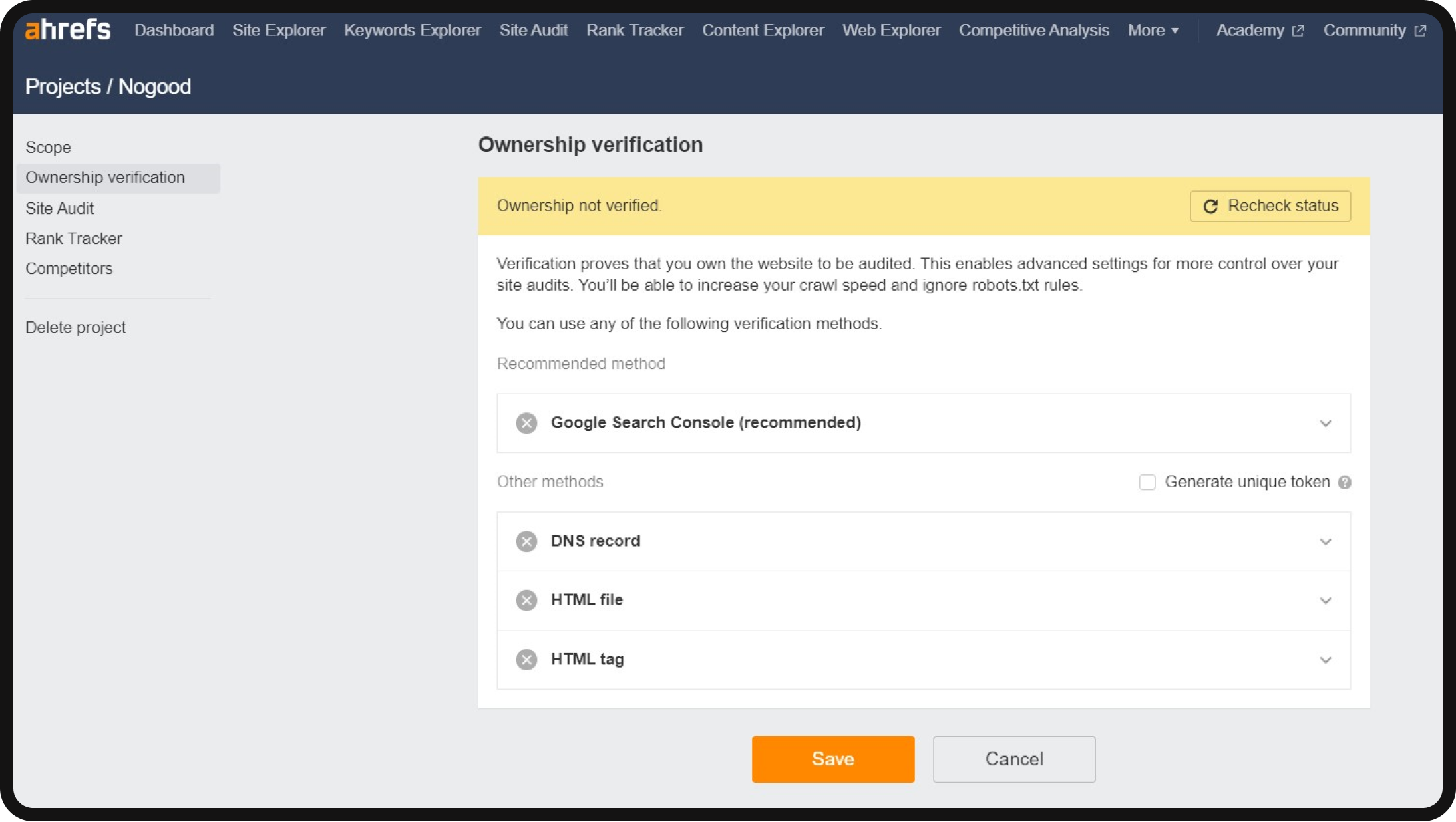
2. Check site audit settings: Before running your initial crawl, review the Site Audit settings. For larger websites, it’s advisable to increase the crawl speed.
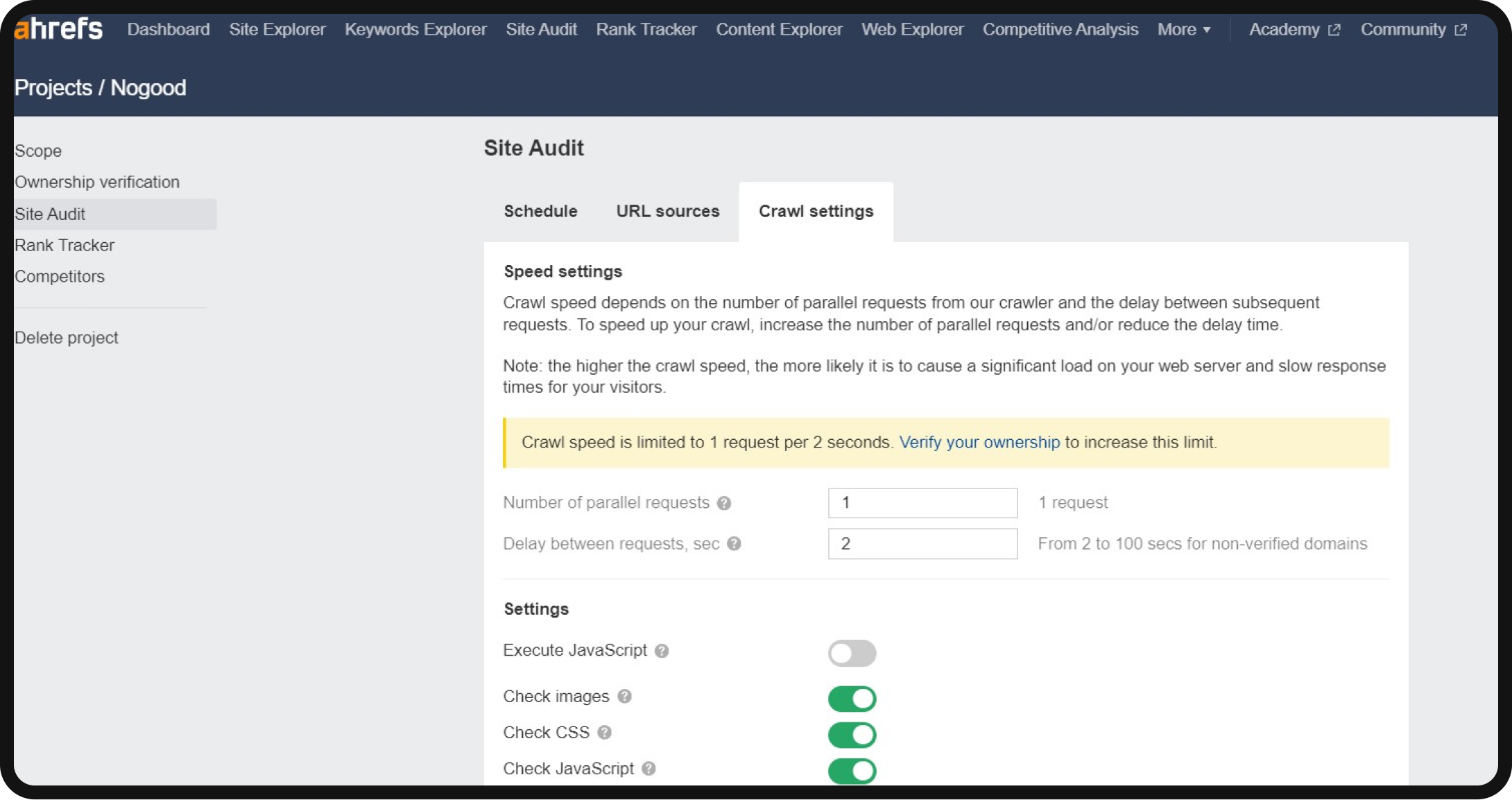
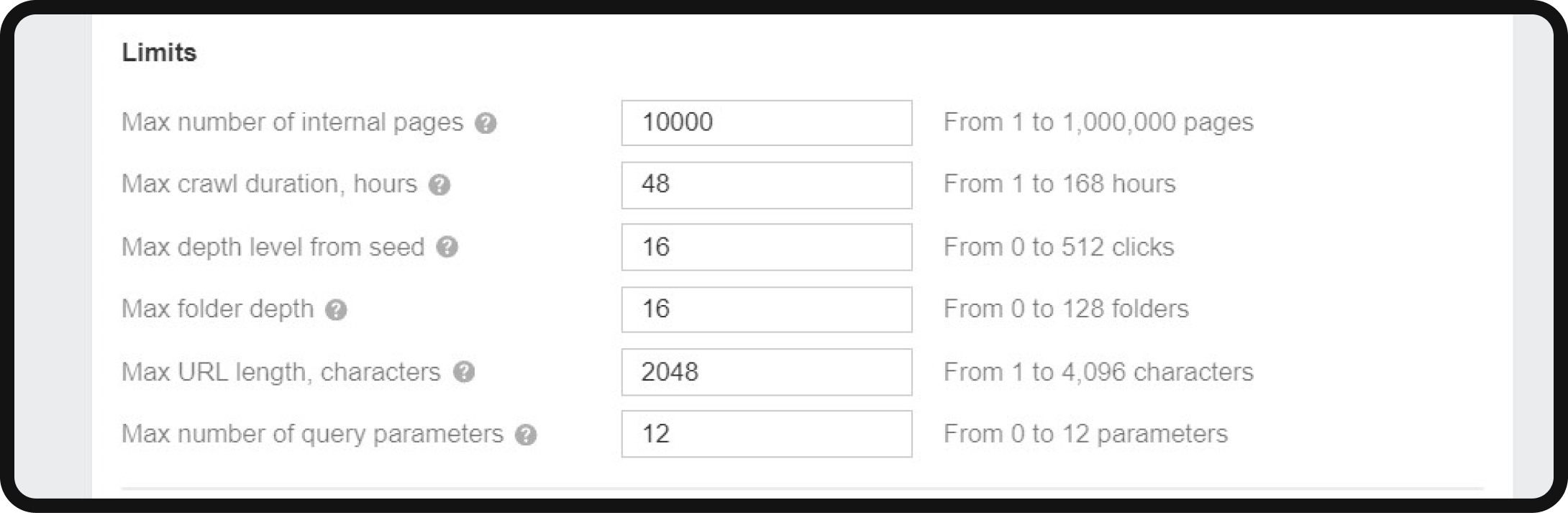
While the standard settings may work for small personal sites, you can modify parameters like the maximum number of pages to crawl under “Limits.”
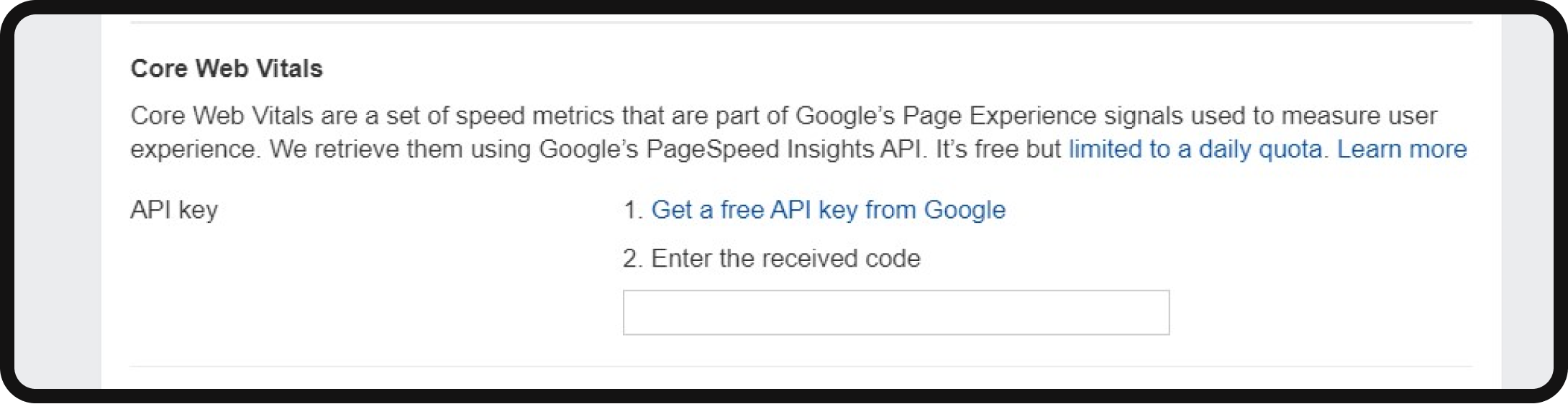
Add your Google API key to the settings if you’re interested in Core Web Vitals (CWV) insights.
3. Run the crawl: Once satisfied with the settings, initiate a new crawl under the “Site Audit” tab.
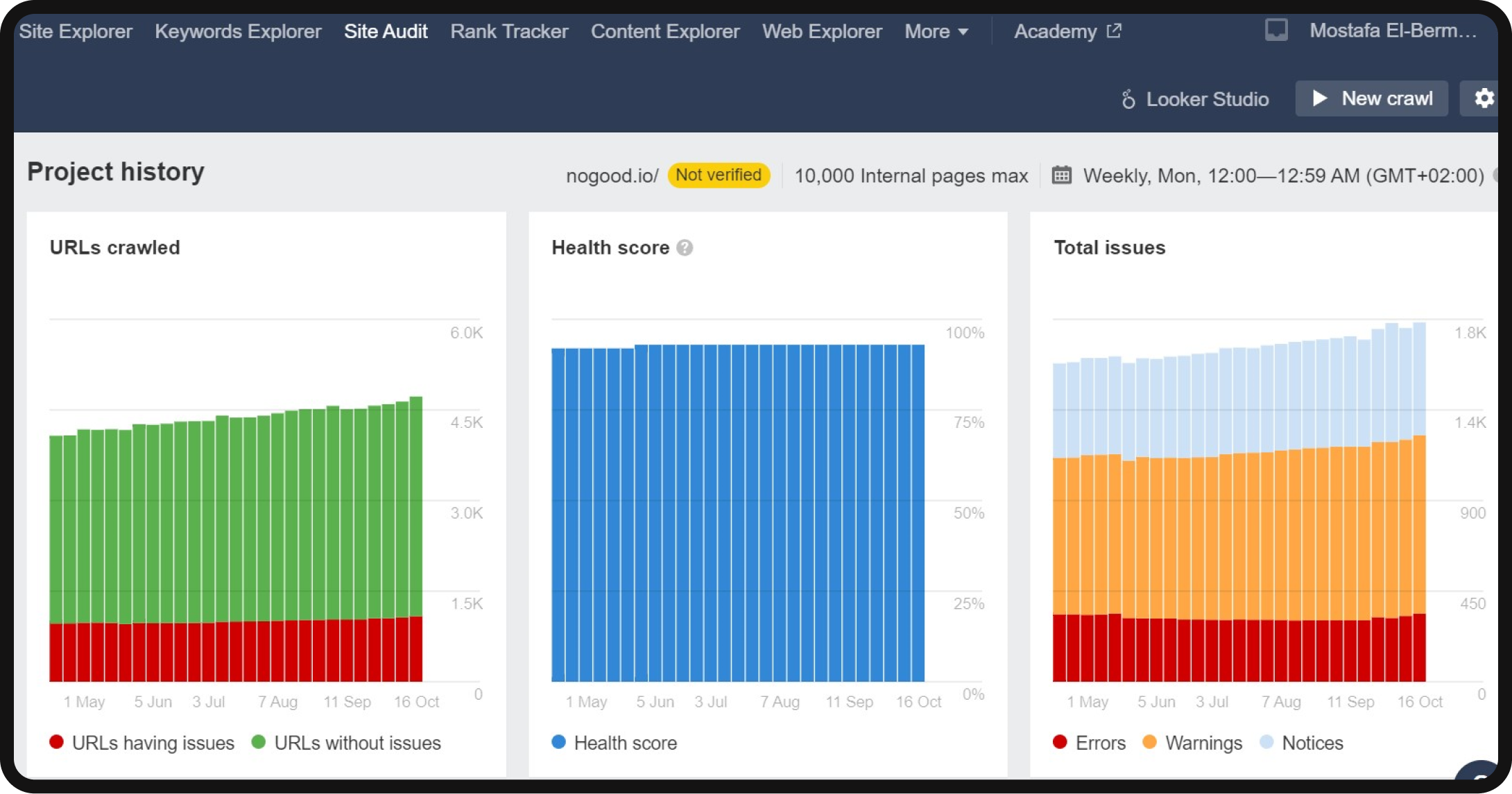
Understanding the results
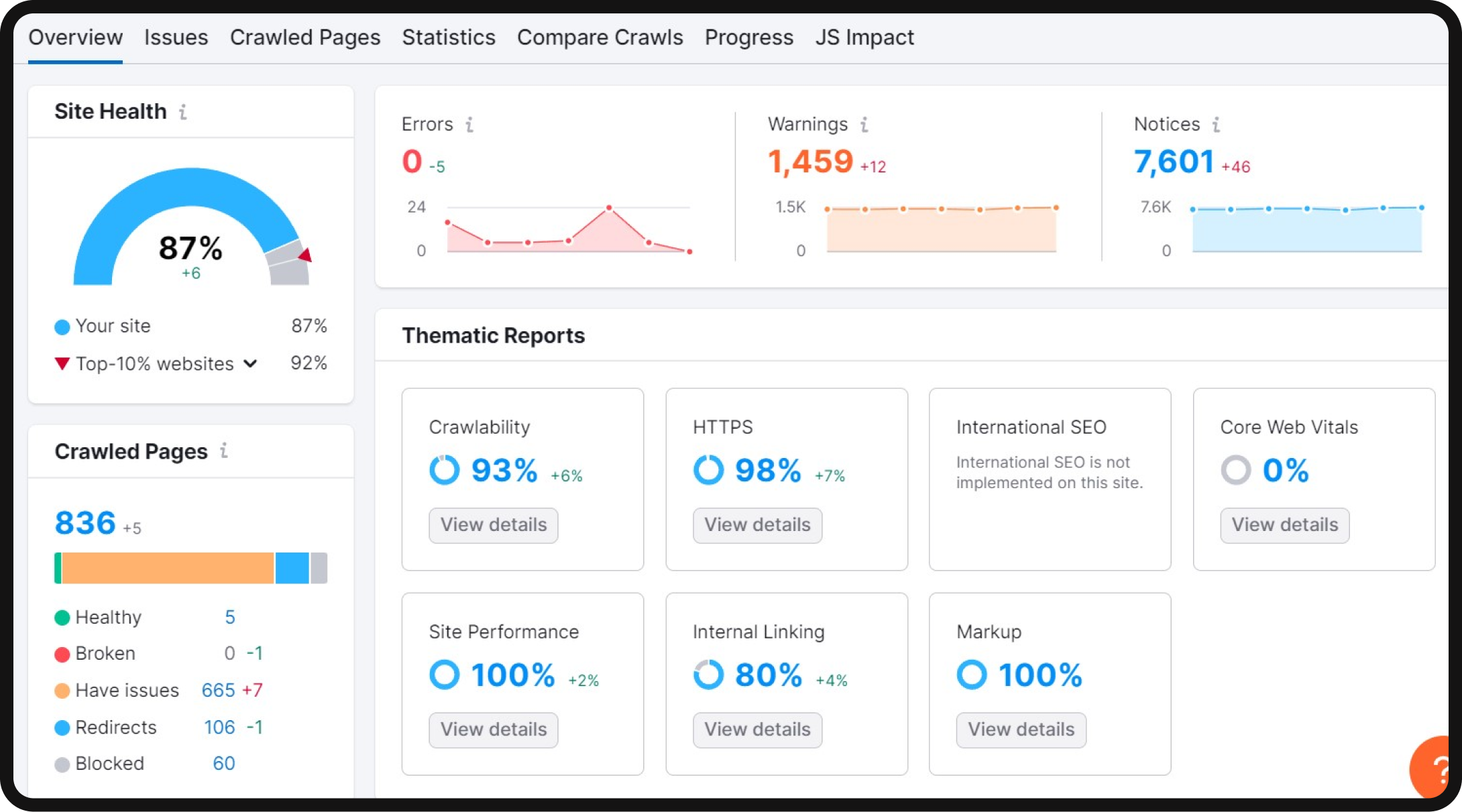
- Overview: After the crawl, you’ll land on the “Overview” page. Here, you’ll find a top-level summary, including the number of indexable and non-indexable pages, top issues, and an overall website health score rated out of 100. This health score provides a quick and understandable metric for assessing your website’s overall health.
- All issues: To delve deeper into the audit findings, navigate to the “All Issues” tab. This section summarizes the problems the crawler has detected, prioritizes them based on their significance, and guides how to rectify them.
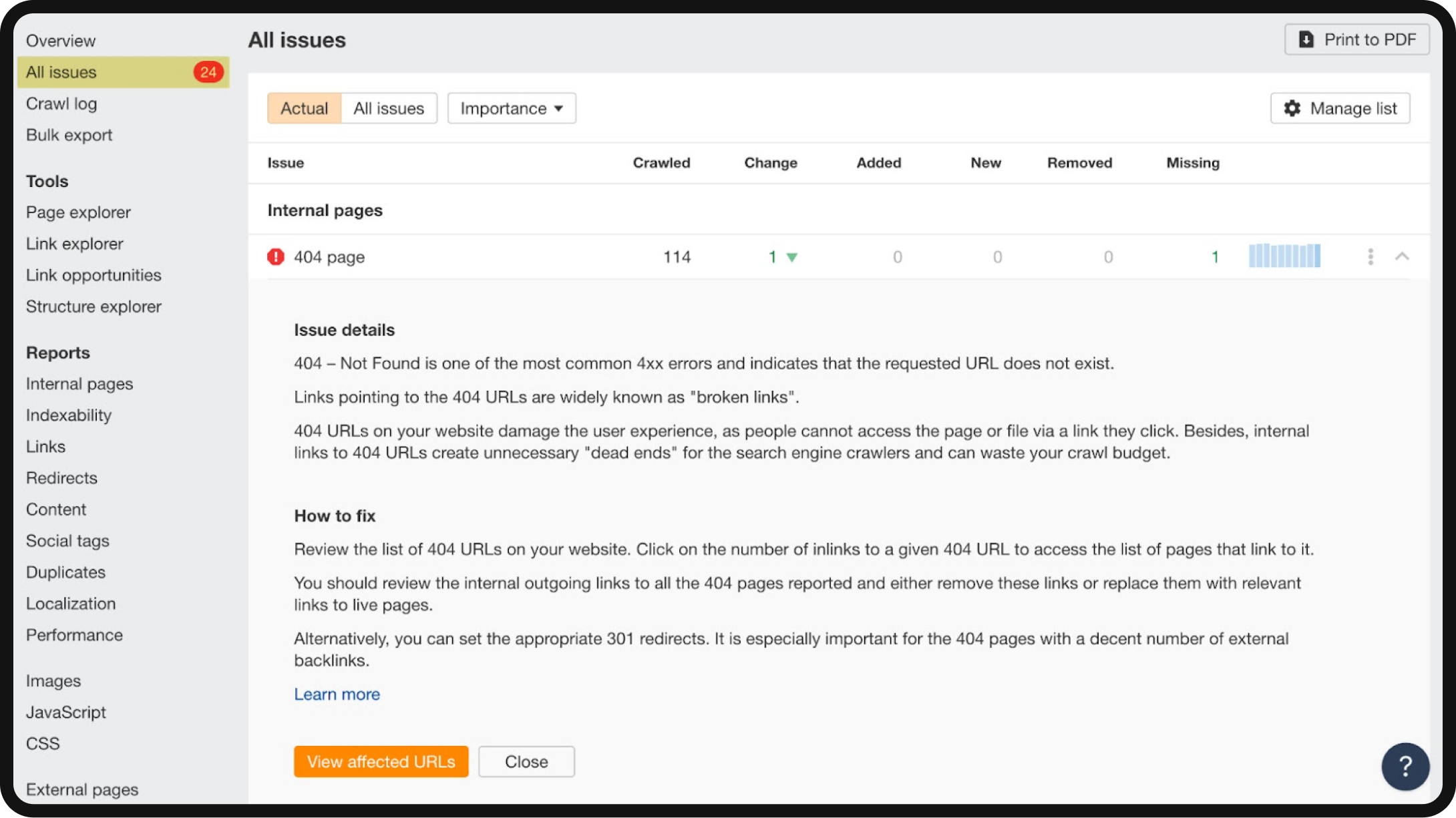
This report and other tools serve as a valuable resource for identifying issues that may impede your performance on the Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs).
Step 2: Finding indexation and crawlability issues
Ensuring that search engines can efficiently crawl and index your website is fundamental for achieving visibility on SERPs and ranking for relevant keywords. Detecting crawlability issues is crucial for maintaining a well-optimized website. Here are key considerations and actions to identify and address indexation and crawlability issues:
1. Indexation errors
2. Robots.txt errors
3. Robots meta tags
4. Prioritize checking the sitemap
5. Optimize the crawl budget
1. Indexation errors
- Priority: High
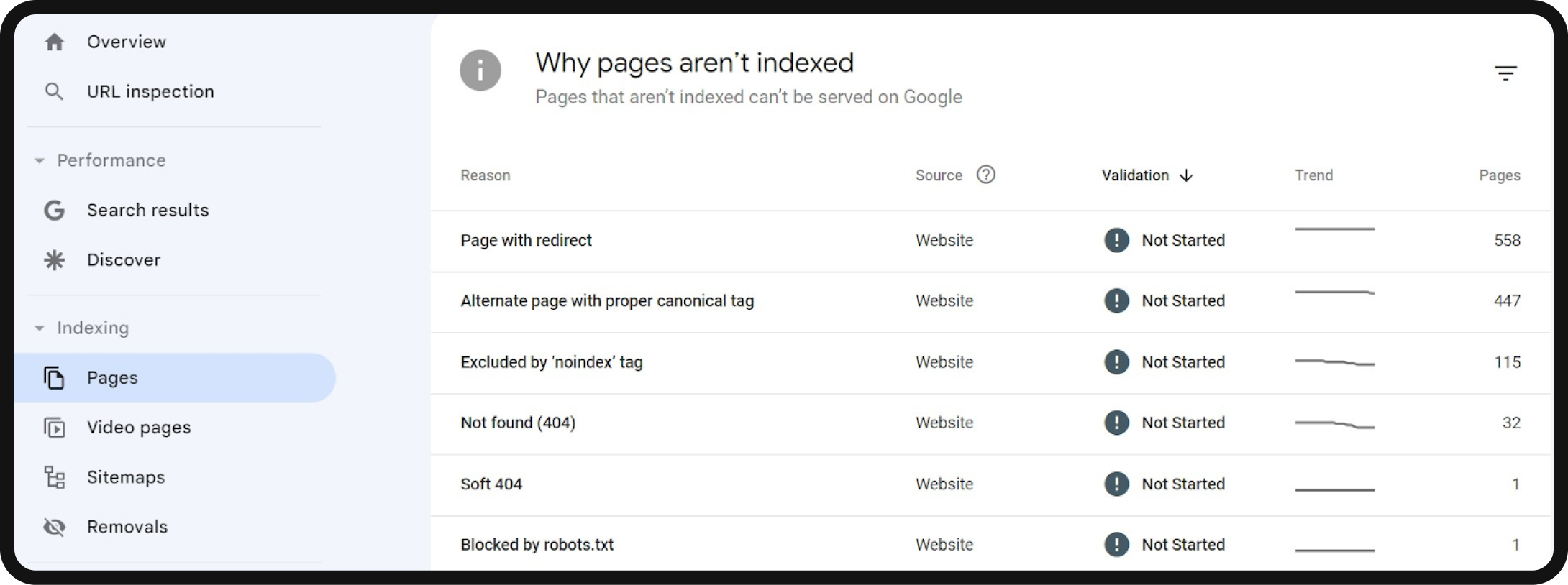
- Google Search Console: Check your website’s indexation status in Google Search Console using the Coverage report. This report provides insights into which pages are indexed, pages with warnings, and excluded pages, along with reasons for exclusion. Pages must be indexed without issues to appear in search results.
2. Robots.txt errors
- Priority: High
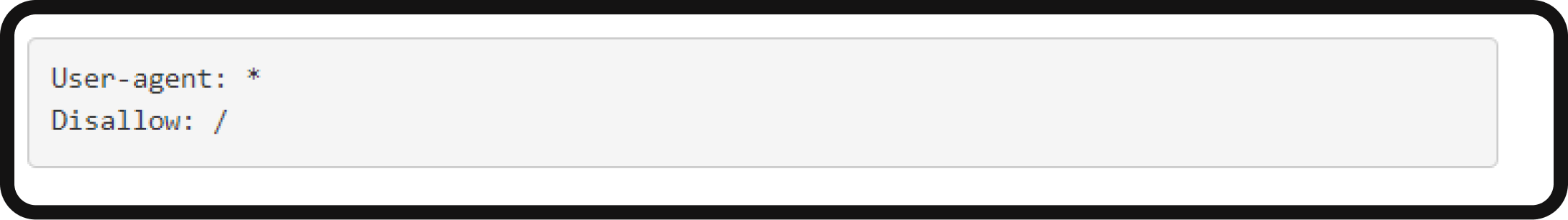
- Inspecting the robots.txt file: Review the robots.txt file to ensure it correctly guides search engine crawlers. Errors in the robots.txt file may inadvertently block pages from being crawled and indexed. Google tends to abide by robots.txt directives. Here is what a robots.txt file looks like (which tells search engines not to crawl pages):
You also have the option to verify the accessibility and index status of an individual page by entering its URL into the search bar within Google Search Console. If the page is accessible but hasn’t been indexed, you can initiate a “Request Indexing” process.
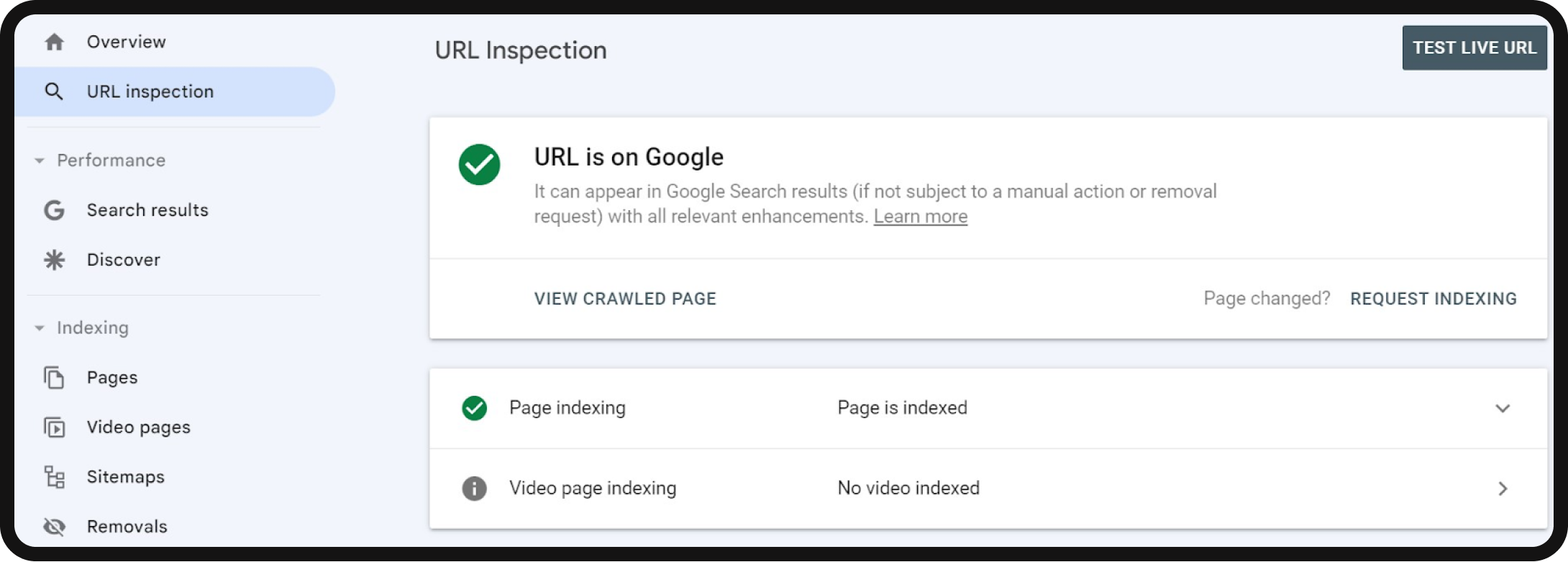
3. Robots meta tags
- Priority: High
- Understanding robots meta tags: Robots meta tags placed in the section of a webpage dictate how search engines should crawl and index the page. “noindex” tags prevent indexing, while other tags like “max-snippet” or “max-image-preview” provide specific indexing instructions. Ensure proper usage of these tags to avoid unintended consequences.
In the absence of robots meta tags on the page, search engines understand it as “index, follow.” This signifies that they have permission to index the page and traverse all its links.
However, the “noindex” tag serves various purposes:
- Excluding thin pages with minimal value for users.
- Keeping pages in a staging environment hidden from search engines.
- Hiding admin and thank-you pages.
- Preventing the indexing of internal search results.
- Concealing PPC landing pages.
- Temporarily concealing pages related to upcoming promotions, contests, or product launches.
- Managing duplicate content through canonical tags to indicate the preferred version for indexing.
- Nevertheless, improper use of these attributes can lead to significant indexability issues. Accidentally, using the wrong attribute can adversely affect your visibility on the SERPs, so exercise caution when implementing them.
4. Prioritize checking the sitemap
- Priority: High
- XML sitemap: An XML sitemap helps guide search engines by providing instructions on which pages to crawl and index. Pages excluded from the sitemap may not be prioritized for crawling. Confirm that all important pages are included in your sitemap and avoid including irrelevant or broken pages. You can check the sitemap by heading to Ahrefs’ Site audit > All issues > Other. The crucial point to remember is to confirm that all the significant pages you intend to have indexed are present in your sitemap while excluding any irrelevant entries.
5. Optimizing the crawl budget
- Priority: High (for large websites)
- Crawl budget: Crawl budget refers to how many pages a search engine can crawl and how quickly. Factors influencing the crawl budget include the number of website resources and the perceived value of indexable pages. Ensure that critical pages are part of your daily crawl budget by making them popular, optimizing for organic traffic, and internal linking.
- Crawl Stats report in GSC: Use the Crawl Stats report in Google Search Console to gain insight into your site’s crawling patterns and identify issues that Googlebot flagged.
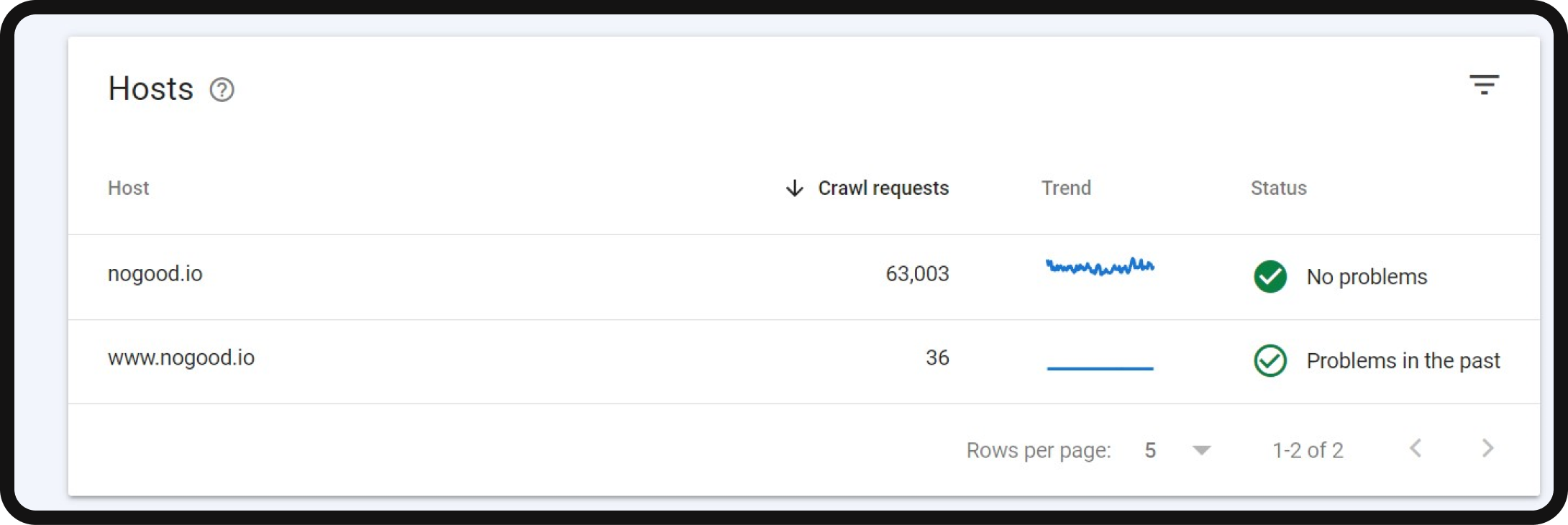
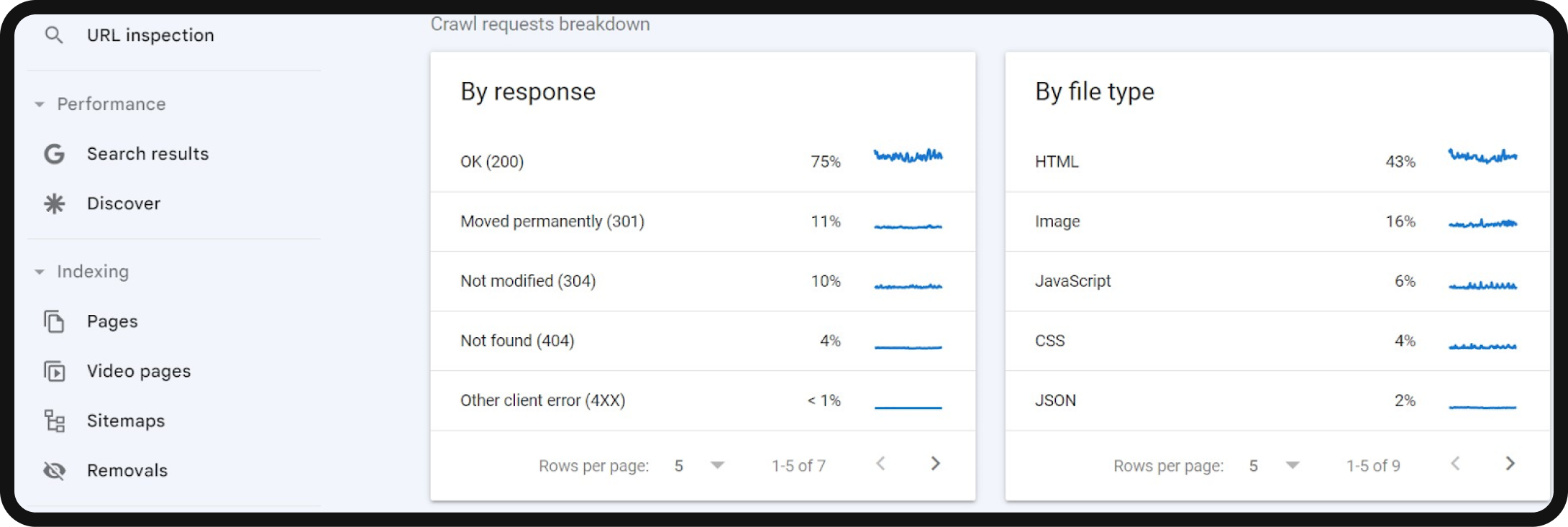
- Flagged crawl statuses: Pay attention to flagged crawl statuses, which indicate potential page indexing or crawlability issues.
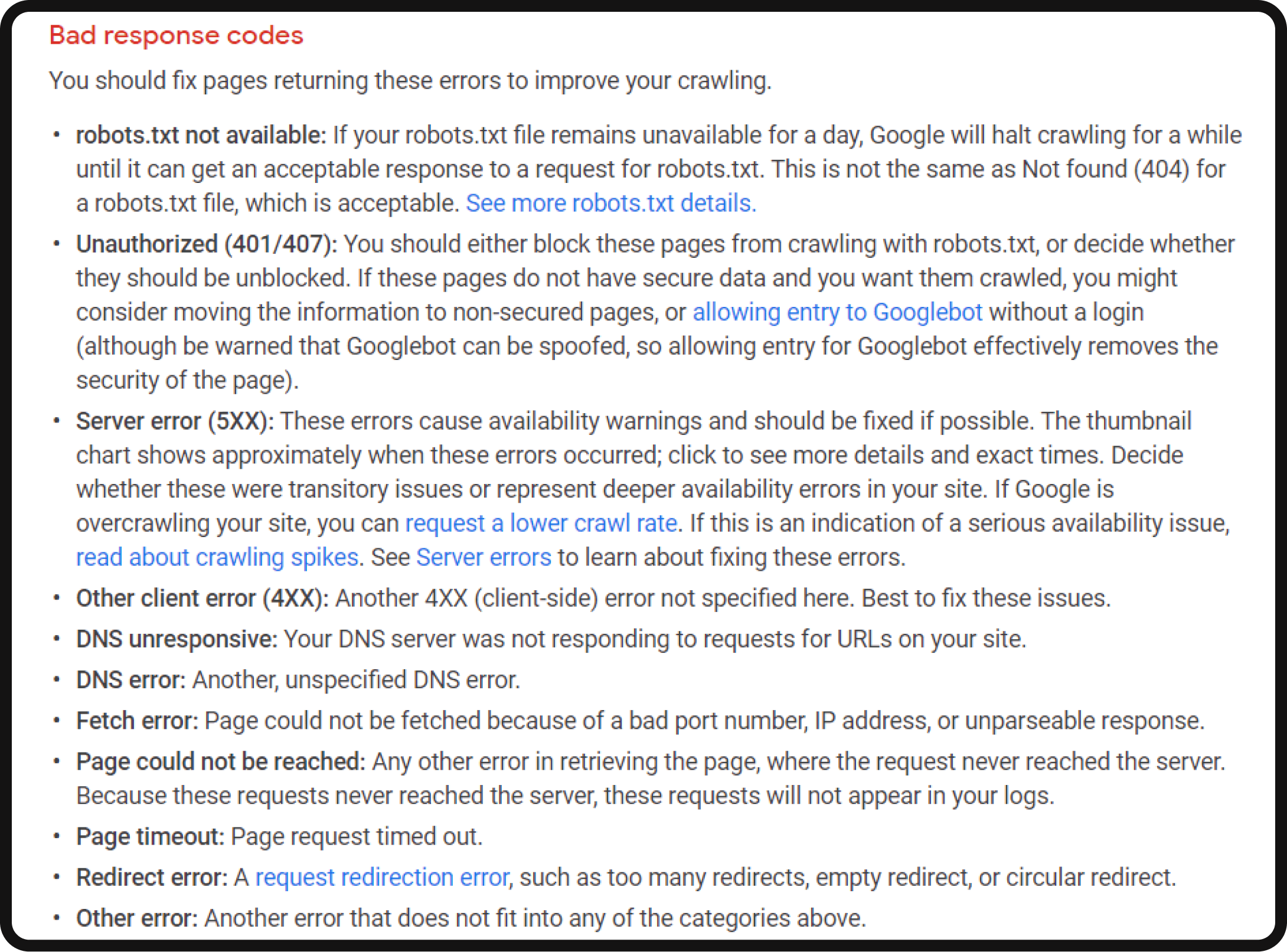
Step 3: Site speed and performance analysis
Measuring and analyzing website speed
- Priority: Low
Site speed has emerged as a prominent concern within the SEO community, with notable significance following Google’s announcement that mobile speed is a ranking factor. Since May 2021, Google has introduced Core Web Vitals (CWV), a set of speed metrics that influence page rankings. These metrics include:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Evaluates visual load time.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability.
- First Input Delay (FID): Gauges interactivity.
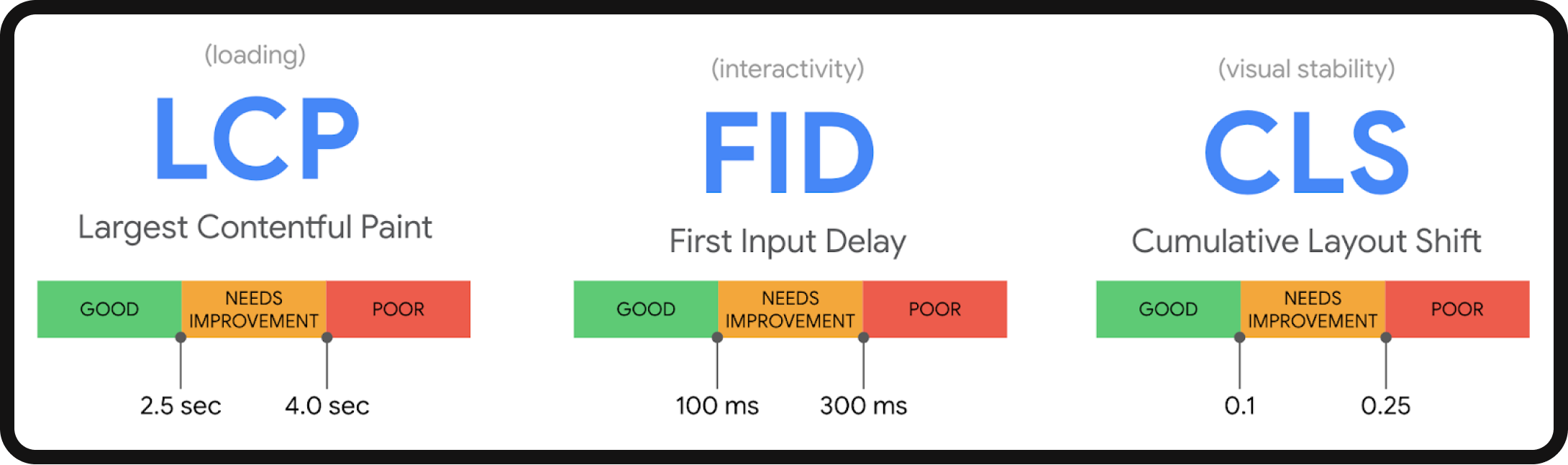
Google’s primary objective in incorporating these metrics is to enhance user experience. Slow-loading websites are met with impatience in today’s fast-paced world, often resulting in visitors leaving before they accomplish their goals.
While sites with minor speed issues may not experience significant ranking improvements, studies indicate that markedly slow websites can benefit from speed optimization. This enhancement may manifest as increased organic traffic, improved click-through rates, and other positive outcomes.
For a more detailed examination of your website’s speed, you can refer to the Ahrefs audit report by navigating to Site Audit > Reports > Performance > Overview.
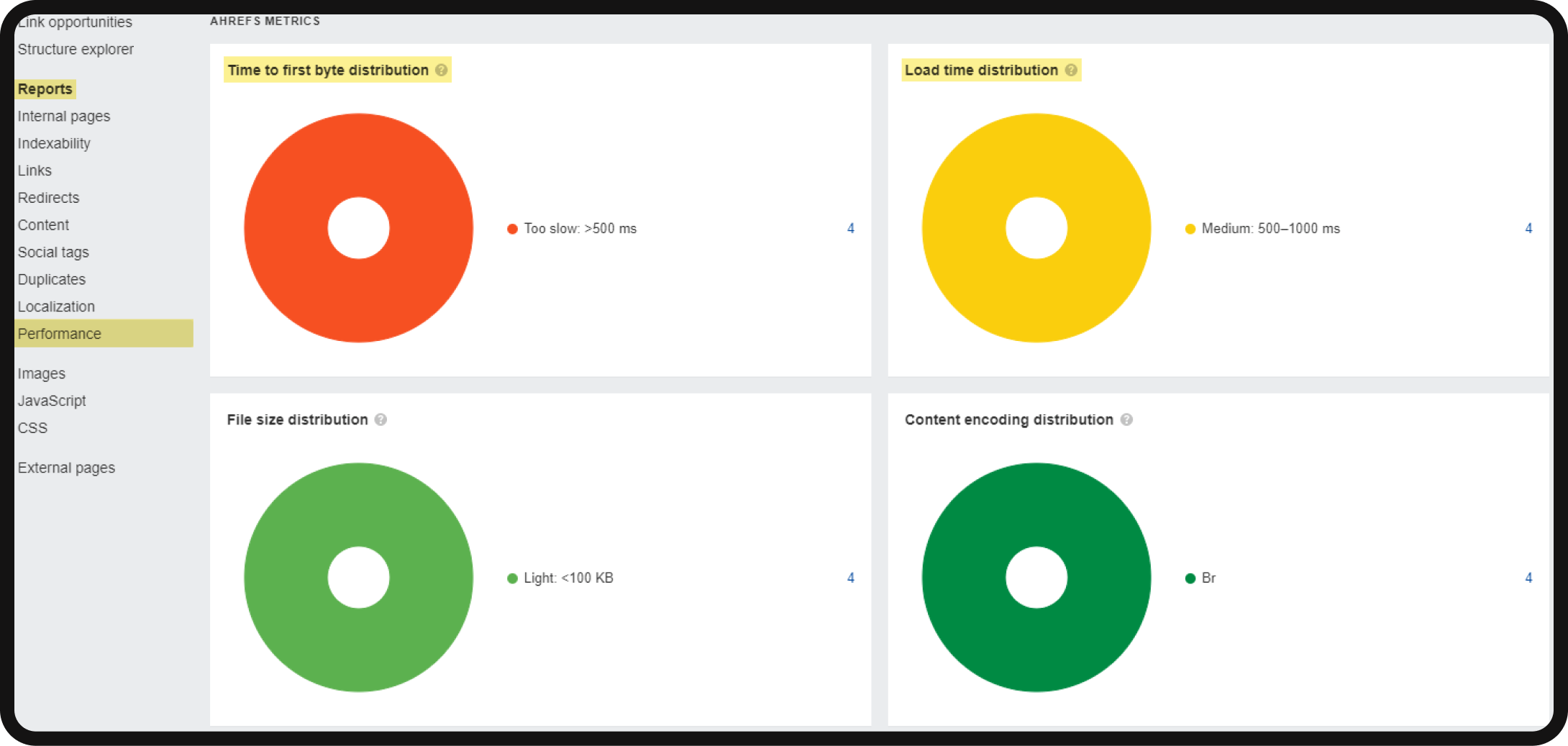
Recommendation for page speed insights
For in-depth page speed insights, enable Core Web Vitals in the Crawl settings. Additionally, there are various exceptional speed testing tools at your disposal. These include Google’s PageSpeed Insights and other tools like GTmetrix, known for providing comprehensive assessments of site speed.
Addressing the optimization of very slow websites can be a complex process. However, beginners can initiate the improvement process by utilizing accessible tools such as WPRocket or NitroPack (both of which are paid solutions) to significantly enhance site speed.
Strategies for improving website speed
While achieving an ideal website speed may not follow a one-size-fits-all formula, website owners can employ various best practices to enhance their site’s speed and reliability. These strategies include:
1. Optimize images
- Image optimization is a key factor in speeding up a website. It involves reducing image resolution, dimensions, and file size through compression. Optimizing images helps decrease loading times, especially since images are often larger files compared to HTML and CSS files.
2. Limit the number of HTTP requests
- Web pages commonly require multiple HTTP requests for assets like images, scripts, and CSS files. Reducing the overall number of required assets is essential, as each request involves a round trip to and from the server, contributing to longer load times. Conducting a speed test can help pinpoint which HTTP requests are causing delays.
3. Use browser HTTP caching
- Leveraging browser caching involves instructing browsers to store copies of static files in a temporary storage location. This enables quicker loading of frequently visited web pages. Browser caching instructions are included in HTTP response headers from the hosting server, reducing data transfer needs and enhancing load times for returning visitors.
4. Remove unnecessary render-blocking JavaScript
- Certain web pages may have extraneous code that loads before critical page content, slowing down overall load times. This issue is prevalent in large websites with multiple contributors. Web page owners can use performance tools to identify and eliminate redundant code on underperforming pages.
5. Limit the use of external scripts
- Scripts from external sources, such as commenting systems, CTA buttons, CMS plugins, or lead-generation popups, can impact webpage speed, leading to ‘content jumping’ or ‘layout shifting.’ Minimizing the use of external scripts, especially on mobile devices, helps ensure smoother page loading.
6. Limit redirect usage
- Redirects, while sometimes necessary, can add fractions of a second, or even seconds, to load times. Overuse of redirects, especially on larger websites with multiple contributors, can lead to performance issues. Clear redirect guidelines and periodic assessments are essential for reducing unnecessary redirects.
7. Minify CSS and JavaScript files
- Minification involves removing non-essential elements from code, such as comments, whitespace, and unnecessary semicolons. This results in smaller CSS and JavaScript files that load faster, consume less bandwidth and enhance performance. Although the gains may be marginal, minification remains a crucial practice.
8. Use effective third-party services
- Vital website functions depend on third-party services. Ensure their effectiveness by focusing on the following areas:
- Hosting: Select a server with a swift response time (under 200 ms) and a reliable track record to avoid slow origin server responses.
- DNS: Opt for DNS services that promptly and consistently translate domains into IP addresses, a critical step in the page loading process.
- Caching: Utilize a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to cache web content in multiple locations worldwide, reducing the distance user requests must travel to reach the origin server.
- Cybersecurity: Guard against performance-degrading factors like DDoS attacks and malicious bots by selecting a web application security provider that effectively filters out malicious traffic without hampering legitimate access.
Implementing these strategies can significantly enhance your website’s speed and, by extension, the user experience and SEO performance.
Step 4: Mobile optimization
- Priority: High
In today’s digital landscape, mobile device usage has surged, with an increasing number of individuals relying on mobile devices for various online activities. For instance, mobile shopping now constitutes a significant portion of the market, as indicated by Datareportal’s extensive study, which reports a 60% market share for mobile commerce.
Considering this mobile-centric shift in user behavior, it’s no surprise that Google has been transitioning toward mobile-first indexing in recent years. From a technical perspective, it’s wise to conduct a secondary audit of your website using Ahrefs’ mobile crawler. By default, Ahrefs’ audit tool utilizes a desktop crawl to assess your site. However, you can conveniently switch to mobile crawling by adjusting the settings under “Crawl Settings” within your “Project Settings.”
Once you’ve executed a second crawl with the mobile crawler, the comparison function within Ahrefs will scrutinize your mobile and desktop sites. It will provide insights into any alterations or the emergence of new issues that are exclusive to the mobile version of your site.
Issue changes between crawls in Ahrefs’ site audit
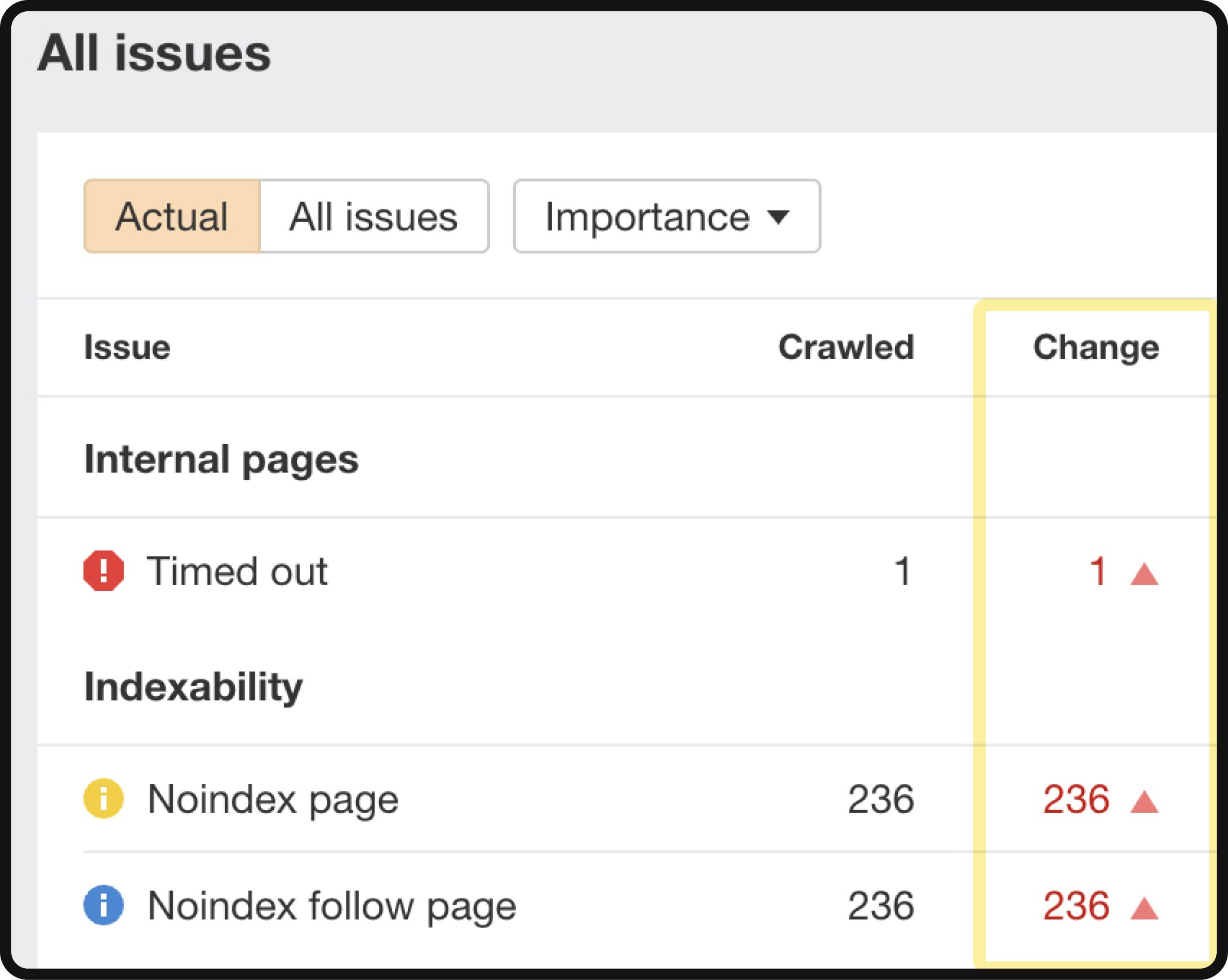
From this point, you can review the metrics related to “New,” “Added,” or “Removed” issues to comprehend the specific alterations that have occurred in each aspect. This mobile audit allows you to pinpoint any changes in your website’s performance and user experience concerning mobile visitors, ensuring that your site is well-optimized for this growing segment of users.
Checklist for optimizing mobile experience
After running the mobile audit, here are some techniques to optimize your mobile experience:
- Responsive web design: Implement responsive design principles to ensure that your website adapts seamlessly to various screen sizes and orientations. This technique involves using flexible layouts, images, and media queries to create a consistent user experience across all devices.
- Mobile-friendly navigation: Simplify your website’s navigation for mobile users. Use mobile-specific menus or navigation bars to enhance usability. Ensure that menus are easy to access, and limit the number of menu items to prevent clutter.
- Fast loading times: Optimize your website for speed on mobile devices. Compress images, reduce HTTP requests, and employ browser caching to improve load times. Fast-loading pages are essential for retaining mobile visitors.
- Touch-friendly design: Ensure that interactive elements, such as buttons and links, are touch-friendly. They should be appropriately sized and spaced to accommodate touch interactions on smaller screens.
- Readable content: Adjust font sizes, line spacing, and content formatting to enhance readability on mobile screens. Avoid excessive use of pop-ups and interstitials that can disrupt the user experience.
- Optimized forms: Simplify forms for mobile users by minimizing required fields and implementing autofill features. Make sure form elements are easy to tap, and provide clear validation messages.
- Mobile SEO best practices: Apply mobile-specific SEO techniques to improve visibility and rankings in mobile search results. This includes optimizing for mobile-friendly keywords, using structured data markup, local SEO, and implementing mobile-specific meta tags.
Step 5: Technical on-page SEO
Addressing on-page issues, even those considered minor, can significantly affect your search engine rankings. Here are the key elements to focus on:
1. Page titles and title tags
2. Meta tags and content optimization
1. Page titles and title tags
- Priority: Medium
- Title tags play a vital role in informing both Google and site visitors about a webpage’s content. Optimize your title tags by keeping them under 60 characters and ensuring they accurately reflect the page’s subject matter. Google often rewrites excessively long title tags, making concise titles important for SEO.
- Tip: You can use this free SERP preview tool to ensure your title tags are up to standard.

2. Meta tags and content optimization
- Priority: Medium
- Meta descriptions provide additional context about a page’s content and can appear in search results as snippets. While Google doesn’t always use them, having compelling meta descriptions can entice more users to click on your listings. Ensure your most important pages have well-written meta descriptions.
- Tip: After ensuring you’ve included your exact-matching target keyword in the meta description, you can use the free SERP preview tool again to ensure your meta description is the correct length.
Step 6: Analyzing and fixing internal links
Internal linking is a crucial aspect of on-page SEO and is vital in improving a website’s visibility and user experience. While many people focus on external backlinks for SEO, internal links are equally important and work hand in hand with backlinks to enhance your website’s overall performance.
Here’s why internal linking is significant and how it can benefit your SEO efforts:
- Enhancing website experience: Internal links provide a smoother and more intuitive navigation experience for website visitors. When users can easily find relevant content or products through internal links, they are more likely to stay longer on your site and engage with multiple pages.
- Creating topical relevancy: Properly siloing topics through internal linking helps establish a clear topical roadmap for both search engines and users. This topical organization makes your content more relevant to specific keywords or themes, which can improve your rankings for those topics.
- Ensuring content crawling: Internal links help search engine crawlers discover and index your website’s content. When all content is effectively linked within your site, it ensures that no pages go unnoticed or unindexed. This can positively impact your site’s overall search visibility.
- Supporting external link building: Internal links also indirectly impact external link-building efforts. When you have a well-organized and content-rich website supported by effective internal linking, it can make your site more appealing to external websites for backlink opportunities.
Finding problematic internal links
You’ll be able to find problematic internal links by navigating to Ahrefs > Enter the page in Site Explorer > Internal links > Customize the type of links you’d like to view.
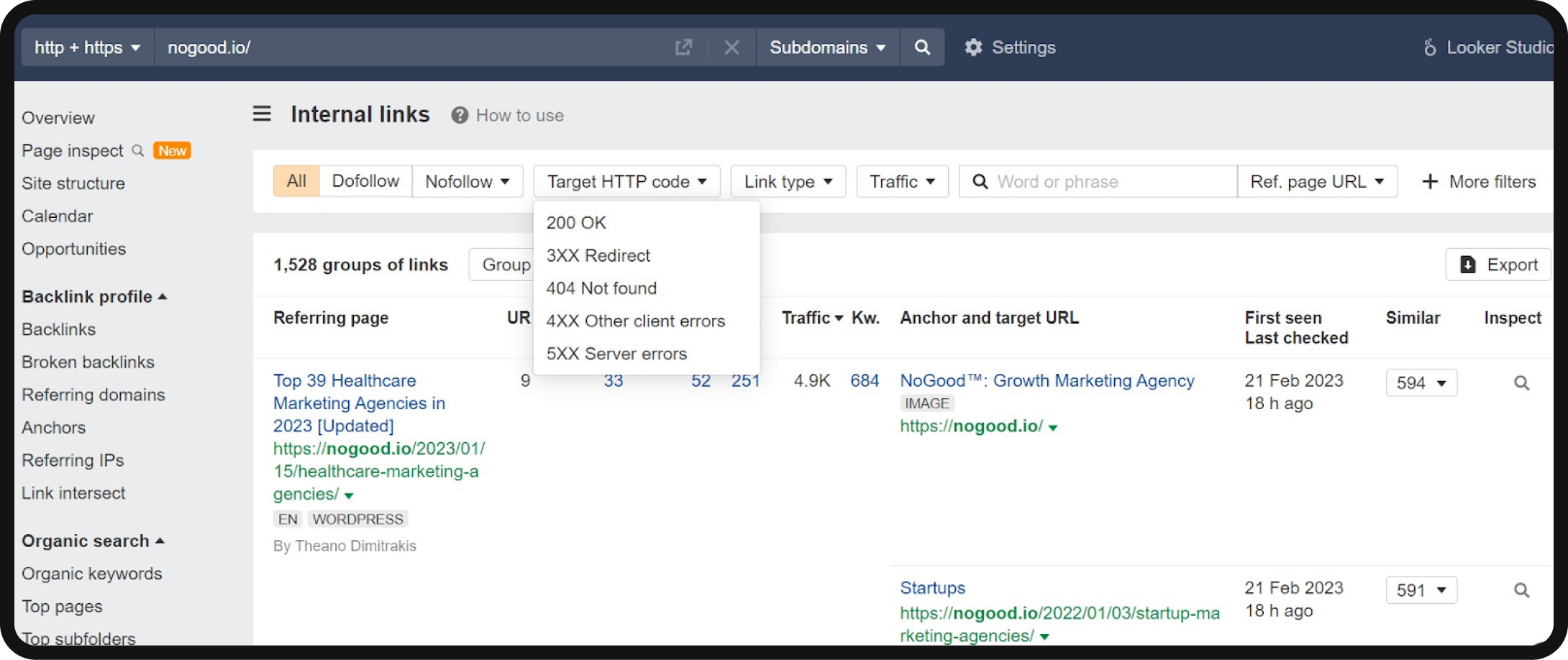
1. Addressing 4xx status codes
- Priority: High
To identify and manage 4xx status code issues on your website, follow these steps within Ahrefs’ Site Audit:
- Navigate to Site Audit.
- Click on “Internal pages” and go to the “Issues” tab.
- Select “4XX page.“
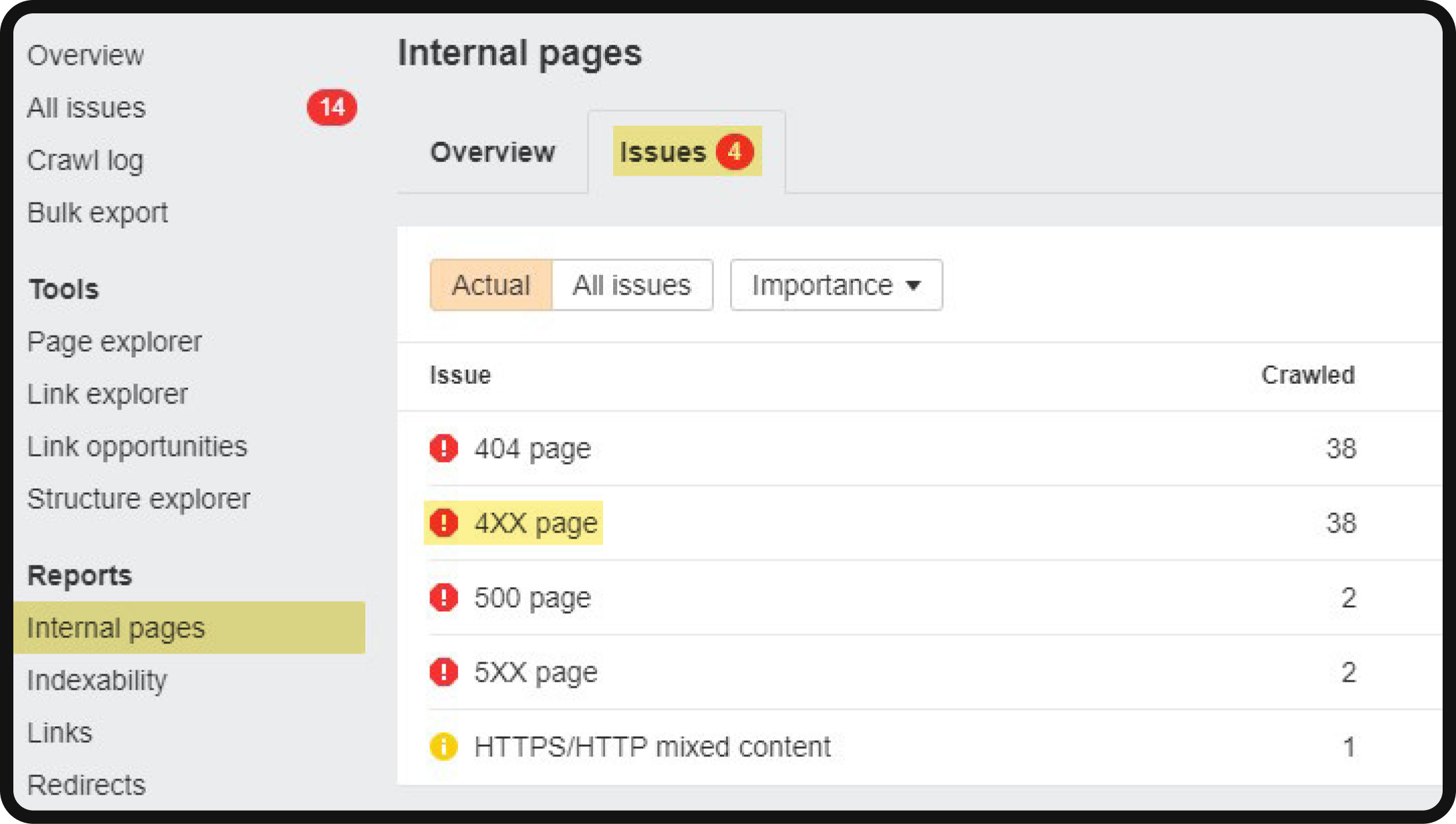
You will find a list of your site’s broken internal pages in the displayed results. It is crucial to address these issues promptly due to their significance in maintaining an optimized website.
Broken internal pages are problematic for two main reasons:
- Link equity waste: These pages waste “link equity,” which is the authority or ranking power passed from one page to another through links. When internal pages are broken, the link equity they could distribute is lost.
- Negative user experience: Broken internal pages provide users with a negative experience, leading to frustration and potentially driving them away from your site.
To resolve these 4xx status code issues, you have a few options:
- Restore the page: If a page was deleted by accident or improperly, you can consider bringing it back to the same address. Restoring the page allows you to retain the link equity associated with it.
- Redirect to a suitable location: If the broken page is no longer relevant or has been replaced, you can set up a redirection to a more appropriate location. It’s essential to update or remove all internal links referring to the broken page to ensure a seamless user experience.
2. Addressing orphan pages
- Priority: High
To manage orphan pages effectively, follow these steps within Ahrefs’ Site Audit:
- Access Site Audit.
- Go to the “Links” section and navigate to the “Issues” tab.
- Select “Orphan page” to view the list of these pages.
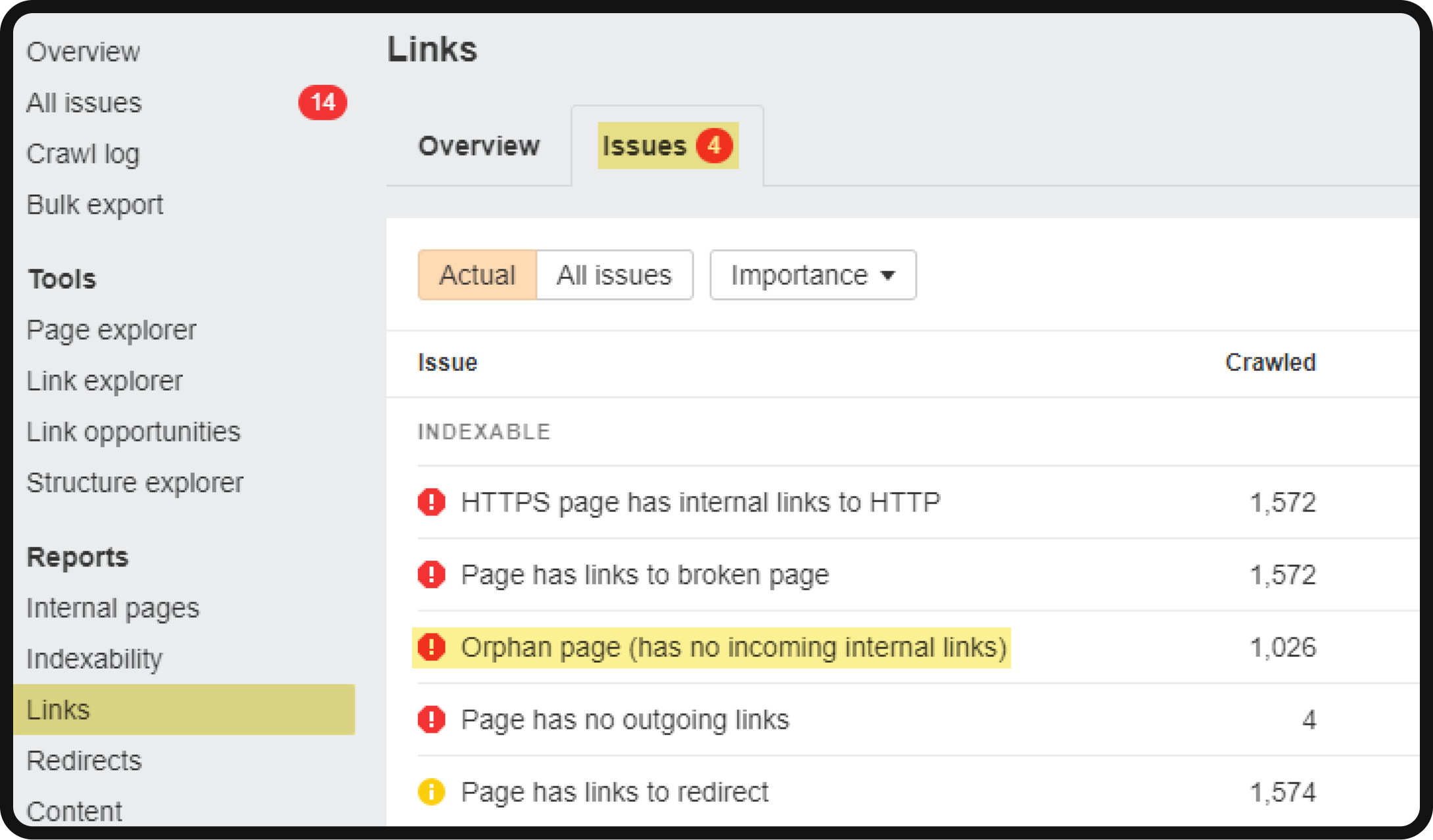
Orphan pages are those with zero incoming internal links, making them less visible to both users and search engines. To address this issue, consider the following reasons why indexable pages should not remain orphaned:
- Link equity transmission: Orphan pages do not receive the benefits of link equity transmission through internal links, as there are none pointing to them. This can hinder their ability to rank effectively.
- Search engine discovery: Google may not find orphan pages unless they are included in your sitemap through Google Search Console or receive backlinks from other websites’ crawled pages.
If your website has several orphaned pages, consider prioritizing them based on organic traffic. By adding internal links to these orphaned pages, especially those still receiving organic traffic, you can significantly improve their visibility and attract more visitors to these pages. This proactive approach can enhance your website’s overall SEO performance.
Step 7: Addressing and identifying image issues
Image optimization
Image optimization is a frequently overlooked aspect of SEO, yet it offers numerous benefits to your website, such as:
- Improved load speed: Optimized images lead to faster page loading times, enhancing the overall user experience.
- Enhanced visibility on Google images: Well-optimized images can drive additional traffic through Google Images search results.
- Engaging user experience: High-quality, well-optimized images contribute to a more visually appealing and engaging website.
- Enhanced accessibility: Image optimization, including the use of alt text, ensures that your website is accessible to individuals with visual impairments who rely on screen readers.
Finding and addressing image optimization issues
To identify and address image issues on your website, use Ahrefs’ Site Audit feature. Follow these steps:
- Access the main audit report: Site Audit > Reports > Images.
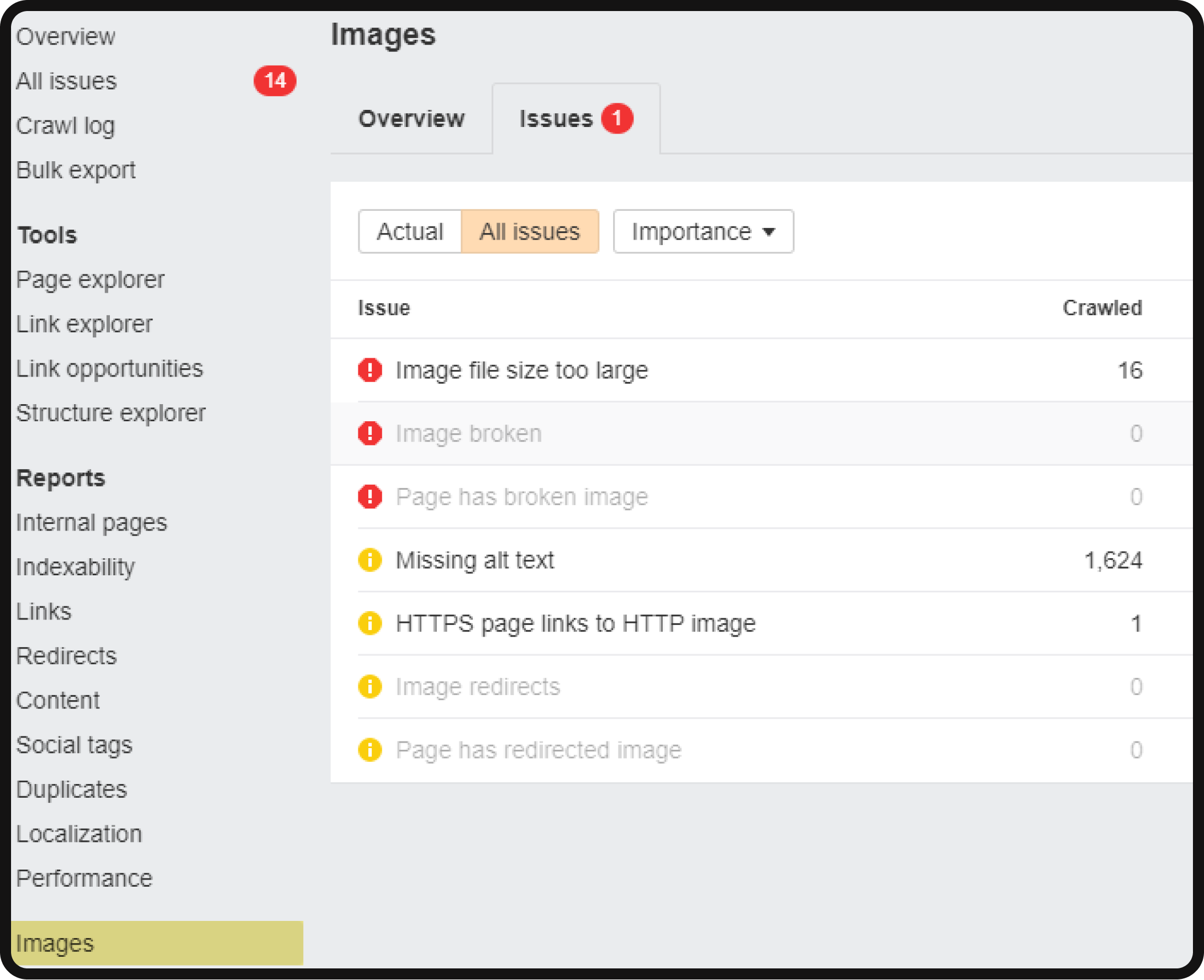
Within the Images section, you’ll find the following image-related issues:
Broken images
- Priority: High
Broken images are images that cannot be displayed on your website. These not only lead to a poor user experience but can also create the impression that your website is poorly maintained and unprofessional. For website owners looking to monetize their sites, this issue can erode trustworthiness.
Image file size too large
- Priority: High
Large image files significantly impact your site’s speed and performance. It’s essential to display images in the smallest possible size and in suitable formats, such as WebP, to optimize site speed. The best practice is to optimize image file sizes before uploading them to your website. Tools like TinyJPG can help. If you need to optimize existing images, various plugins are available for popular content management systems like WordPress, including Imagify and WP-Optimize.
HTTPS pages linking to HTTP images
- Priority: Medium
When HTTPS pages link to HTTP images, it creates “mixed content issues.” This means that a page loads securely via HTTPS, but a resource it links to, like an image or video, is on an insecure HTTP connection. Mixed content is a security concern that can impact ad monetization and degrade the user experience. Certain browsers may restrict unsafe resource requests by default, potentially causing your page not to function correctly if they are blocked.
Missing alt text
- Priority: Low
Alt text, or alternative text, is crucial for image optimization. It describes an image on your website, significantly improving accessibility for visually impaired individuals who use screen readers. Screen readers convert images into audio, effectively describing the image to the site visitor. Properly optimized alt text allows screen readers to inform users with visual impairments about the image content. Alt text can also serve as anchor text for image links, improve rankings on Google Images, and enhance topical relevance on your website.
By addressing these image issues, you can improve your site’s performance, user experience, and accessibility, ultimately contributing to your SEO success.
Step 8: Website architecture and navigation
Effective website architecture and navigation are crucial for enhancing UX and SEO. This step involves optimizing your site’s structure and implementing sitemaps.
Site structure and hierarchy
- Priority: High
Site hierarchy, often referred to as site structure, is the way your website’s pages are systematically organized into subfolders. A well-designed site structure is pivotal for search engine optimization and user experience, as it enhances the ease of navigation and indexing. To evaluate and optimize your site’s hierarchy, follow these key steps:
* For this section, we used SEMrush.
- Assess your site’s hierarchy: Gain a comprehensive view of your site’s hierarchy by navigating to the “Crawled Pages” tab within Site Audit.
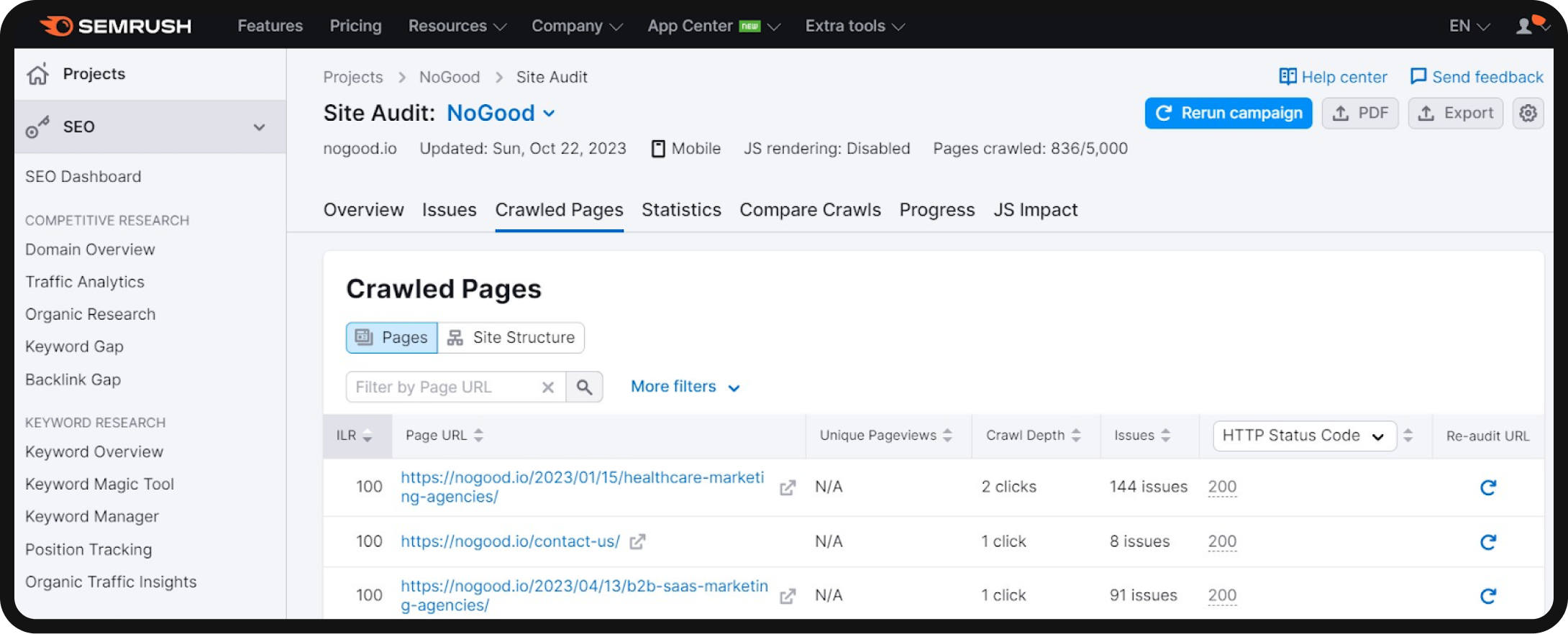
- View the site structure: Switch to the “Site Structure” view. This provides an overview of your website’s subdomains and subfolders. Examine this structure to ensure it is logically organized and easily navigable.
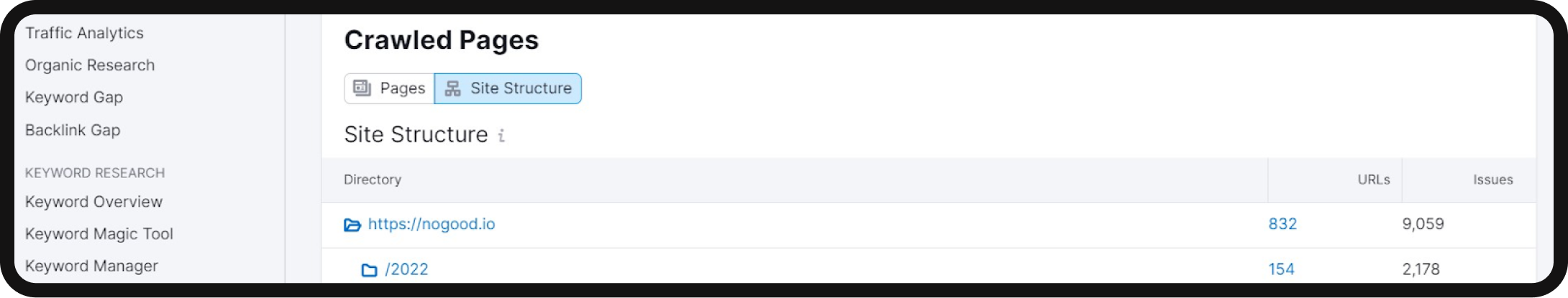
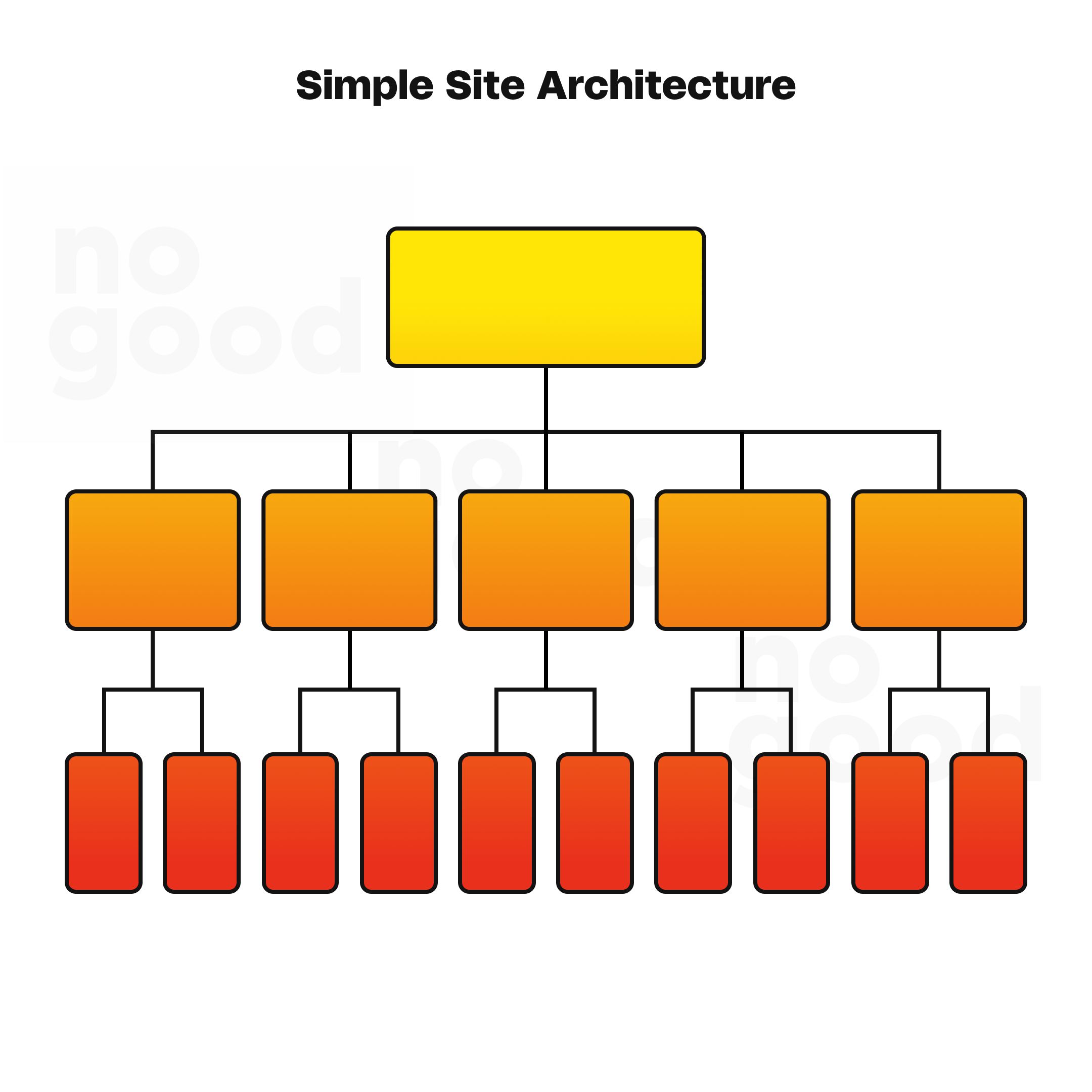
- Aim for a flat architecture: Strive for a flat site architecture that simplifies the user’s journey. Ideally, it should take a user no more than three clicks from the homepage to reach their desired page. A deep hierarchy requiring more than three clicks, may be viewed as less important or relevant by search engines.
- Adjust deep hierarchy: To rectify overly deep site hierarchies, employ internal linking strategies. Adding internal links to pages situated deep within the site structure can make them more accessible. This approach will be explored further in the next chapter.
Effective navigation
- Keep navigation simple: Maintain a straightforward navigation system, avoiding overcomplicated mega menus or unconventional menu item names that might confuse users.
- Ensure logical navigation: Align your navigation with the hierarchy of your pages. Employ breadcrumbs to create a visual representation of the site structure for users to follow.
Navigating through a well-organized site architecture is inherently more user-friendly. When your website’s architecture is transparent and easy to navigate, it enhances the overall user experience and facilitates comprehension for both visitors and search engine bots.
URL structure
- Consistency and clarity: Just as site hierarchy should be consistent and well-organized, your site’s URL structure should mirror the logical hierarchy. A visitor following menu navigation, for example, should see a URL that corresponds to the architecture.
Example:
- Homepage > SEO > Pagination
- URL: domain.com/seo/pagination
- Geographic relevance: For certain websites catering to specific regions, consider using a URL structure that indicates the relevance to a particular country. For instance, a website for Canadian users might use “domain.com/ca” or “domain.ca.”
- User-friendly URLs: Ensure your URL slugs are user-friendly, free of common issues such as underscores, excessive parameters, or excessive length.
Site Audit can assist in identifying and addressing common URL issues, ensuring your website’s URL structure is in line with best practices and conducive to effective SEO and user experience.
Sitemaps
- Priority: High
Sitemaps are essential for providing search engines with a roadmap to navigate your website efficiently. They come in two primary types: XML sitemaps and HTML sitemaps. XML sitemaps are designed for search engines, while HTML sitemaps are for human users. Creating and submitting XML sitemaps to search engines can improve the indexation of your web pages.
A meticulously crafted XML sitemap serves as a guiding beacon for search engines to navigate your website efficiently. Since web crawlers can’t stop and ask for directions, a well-structured sitemap provides Google with clear instructions for the crawling and indexing process.
However, similar to how search engine crawlers can inadvertently be hindered by a misconfigured robots.txt file, there’s potential for errors in sitemaps. Pages can unintentionally be omitted from the sitemap, resulting in lowered priority for indexing by search engines.
Moreover, including irrelevant or broken pages within your sitemap can perplex crawlers, potentially affecting your website’s crawl budget and overall SEO performance. These issues can lead to inefficient indexing, causing valuable content to be overlooked by search engines.
To ensure that your sitemap aligns with your SEO objectives, it’s vital to conduct regular checks. You can scrutinize your sitemap for discrepancies using the Site Audit feature, accessible through the path: Site Audit > All issues > Other.
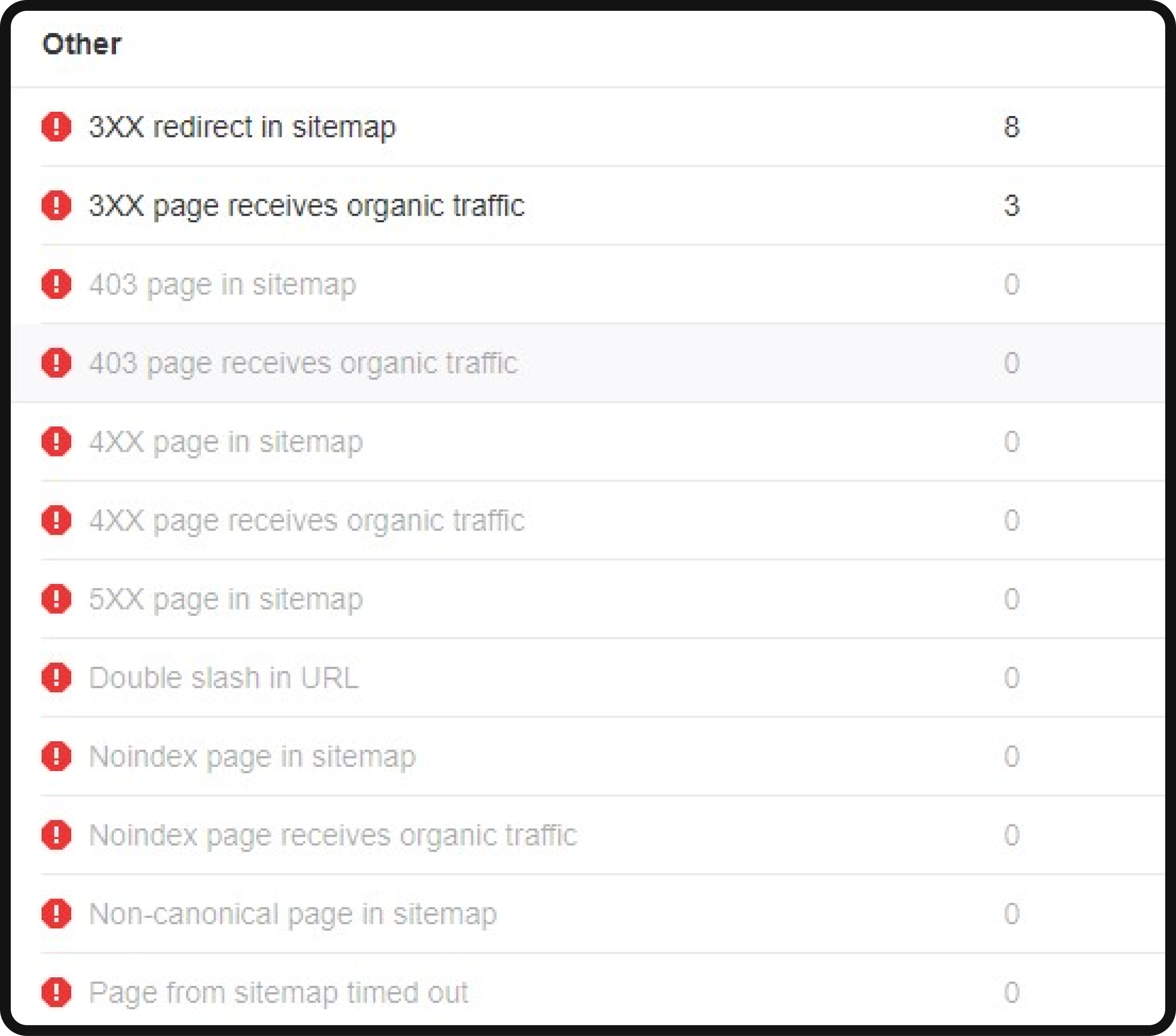
The primary goal in managing your sitemap is to include only the essential pages you want to be indexed, eliminating any extraneous or erroneous entries that might hinder search engine optimization.
Step 9: Finding and fixing HTTPS issues
- Priority: High
Ensuring that your website operates with the HTTPS protocol rather than HTTP is paramount for both security and SEO purposes. HTTPS provides a secure and encrypted connection for your site’s visitors and is authenticated by a third-party vendor through an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate. The use of HTTPS is not only a security measure but also a Google-confirmed ranking signal. Implementing HTTPS is relatively straightforward, but it can introduce certain issues. Here’s how to identify and address HTTPS-related problems as part of your technical SEO audit:
* We used SEMrush to illustrate our point.
- Access the “HTTPS” report: Start by accessing the “HTTPS” report within the Site Audit Overview. This report will provide you with a comprehensive list of issues related to HTTPS.
- Identify issues: Within the HTTPS report, you will see a breakdown of the issues affecting your website.
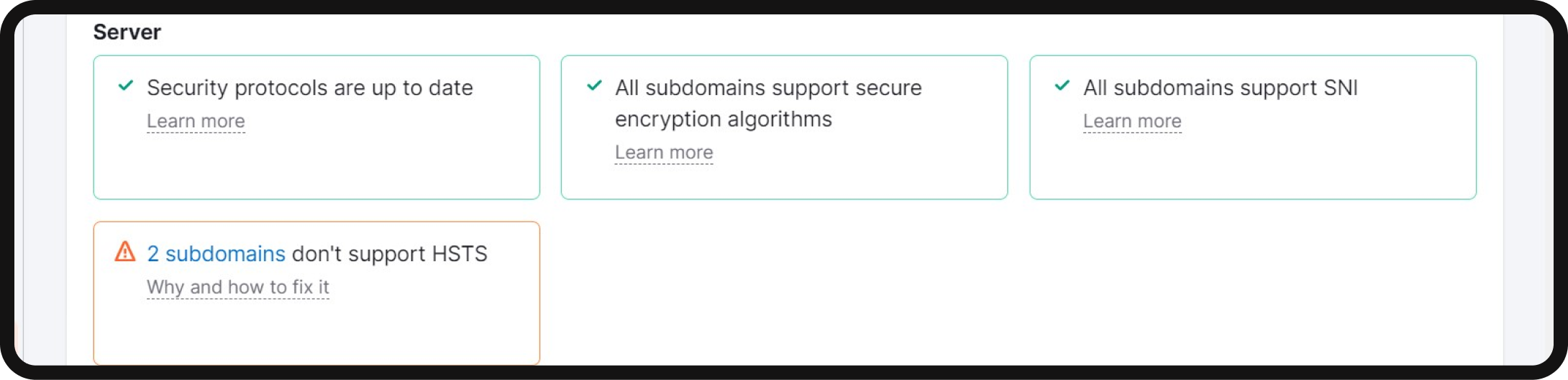
These issues may include:
- Expired certificate: This issue highlights whether your security certificate is due for renewal. It’s essential to maintain a valid certificate to ensure your website’s security and trustworthiness.
- Old security protocol version: This issue indicates if your website is utilizing an outdated SSL or TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocol. Staying updated with the latest security protocols is crucial for maintaining a secure connection.
- No server name indication: This problem informs you whether your server supports SNI (Server Name Indication). SNI allows you to host multiple certificates on the same IP address, thereby enhancing security and flexibility.
- Mixed content: The mixed content issue checks if your site contains any unsecured content, which could trigger a “not secure” warning in web browsers. Mixed content can compromise the integrity of the secure connection provided by HTTPS.
- Addressing HTTPS issues: For each issue identified in the HTTPS report, you will receive advice on how to rectify the problem. It’s crucial to follow the recommended steps to ensure that your website maintains a secure and reliable HTTPS connection.
Incorporating HTTPS into your website’s architecture not only safeguards the data and privacy of your visitors but also aligns with Google’s SEO best practices. By consistently monitoring and addressing HTTPS-related issues through your technical SEO audit, you can enhance your website’s security and maintain its trustworthiness in the eyes of both search engines and users.
Step 10: Fixing code issues
- Priority: Medium
In the world of SEO, it’s important to remember that search engines perceive your website as lines of code. In this step, we’ll delve into the code-related aspects of your technical SEO audit and explore how to ensure your website’s code is optimized for search engines.
* We’ll be using SEMrush to illustrate our point in this section.
Meta tag issues
Meta tags play a significant role in conveying information to search engine bots. The two essential meta tags to focus on are the title tag and the meta description. The title tag defines the page’s title and appears as the clickable link in search results. Meanwhile, the meta description offers a brief summary of the page’s content. These tags may not directly influence rankings, but well-optimized meta tags can enhance your website’s overall SEO.
To identify issues related to meta tags in your Site Audit report, select the “Meta tags” category within the “Issues” tab.
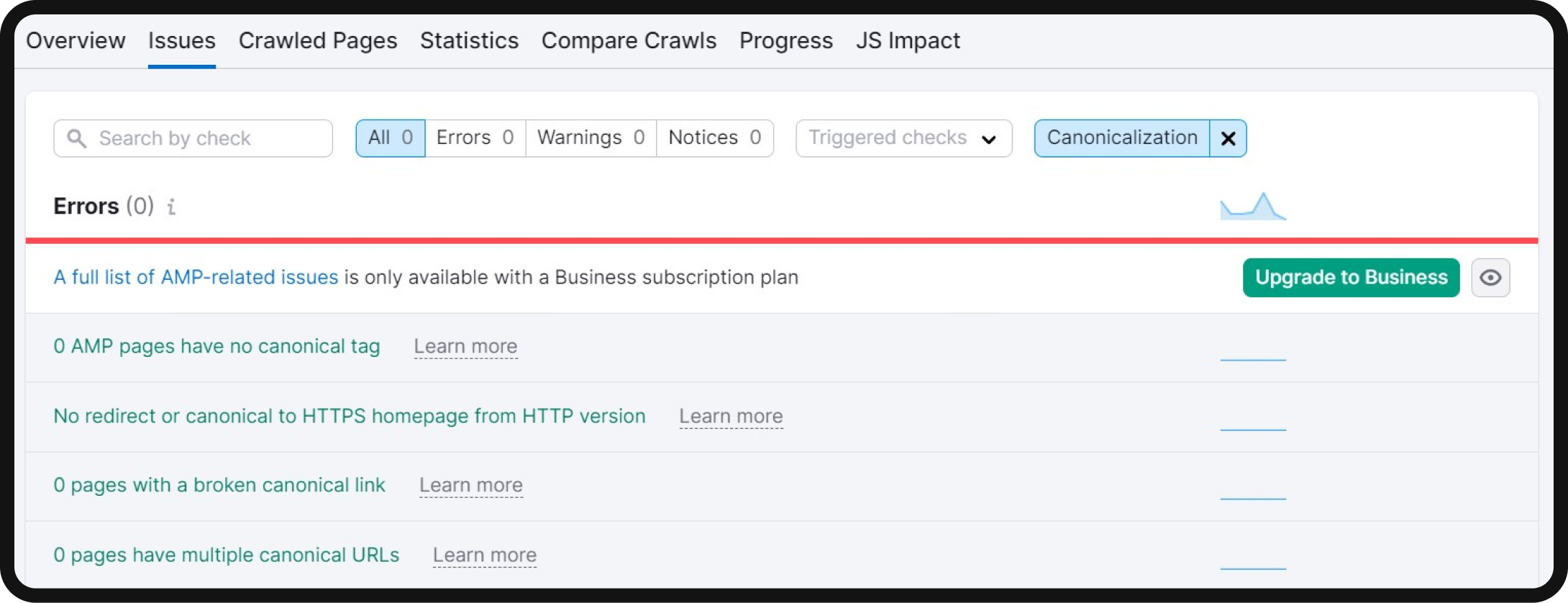
Canonical tag issues
Canonical tags are critical for specifying the primary version of a page, especially when dealing with duplicate or similar content. The canonical tag helps search engines understand which version of a page should be indexed. Common canonicalization issues include missing or multiple canonical tags, which can affect your site’s SEO performance.
You can detect these issues in the Site Audit tool by navigating to the “Canonicalization” category within the top filter in the “Issues” section.
Hreflang attribute issues
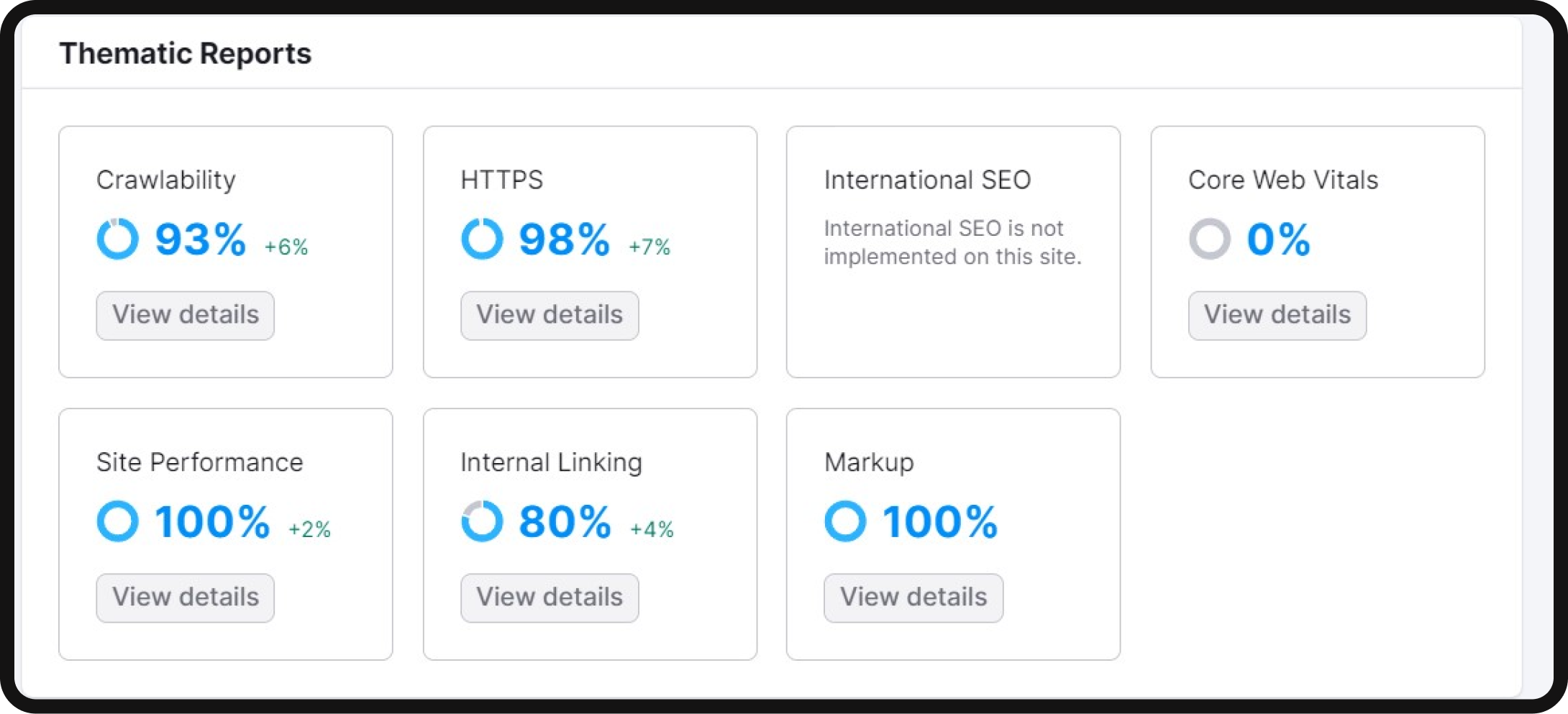
The hreflang attribute is vital for websites targeting international audiences. It specifies the target region and language of a page, ensuring users see the right version of your content based on their location and language preferences. To audit hreflang annotations, you can use the “International SEO” thematic report in Site Audit, which provides a comprehensive overview of hreflang issues on your site.
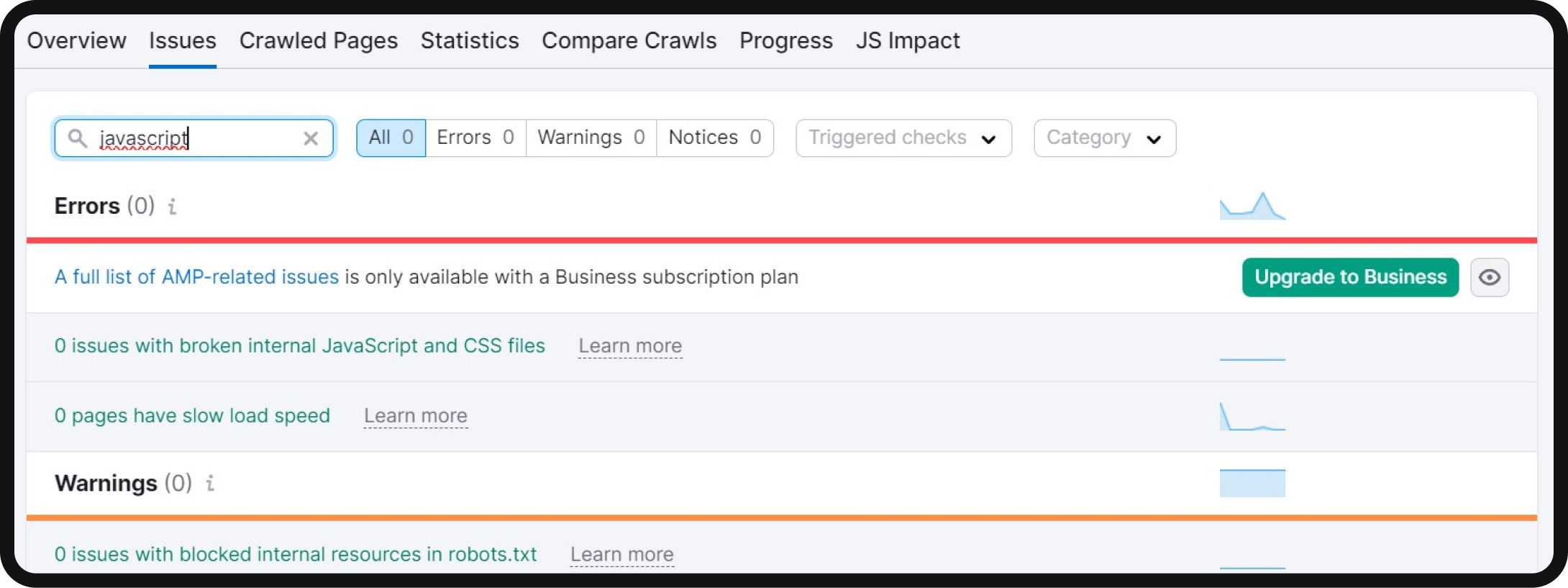
JavaScript issues
JavaScript is a programming language used to create interactive elements on web pages. Search engines, like Google, rely on JavaScript files to render web pages for indexing. If Google can’t access and render JavaScript files correctly, it may not index your pages accurately. The Site Audit tool can identify broken JavaScript files and flag affected pages.
To assess how Google renders a page using JavaScript, you can use the “URL Inspection Tool” in Google Search Console. It allows you to inspect and verify the live version of your page as Google renders it, helping you identify potential issues.
Structured data issues
Structured data, often implemented using Schema.org markup, provides search engines with additional information about your content. This structured data helps search engines index and categorize your pages more accurately and enables the potential appearance of rich results in search engine result pages.
Google’s “Rich Results Test” tool can help you determine if your page qualifies for rich results. Simply input your URL, and the tool will detect structured data items on your page. It will list any issues related to structured data items and provide links to Google’s documentation for issue resolution.
For a comprehensive view of your structured data issues, you can also use the “Markup” thematic report within the Site Audit tool. This report details the structured data types your site employs and lists any invalid items.
By addressing these code-related issues, you can ensure that your website’s code is well-optimized for search engines, improving your site’s overall SEO performance.
Step 11: Finding and fixing status codes with issues
- Priority: Medium
HTTP status codes indicate a website server’s response to the browser’s request to load a page. While there are several status code categories, we’ll focus on 3XX, 4XX, and 5XX statuses, as they often require attention during a technical SEO audit.
* We used SEMrush to illustrate our point.
1. Open the “Issues” tab in Site Audit and select the “HTTP Status” category
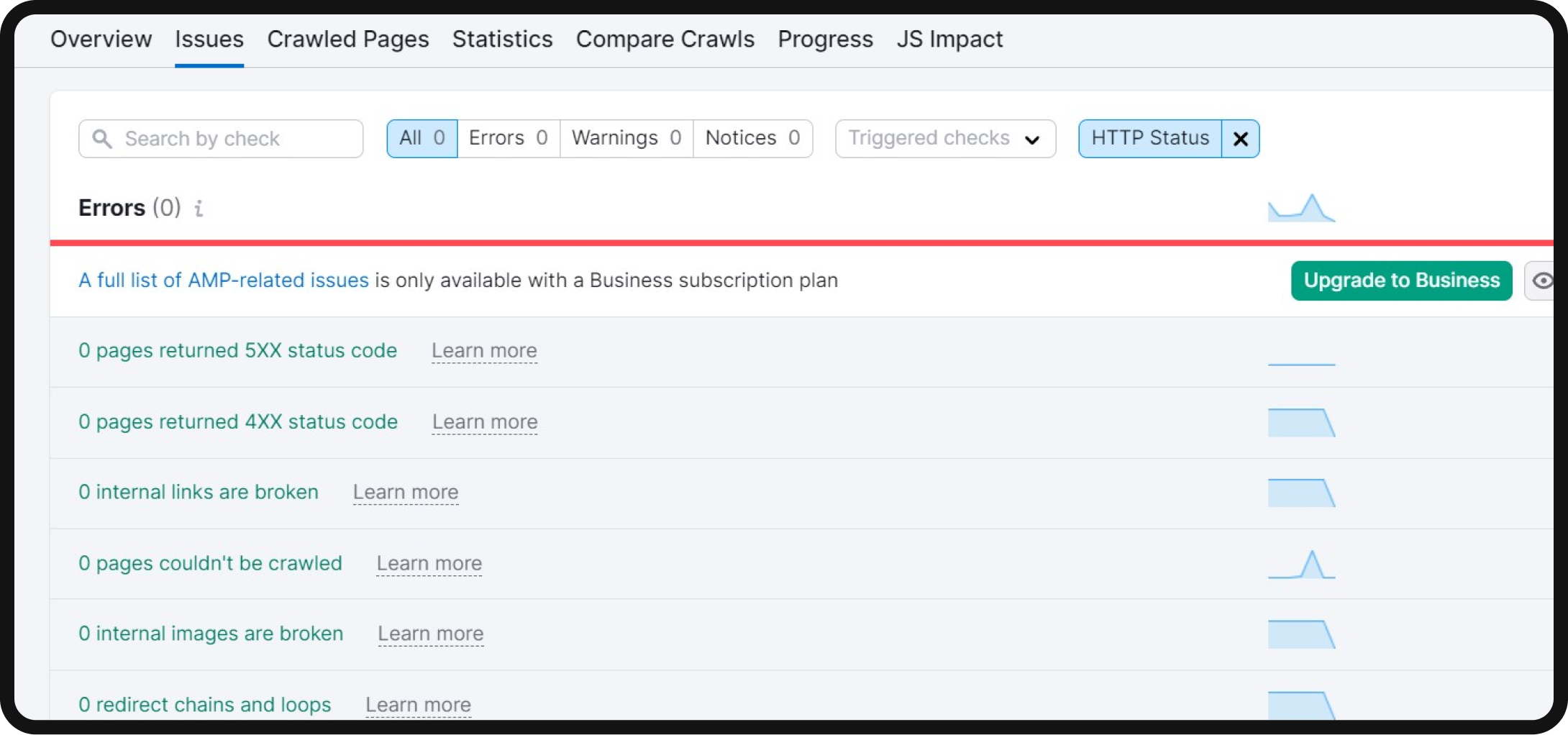
In your technical SEO audit, start by navigating to the “Issues” tab within the Site Audit tool. Then, filter the issues by selecting the “HTTP Status” category from the top filter menu.
3XX status codes
3XX status codes indicate redirects, which occur when users or search engine crawlers are redirected from one page to another. While not all 3XX redirects are problematic, they should be used correctly to ensure a smooth user experience.
Common 3XX issues
- Redirect chains: Multiple redirects between the original and final URL.
- Redirect loops: The original URL redirects to a second URL that, in turn, redirects back to the original.
To address 3XX issues, use the Site Audit tool to detect all your redirects and follow the provided instructions to resolve any errors.
4XX status codes
4XX errors indicate that a requested page cannot be accessed. The most common 4XX error is the “404 error,” which means the page is not found.
If Site Audit identifies pages with 4XX status codes, you should remove all internal links pointing to those pages. Follow these steps:
- Open the specific 4XX issue by clicking on the number of affected pages.
- Review the list of all affected URLs.
- Click “View broken links” to identify internal links pointing to the 4XX pages listed in the report.
- Remove or replace these internal links with relevant alternatives.
5XX status codes
5XX errors are server-side issues indicating that the server couldn’t fulfill the request. They can occur for various reasons, including temporary server unavailability, incorrect server configuration, or server overload.
To address 5XX errors, investigate the underlying reasons for these server-related errors and make necessary fixes if possible.
During your technical SEO audit, it’s crucial to address issues related to HTTP status codes to ensure a smooth user experience and maintain the integrity of your website’s SEO.
Step 12: Reporting and monitoring
- Priority: High
A vital component of your technical SEO audit is creating a comprehensive report that documents the findings and recommendations. This report serves as a roadmap for addressing the identified issues and improving your website’s performance in search engines. Key elements of the report may include:
- Executive summary: A concise overview of the audit’s objectives, key findings, and high-priority recommendations.
- Technical analysis: Detailed insights into the technical issues discovered during the audit, categorized by priority levels. This section should provide context for each issue and offer actionable solutions.
- On-page SEO analysis: Evaluation of on-page elements, including title tags, meta descriptions, headings, and more. Recommendations for optimizing these elements are typically included.
- Mobile optimization: Assessing the website’s mobile-friendliness, performance, and responsiveness. Highlight areas for improvement, such as mobile page speed and user experience.
- Internal linking: A summary of internal linking issues and recommendations for improving the website’s internal link structure.
- Image optimization: A review of image-related issues, such as broken images, large file sizes, and missing alt text. Suggest strategies for optimizing images.
- Security and HTTPS: Analyze security-related issues and provide guidance on implementing HTTPS and addressing potential security concerns.
- Site structure and hierarchy: Evaluate the site’s structure, hierarchy, and URL structure. Recommend adjustments to enhance user experience and search engine crawlability.
- Code issues: Examine the website’s code and markup, including meta tags, canonical tags, hreflang attributes, JavaScript, and structured data. Offer solutions to rectify code-related problems.
- HTTP status codes: Summarize any issues related to 3XX, 4XX, and 5XX status codes. Provide guidance on addressing redirects, page not found errors, and server-related problems.
Setting up ongoing monitoring and maintenance
An effective SEO audit is not a one-time task but an ongoing process. To maintain and improve your website’s performance, it’s crucial to set up continuous monitoring and maintenance procedures. This includes:
- Regular audits: Schedule periodic technical SEO audits to ensure that new issues are promptly identified and addressed. These audits may vary in frequency based on your website’s size and complexity.
- Content updates: Keep your content fresh and up-to-date. Regularly review and refresh existing content to maintain its relevance and quality.
- Performance monitoring: Monitor website performance metrics such as load speed, mobile responsiveness, and user experience. Identify areas for improvement and address them promptly.
- Security updates: Stay vigilant for security vulnerabilities and implement security updates and patches to protect your website and user data.
- Algorithm changes: Stay informed about search engine algorithm updates and adjust your SEO strategies as needed to maintain or improve rankings.
The importance of regular audits
Regular technical SEO audits are essential for several reasons:
- Preventative maintenance: Audits help identify and address issues before they become major problems that can negatively impact your website’s performance and rankings.
- Algorithm adaptation: Search engines frequently update their algorithms. Regular audits allow you to adapt your website to align with these changes.
- Competitive edge: Ongoing optimization keeps your website competitive, ensuring it ranks well and maintains visibility in search results.
- Improved user experience: Regular audits help maintain a positive user experience, which is crucial for retaining and attracting visitors.
- Security: Staying on top of security vulnerabilities is vital to protect both your website and user data.
The reporting and monitoring phase is where your technical SEO audit transitions into an actionable plan. By regularly assessing your website’s health, addressing issues, and adapting to industry changes, you can ensure your website remains effective, competitive, and user-friendly in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
So, how long does a technical SEO audit take?
The duration of a technical SEO audit can vary based on the website’s complexity and size, but it typically takes anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks (40 – 60 hours). The audit process involves an in-depth analysis of technical SEO factors, including performance scores, indexation issues, and user experience. Advanced SEO tools expedite the examination of technical site audit aspects, making the process more efficient.
The thorough assessment of these elements ensures that the website is optimized for search engines, leading to improved organic search traffic. The time invested in the audit is well worth it, as addressing technical SEO issues discovered during the process can significantly enhance a site’s overall performance and user experience.
This guide has given you a solid foundation in the world of technical SEO audits, shedding light on essential factors like site speed, mobile optimization, and indexation. However, the realm of technical SEO is deep and ever-evolving, and there’s so much more to explore. For a thorough analysis and tailored solutions to elevate your website’s performance, we encourage you to reach out to our team of seasoned SEO experts. Together, we can unlock the full potential of your online presence and ensure your website ranks at the top while delivering exceptional user experiences.